Astronomy – Studying the Stars & Space
... • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may indicate a • A collapsed star can black holes’ existence become a pulsar ...
... • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may indicate a • A collapsed star can black holes’ existence become a pulsar ...
Patterns in the Night Sky
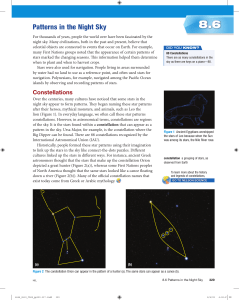
... Over the centuries, many cultures have noticed that some stars in the night sky appear to form patterns. They began naming these star patterns after their heroes, mythical monsters, and animals, such as Leo the lion (Figure 1). In everyday language, we often call these star patterns constellations. ...
... Over the centuries, many cultures have noticed that some stars in the night sky appear to form patterns. They began naming these star patterns after their heroes, mythical monsters, and animals, such as Leo the lion (Figure 1). In everyday language, we often call these star patterns constellations. ...
unit030
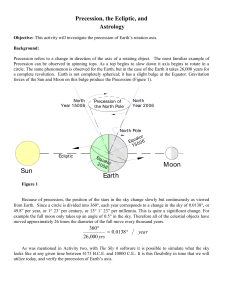
... 49.8” per year, or 1 23’ per century, or 13 1’ 23” per millennia. This is quite a significant change. For example the full moon only takes up an angle of 0.5 in the sky. Therefore all of the celestial objects have moved approximately 26 times the diameter of the full move every thousand years. ...
... 49.8” per year, or 1 23’ per century, or 13 1’ 23” per millennia. This is quite a significant change. For example the full moon only takes up an angle of 0.5 in the sky. Therefore all of the celestial objects have moved approximately 26 times the diameter of the full move every thousand years. ...
Star project
... • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
... • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
Groups of Stars
... A spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Berenices A barred-spiral galaxy in the Fornax cluster ...
... A spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Berenices A barred-spiral galaxy in the Fornax cluster ...
The Marathon
... collection of six or seven stars to the naked eye. A simple pair of binoculars will reveal dozens of beautiful blue stars. Next is the first globular cluster on our list, M79. To track down this cluster, the equivalent of 90,000 suns, use the magnitude 2.84 Beta Leporis located 4° southwest of M79. ...
... collection of six or seven stars to the naked eye. A simple pair of binoculars will reveal dozens of beautiful blue stars. Next is the first globular cluster on our list, M79. To track down this cluster, the equivalent of 90,000 suns, use the magnitude 2.84 Beta Leporis located 4° southwest of M79. ...
description
... zenith appear high, near the top of the sky (middle of the circle on the Star Map). Celestial sphere = giant imaginary sphere that surrounds Earth. Stars & constellations appear to be attached to this imaginary sphere. Little Dipper = shaped like a small ladle or spoon. The end star of the Littl ...
... zenith appear high, near the top of the sky (middle of the circle on the Star Map). Celestial sphere = giant imaginary sphere that surrounds Earth. Stars & constellations appear to be attached to this imaginary sphere. Little Dipper = shaped like a small ladle or spoon. The end star of the Littl ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... cloud around it, lit by Antares hot companion star. In the next few million years or so, Antares may explode as a supernova -so keep your eyes on the Scorpion if you're the patient sort. Just NE of Scorpio in the Milky Way are the stars of Sagittarius the Archer, making a pattern a bit like a teapot ...
... cloud around it, lit by Antares hot companion star. In the next few million years or so, Antares may explode as a supernova -so keep your eyes on the Scorpion if you're the patient sort. Just NE of Scorpio in the Milky Way are the stars of Sagittarius the Archer, making a pattern a bit like a teapot ...
