Chapter 13 Lesson 3 Notes
... The planets are divided into four ___________________ planets and four ___________________ planets. The planets are separated by a huge ___________________ ___________________ between Mars and ___________________. The asteroid ___________________ is a ring shaped area where many small, rocky bodies ...
... The planets are divided into four ___________________ planets and four ___________________ planets. The planets are separated by a huge ___________________ ___________________ between Mars and ___________________. The asteroid ___________________ is a ring shaped area where many small, rocky bodies ...
Distance to Stars
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
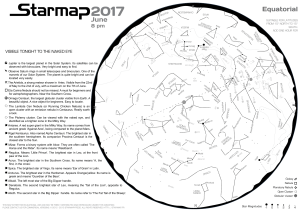
20 pm - Starmap
... The map shows what you see looking at the zenith. The apparent inversion of East and West compared to road maps is normal. Hold the map face down above your head, and the cardinal points will be oriented as usual. As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its ...
... The map shows what you see looking at the zenith. The apparent inversion of East and West compared to road maps is normal. Hold the map face down above your head, and the cardinal points will be oriented as usual. As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its ...
2. A giant hand took one of the planets discovered
... 2. A giant hand took one of the planets discovered around other stars and put it in the solar system at the same distance from the sun as from its star. The mass of the planet is approximately that of Jupiter and the orbit is approximately that of Earth. These are the “hot Jupiters”, as big as Jupit ...
... 2. A giant hand took one of the planets discovered around other stars and put it in the solar system at the same distance from the sun as from its star. The mass of the planet is approximately that of Jupiter and the orbit is approximately that of Earth. These are the “hot Jupiters”, as big as Jupit ...
January SKY Newsletter 2012
... then reverse direction and wind up back in Leo by early February. This change in position illustrates the retrograde motion of Mars. January is an excellent time to view Mars through a telescope if you want to see the north polar cap and possibly some surface markings. This is also a good time to vi ...
... then reverse direction and wind up back in Leo by early February. This change in position illustrates the retrograde motion of Mars. January is an excellent time to view Mars through a telescope if you want to see the north polar cap and possibly some surface markings. This is also a good time to vi ...
angular size - Particle and Astroparticle Physics
... Eighty-eight constellations cover the entire sky • Ancient peoples looked at the stars and imagined groupings made pictures in the sky • We still refer to many of these groupings • Astronomers call them constellations (from the Latin for “group of stars”) ...
... Eighty-eight constellations cover the entire sky • Ancient peoples looked at the stars and imagined groupings made pictures in the sky • We still refer to many of these groupings • Astronomers call them constellations (from the Latin for “group of stars”) ...
Astro 10 Practice Test 3
... b. The helium in their cores has all been used up, which means they’ve started buring hydrogen for the first time. c. They have been ejected from the cluster by gravitational encounters with other stars. d. They’ve run out of hydrogen to burn in their cores, and have evolved into red giants. ...
... b. The helium in their cores has all been used up, which means they’ve started buring hydrogen for the first time. c. They have been ejected from the cluster by gravitational encounters with other stars. d. They’ve run out of hydrogen to burn in their cores, and have evolved into red giants. ...
8th Grade Midterm Test Review
... higher) density than gas giant planets? • The terrestrial planets have a higher density than the gas giant planets ...
... higher) density than gas giant planets? • The terrestrial planets have a higher density than the gas giant planets ...
Way Milky the MAPPING
... Consider the center of the Milky Way. More than 24,000 light-years from the sun—near the intersection of the constellations of Sagittarius and Scorpius—the center of our spiral galaxy is home to a dense concentration of stars that date to within a few billion years of the birth of the universe. Tho ...
... Consider the center of the Milky Way. More than 24,000 light-years from the sun—near the intersection of the constellations of Sagittarius and Scorpius—the center of our spiral galaxy is home to a dense concentration of stars that date to within a few billion years of the birth of the universe. Tho ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? Blue and White 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? Blue and White (also, hottest) a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? The hotter the star, the more energy it has b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? Along ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? Blue and White 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? Blue and White (also, hottest) a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? The hotter the star, the more energy it has b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? Along ...
01-ChapterRadiation
... Infrared - “heat waves” Visible Light - detected by your eyes Ultraviolet - causes sunburns X-rays - penetrates tissue Gamma Rays - most energetic ...
... Infrared - “heat waves” Visible Light - detected by your eyes Ultraviolet - causes sunburns X-rays - penetrates tissue Gamma Rays - most energetic ...
Five Women at the Crossroads of Astronomy - Physics
... classifications Miss Cannon used plate B 9431 which was made with an exposure of 140 minutes in 1893. A glance at that remarkable early photograph will suggest why Miss Cannon was captivated by stellar spectra and was led to devote a long and happy career to the classification of faint stars. – H. S ...
... classifications Miss Cannon used plate B 9431 which was made with an exposure of 140 minutes in 1893. A glance at that remarkable early photograph will suggest why Miss Cannon was captivated by stellar spectra and was led to devote a long and happy career to the classification of faint stars. – H. S ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
Our Place in Space
... Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 1: Have you ever looked up into the night sky and wondered what was out there? Group 2: Throughout time, astronomers have gazed to the heavens, hoping to find clues about our place in the universe. Group 3: Long ago people assumed that Earth was the cent ...
... Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 1: Have you ever looked up into the night sky and wondered what was out there? Group 2: Throughout time, astronomers have gazed to the heavens, hoping to find clues about our place in the universe. Group 3: Long ago people assumed that Earth was the cent ...
Chapter 40
... technical name is Mz3, resembles an ant when observed using ground-based telescopes. The nebula lies within our galaxy between 3,000 and 6,000 light years from Earth. ...
... technical name is Mz3, resembles an ant when observed using ground-based telescopes. The nebula lies within our galaxy between 3,000 and 6,000 light years from Earth. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
... 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
... 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.