Classification and structure of galaxies
... How do we know what our Galaxy looks like? We can see: • Stars and star clusters – microwaves generated by water from H II regions (called the MASER technique) traces the Milky Way’s spiral arms • Nebulae – infrared light (detected by the Spitzer Space Telescope) shows the outline of the heat genera ...
... How do we know what our Galaxy looks like? We can see: • Stars and star clusters – microwaves generated by water from H II regions (called the MASER technique) traces the Milky Way’s spiral arms • Nebulae – infrared light (detected by the Spitzer Space Telescope) shows the outline of the heat genera ...
Homework 1 - Course Pages of Physics Department
... were created in supernova explosions and mixed with the interstellar gas and dust, from which the earth was formed. According to supernova calculations the uranium isotopes are produced in ratio 235 U/238 U = 1.3 ± 0.2. What does this tell us about the age of the earth and the age of the universe? 2 ...
... were created in supernova explosions and mixed with the interstellar gas and dust, from which the earth was formed. According to supernova calculations the uranium isotopes are produced in ratio 235 U/238 U = 1.3 ± 0.2. What does this tell us about the age of the earth and the age of the universe? 2 ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-7. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from Earth, which one looks brighter in the night sky? Explain why.? The blue star, being hotter than the red star, will appear brighter since the two stars are the same size and same distance from the earth ...
... 10-7. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from Earth, which one looks brighter in the night sky? Explain why.? The blue star, being hotter than the red star, will appear brighter since the two stars are the same size and same distance from the earth ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #2 Problem 1
... Due Friday, Jan 31, 2014 by 5pm, in Steidel’s mailbox in 249 Cahill ...
... Due Friday, Jan 31, 2014 by 5pm, in Steidel’s mailbox in 249 Cahill ...
chapter-30-pp
... slightly toward blue. This is called a “blue shift”. This is caused by shorter light waves as it moves toward Earth. ...
... slightly toward blue. This is called a “blue shift”. This is caused by shorter light waves as it moves toward Earth. ...
Answers for the HST Scavenger Hunt
... Define this term. The spherical outer boundary of a black hole. Once matter crosses this threshold, the speed required for it to escape the black hole’s gravitational grip is greater than the speed of light. When scientists used the HST to study Cygnus X-1, they were able to observe two of these eve ...
... Define this term. The spherical outer boundary of a black hole. Once matter crosses this threshold, the speed required for it to escape the black hole’s gravitational grip is greater than the speed of light. When scientists used the HST to study Cygnus X-1, they were able to observe two of these eve ...
Understanding Stars
... • Luminosity: how much energy the star puts out. – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • Big luminosities are bright – 1 order of magnitude is roughly equal to 20 units of luminosity Absolute Magnitude and Luminosity • 2 different ways of measuring the same thing – like Cels ...
... • Luminosity: how much energy the star puts out. – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • Big luminosities are bright – 1 order of magnitude is roughly equal to 20 units of luminosity Absolute Magnitude and Luminosity • 2 different ways of measuring the same thing – like Cels ...
File - Adopt A Constellation
... • Milky Way – One of the billions of galaxies that make up the universe. The sun is one of the billions of stars in the Milky Way. • The Milky Way is a large spiral galaxy. • The Sun and its planets (including Earth) lie in this quiet part of the galaxy, about half way out from the center. • The Mi ...
... • Milky Way – One of the billions of galaxies that make up the universe. The sun is one of the billions of stars in the Milky Way. • The Milky Way is a large spiral galaxy. • The Sun and its planets (including Earth) lie in this quiet part of the galaxy, about half way out from the center. • The Mi ...
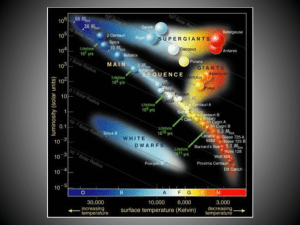
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Astronomers reasoned that if a star were hotter, it should have a higher luminosity, and a cooler star would be dimmer. As it turns out, most stars fit this pattern. They can be found on the HR Diagram in the large group that stretches across the middle of the diagram. These are called the Main Sequ ...
... Astronomers reasoned that if a star were hotter, it should have a higher luminosity, and a cooler star would be dimmer. As it turns out, most stars fit this pattern. They can be found on the HR Diagram in the large group that stretches across the middle of the diagram. These are called the Main Sequ ...
Astronomy Chapter 13 Name
... D. A type of binary star in which the spectrum lines exhibit a changing Doppler shift as a result of the orbital motion of one star around the other ...
... D. A type of binary star in which the spectrum lines exhibit a changing Doppler shift as a result of the orbital motion of one star around the other ...
Name____________________________________________________________________ Astronomy Packet 2 1) The Mayans tracked which celestial bodies____________________________________
... or____________________________. Which rose in late______________ and signaled the __________________________ which was of importance for agriculture in this desert society. The stars in the modern constellation of Orion symbolized the ______________ of the God_______________ and also line up perfec ...
... or____________________________. Which rose in late______________ and signaled the __________________________ which was of importance for agriculture in this desert society. The stars in the modern constellation of Orion symbolized the ______________ of the God_______________ and also line up perfec ...
Page 25 - Types of Galaxies
... smooth, ball-shaped appearance. • Ellipticals contain old stars, and possess little gas or dust. • They are classified by the shape of the ball, which can range from round to oval (baseball-shaped to football-shaped). • The smallest elliptical galaxies (called "dwarf ellipticals") are probably the m ...
... smooth, ball-shaped appearance. • Ellipticals contain old stars, and possess little gas or dust. • They are classified by the shape of the ball, which can range from round to oval (baseball-shaped to football-shaped). • The smallest elliptical galaxies (called "dwarf ellipticals") are probably the m ...
The Life of a Star
... • As long as they have hydrogen atoms to fuse into helium atoms they just keep on releasing lots of energy. ...
... • As long as they have hydrogen atoms to fuse into helium atoms they just keep on releasing lots of energy. ...
Announcements Evolution of High-Mass Stars: Red Supergiants
... Period-Luminosity Relation • The connection between a Cepheid’s pulse period and its luminosity. ...
... Period-Luminosity Relation • The connection between a Cepheid’s pulse period and its luminosity. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.