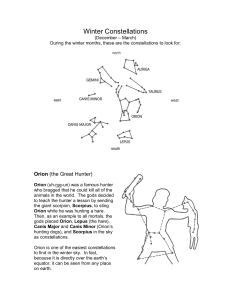
seven winter constellations
... Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in the sky as constellations. Orion is one of the easiest constellations to find in the winter sky. In fact, because it is directly over the earth’s equator, it can be seen from any place on earth. ...
... Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in the sky as constellations. Orion is one of the easiest constellations to find in the winter sky. In fact, because it is directly over the earth’s equator, it can be seen from any place on earth. ...
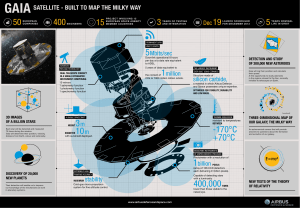
3m 10m -170°C +70°C 400,000
... a material in which Airbus Defence and Space possesses unique expertise. OPTIMISED FOR STABILITY, DURABILITY AND LOW MASS ...
... a material in which Airbus Defence and Space possesses unique expertise. OPTIMISED FOR STABILITY, DURABILITY AND LOW MASS ...
ppt
... • Apparent magnitude - doesn't measure how bright objects actually are; it measures how bright they appear to us, which also depends on how close they are eg Sun has m = -26.74 • Absolute magnitude - measures how bright objects actually are -- it is defined as the apparent magnitude that an object w ...
... • Apparent magnitude - doesn't measure how bright objects actually are; it measures how bright they appear to us, which also depends on how close they are eg Sun has m = -26.74 • Absolute magnitude - measures how bright objects actually are -- it is defined as the apparent magnitude that an object w ...
Stars Powerpoint
... When neutron stars form, they maintain the momentum of the entire star, but now they’re just a few kilometers across. This causes them to spin at tremendous rates, sometimes as fast as hundreds of times a second. ...
... When neutron stars form, they maintain the momentum of the entire star, but now they’re just a few kilometers across. This causes them to spin at tremendous rates, sometimes as fast as hundreds of times a second. ...
Document
... Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as which type of star? ___________________________________________ ...
... Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as which type of star? ___________________________________________ ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 31. Create a flow-map that properly sequences the formation of the solar system? solar nebula forms, nuclear fusion begins in the sun, planetesimals form, planets form 32. A group of stars that form patterns in the sky is called constellation. 33. To express the distance between the Milky Way galaxy ...
... 31. Create a flow-map that properly sequences the formation of the solar system? solar nebula forms, nuclear fusion begins in the sun, planetesimals form, planets form 32. A group of stars that form patterns in the sky is called constellation. 33. To express the distance between the Milky Way galaxy ...
Midterm II Jeopardy
... $200 - This planet occasionally has dust storms which obscure its ENTIRE surface. (Mars) $400 - You can only see these planets close to the horizon (45 degrees or less). (Venus & Mercury) $600 - This is how we observed the rings around Uranus. (Occultation) $800 - These two planets most closely rese ...
... $200 - This planet occasionally has dust storms which obscure its ENTIRE surface. (Mars) $400 - You can only see these planets close to the horizon (45 degrees or less). (Venus & Mercury) $600 - This is how we observed the rings around Uranus. (Occultation) $800 - These two planets most closely rese ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Data: Lots of nebulous spots known in the nightsky • Questions: What are they? All the same? Different things? • Need more observations! Build bigger telescopes ...
... • Data: Lots of nebulous spots known in the nightsky • Questions: What are they? All the same? Different things? • Need more observations! Build bigger telescopes ...
File
... Answer the following questions in your notebook. Write the complete question and write your answer in complete sentences. 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of t ...
... Answer the following questions in your notebook. Write the complete question and write your answer in complete sentences. 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of t ...
20.1 Notes
... If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 – 3 solar masses it becomes a _______________ star, a very dense star that is a source of pulsating radio waves called _____________. ...
... If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 – 3 solar masses it becomes a _______________ star, a very dense star that is a source of pulsating radio waves called _____________. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.