100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
Astronomy Powerpoint
... Since that time it has still yet to make a complete orbit around the sun, because one Neptune year lasts 165 Earth years! ...
... Since that time it has still yet to make a complete orbit around the sun, because one Neptune year lasts 165 Earth years! ...
deep space - altaastronomy
... the speed of light) is called the Schwarzschild radius. • The surface of an imaginary sphere with radius equal to the Schwarzschild radius and centered on the black hole is called the event horizon. • The Schwarzschild radius of any object depends on its ...
... the speed of light) is called the Schwarzschild radius. • The surface of an imaginary sphere with radius equal to the Schwarzschild radius and centered on the black hole is called the event horizon. • The Schwarzschild radius of any object depends on its ...
File
... 20. What will eventually happen to all stars regardless of their mass? All stars will run out of fuel and die. ...
... 20. What will eventually happen to all stars regardless of their mass? All stars will run out of fuel and die. ...
Winter - Dark Sky Discovery
... On the other side of Polaris is a W of stars (or an M depending on which way up it happens to be; the stars appear to rotate anti-clockwise round Polaris once every 24 hours). This is the constellation of Cassiopeia. These stars in the northern sky are the same all year round, so you will always be ...
... On the other side of Polaris is a W of stars (or an M depending on which way up it happens to be; the stars appear to rotate anti-clockwise round Polaris once every 24 hours). This is the constellation of Cassiopeia. These stars in the northern sky are the same all year round, so you will always be ...
Astrology, calendars and the dating of Christian festivals.
... earth. It is much more luminous, intrinsically, than the sole star that appears brighter than it from Earth—Sirius which is a mere 22 times more luminous than our sun, and depends on being much closer to us to beat its rival in apparent magnitude. In fact, for a large fraction of stars in the local ...
... earth. It is much more luminous, intrinsically, than the sole star that appears brighter than it from Earth—Sirius which is a mere 22 times more luminous than our sun, and depends on being much closer to us to beat its rival in apparent magnitude. In fact, for a large fraction of stars in the local ...
WHAT IS A STAR? - cloudfront.net
... which forms into a star. Dust and gas particles exert a gravitational force on each other which keeps pulling them closer together. ...
... which forms into a star. Dust and gas particles exert a gravitational force on each other which keeps pulling them closer together. ...
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache
... aspect, the native is reduced to being a door-keeper, admitting and saluting guests. [2] Ptolemy attributes a mercurial-saturnine nature to the constellation as a whole, but notes the principal star Arcturus (from Arktouros 'Bear Guard': arktos, bear + ouros, guard - from its position behind Ursa Ma ...
... aspect, the native is reduced to being a door-keeper, admitting and saluting guests. [2] Ptolemy attributes a mercurial-saturnine nature to the constellation as a whole, but notes the principal star Arcturus (from Arktouros 'Bear Guard': arktos, bear + ouros, guard - from its position behind Ursa Ma ...
Astronomy Review revised Key
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Discussion Activity #10
... 2. Suppose star A has a parallax angle of 1/20 of an arcsecond and star B has a parallax angle of 1/40 of an arcsecond. What can you say about the relative positions of stars A and B? A. B. C. D. ...
... 2. Suppose star A has a parallax angle of 1/20 of an arcsecond and star B has a parallax angle of 1/40 of an arcsecond. What can you say about the relative positions of stars A and B? A. B. C. D. ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... 4. How can you use the stars to tell your latitude on the Earth? Find Polaris in the sky, The “north star” it is above the north pole and you can find your latitude by measuring the angle from the horizon it is at. 5. Will the Sun ever be straight overhead here in Massachusetts? Nope. The sun is onl ...
... 4. How can you use the stars to tell your latitude on the Earth? Find Polaris in the sky, The “north star” it is above the north pole and you can find your latitude by measuring the angle from the horizon it is at. 5. Will the Sun ever be straight overhead here in Massachusetts? Nope. The sun is onl ...
Stars
... the seas with the stars' help. Characters of myth and legend were used to name and tell the stories of the stars such as the group of stars that looked like a man with a sword (or bow and arrow) was named Orion, for the famous hunter in Greek mythology. ...
... the seas with the stars' help. Characters of myth and legend were used to name and tell the stories of the stars such as the group of stars that looked like a man with a sword (or bow and arrow) was named Orion, for the famous hunter in Greek mythology. ...
January 2012 - Powerhouse Museum
... for January 2012 at about 8.30 pm (summer time) and at about 7.30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations, the chart will still apply but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness ...
... for January 2012 at about 8.30 pm (summer time) and at about 7.30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations, the chart will still apply but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... Venus is in the west in the evening twilight throughout the month and is unfavourable. Mars is just west of south at dusk throughout this month and is poorly placed for observation. In the first days of the month, however it makes a near-equilateral triangle with Saturn and Antares, but low down. Ju ...
... Venus is in the west in the evening twilight throughout the month and is unfavourable. Mars is just west of south at dusk throughout this month and is poorly placed for observation. In the first days of the month, however it makes a near-equilateral triangle with Saturn and Antares, but low down. Ju ...
Review 1 Solutions
... 9. What is spherical aberration, and how is it corrected? Spherical aberration is a problem in reflecting telescopes that use spherical mirrors—light does not reflect to a single focus point for this shape. It can be corrected by using parabolic mirrors instead of spherical ones. 10. Why do stars tw ...
... 9. What is spherical aberration, and how is it corrected? Spherical aberration is a problem in reflecting telescopes that use spherical mirrors—light does not reflect to a single focus point for this shape. It can be corrected by using parabolic mirrors instead of spherical ones. 10. Why do stars tw ...
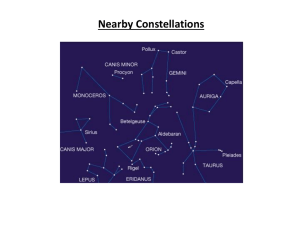
Nearby Constellations
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
Branches of Earth Science
... Galaxy is a huge collection of stars bound by ______________ o Contain various star ______________ ______________ of galaxies in the universe 3 types of galaxies o Spiral o Elliptical o Irregular ...
... Galaxy is a huge collection of stars bound by ______________ o Contain various star ______________ ______________ of galaxies in the universe 3 types of galaxies o Spiral o Elliptical o Irregular ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 13. (2 pts.) In the TV show Star Trek, the fastest the Enterprise can travel is warp 9 (1516 times the speed of light). How long would it take to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other moving at warp 9? What about from our solar system to the Galactic center? (Express your answers in the mos ...
... 13. (2 pts.) In the TV show Star Trek, the fastest the Enterprise can travel is warp 9 (1516 times the speed of light). How long would it take to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other moving at warp 9? What about from our solar system to the Galactic center? (Express your answers in the mos ...
Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The
... 3.a) How would our sun be classified? b) How long is the life time of our sun? c) As our sun ages how will it change? 4. Which star type in the table would be considered a dwarf star? Explain your answer. 5. Which star type is most similar to the Sun? Explain your answer. 6. Which star types are lik ...
... 3.a) How would our sun be classified? b) How long is the life time of our sun? c) As our sun ages how will it change? 4. Which star type in the table would be considered a dwarf star? Explain your answer. 5. Which star type is most similar to the Sun? Explain your answer. 6. Which star types are lik ...
The Sky and Its Motion - west
... are required to see it from the perspective of the original astronomers 1000’s of years ago. ...
... are required to see it from the perspective of the original astronomers 1000’s of years ago. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.