Life in the Universe
... On a clear night, with 20/20 vision, one can see about 3,000 stars at a given time. Ancient astronomers traced out “pictures” using groups of these stars. “Group of Stars” in Latin constellations ...
... On a clear night, with 20/20 vision, one can see about 3,000 stars at a given time. Ancient astronomers traced out “pictures” using groups of these stars. “Group of Stars” in Latin constellations ...
t2 images part 1
... The rate at which galaxies are receding from each other is proportional to their distance from each other: v=H* d Where H is the Hubble Constant If the Universe is expanding, it stands that at some point in the past everything in the Universe was all concentrated at the same point and began ...
... The rate at which galaxies are receding from each other is proportional to their distance from each other: v=H* d Where H is the Hubble Constant If the Universe is expanding, it stands that at some point in the past everything in the Universe was all concentrated at the same point and began ...
stars & galaxies
... light years thick. • Our sun is located 30,000 light years from the nucleus. • It takes the sun 200 million years to make one rotation around the center. ...
... light years thick. • Our sun is located 30,000 light years from the nucleus. • It takes the sun 200 million years to make one rotation around the center. ...
Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy
... Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy The ______________ _________ Galaxy ...
... Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy The ______________ _________ Galaxy ...
Galaxy
... shape One of the closest neighboring galaxies to the Milky Way is an irregular galaxy It is about 160,000 light years away ...
... shape One of the closest neighboring galaxies to the Milky Way is an irregular galaxy It is about 160,000 light years away ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • If Earth orbited the Sun, ancient astronomers believed that they would see differences in angular separation of stars as the Earth rotated around the Sun • Since they saw no changes in angular separation of the stars, they assumed the Earth was the center of the universe • They could not fathom th ...
... • If Earth orbited the Sun, ancient astronomers believed that they would see differences in angular separation of stars as the Earth rotated around the Sun • Since they saw no changes in angular separation of the stars, they assumed the Earth was the center of the universe • They could not fathom th ...
SNC1PL The Life Cycle of Stars
... When the protostar reaches critical density and temperature (~15x107°C), the gravitational forces pulling matter towards the center are so strong that it causes nuclear fusion to begin. This event causes a chain reaction that will continue for the star’s entire lifespan. ...
... When the protostar reaches critical density and temperature (~15x107°C), the gravitational forces pulling matter towards the center are so strong that it causes nuclear fusion to begin. This event causes a chain reaction that will continue for the star’s entire lifespan. ...
Unit E Space Exploration Section 1 Notnd Space has changed over
... in the vicinity of a nonrotating black hole. ...
... in the vicinity of a nonrotating black hole. ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... 3 billion stars can be seen through telescopes on the surface 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble ...
... 3 billion stars can be seen through telescopes on the surface 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble ...
Planetarium Key Points
... Constellation shape change with epoch and observer position; shape is not for ever becouse of star’s proper motion, but no detectable change during human life at naked eye Constellations and asterisms; we use structures invented by assirian priests in XII century BC: Orion, Ursa Major, Ursa Mino ...
... Constellation shape change with epoch and observer position; shape is not for ever becouse of star’s proper motion, but no detectable change during human life at naked eye Constellations and asterisms; we use structures invented by assirian priests in XII century BC: Orion, Ursa Major, Ursa Mino ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Once The Sky is open, go to Data → Location and confirm the location is Seattle, Washington (if not, you can choose this from the predefined list). Next go to Data → Time and set the time for 9 p.m. tonight. If you have time, you may wish to play with some of the following controls: on the second li ...
... Once The Sky is open, go to Data → Location and confirm the location is Seattle, Washington (if not, you can choose this from the predefined list). Next go to Data → Time and set the time for 9 p.m. tonight. If you have time, you may wish to play with some of the following controls: on the second li ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. • What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
... than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. • What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
Infinity Express
... Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. (By end of grade 2). The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from Earth. (By end of grade 5). Patterns of t ...
... Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. (By end of grade 2). The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from Earth. (By end of grade 5). Patterns of t ...
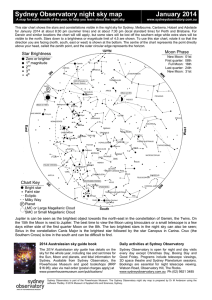
Sydney Observatory night sky map January 2014
... for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness ...
... for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness ...
stars - science1d
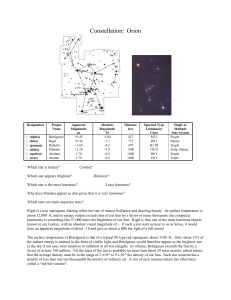
... Earth) resembles a recognizable form Astronomers have officially listed a total of 88 ...
... Earth) resembles a recognizable form Astronomers have officially listed a total of 88 ...
Recomendación de una estrategia
... notable for the arching band of our Milky Way Galaxy and the interesting field of stars, nebulas, and galaxies. ...
... notable for the arching band of our Milky Way Galaxy and the interesting field of stars, nebulas, and galaxies. ...
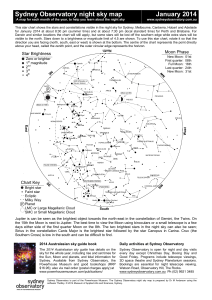
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
... for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness ...
... for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness ...
STUDY GUIDE:
... Star clusters can be open (also called galactic) or globular. There are fewer and more sparse stars found in an open cluster than globular one. Stars in an open cluster are usually about the same age. One of the more famous visible open clusters is the Pleiades (also known as the Seven Sisters) in T ...
... Star clusters can be open (also called galactic) or globular. There are fewer and more sparse stars found in an open cluster than globular one. Stars in an open cluster are usually about the same age. One of the more famous visible open clusters is the Pleiades (also known as the Seven Sisters) in T ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.