* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nearby Constellations
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
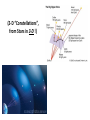
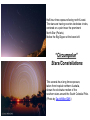
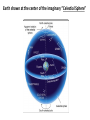
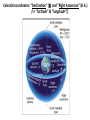
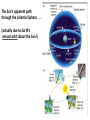
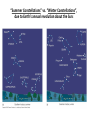
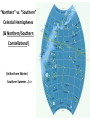
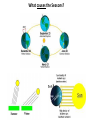
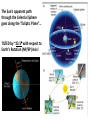
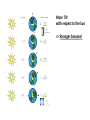
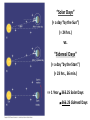
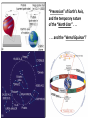
Nearby Constellations (2-D “Constellations”, from Stars in 3-D !) Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. “Circumpolar” Stars/Constellations This several-hour-long time exposure, taken from tropical northern Australia, shows the clockwise motion of the southern stars around the South Celestial Pole. (Photo by David Miller/DMI.) Earth shown at the center of the imaginary “Celestial Sphere” Celestial coordinates: “Declination” (d) and “Right Ascension” (R.A.) (=> “latitude” & “longitude”!) The Sun’s apparent path through the Celestial Sphere . . . (actually due to Earth’s annual orbit about the Sun!) “Summer Constellations” vs. “Winter Constellations”, due to Earth’s annual revolution about the Sun: Earth, Sun, and the “Zodiac Constellations” through the Seasons “Summer Signs” = “Winter Constellations”; “Winter Signs” = “Summer Constellations” An Earth-bound Observer sees only half the sky at any one time! “Time Zones” (artificial!), & some famous Meridians around the globe: “Northern” vs. “Southern” Celestial Hemispheres (& Northern/Southern Constellations!) (In Northern Winter/ Southern Summer…) => What causes the Seasons? Seasonal observations Above is for a Northern Hemisphere location (“Summer” = Higher Sun and Longer Daytimes!) “Land of the Midnight Sun”? (Or the Noon Darkness…?) A good view from Stonehenge! (Sunrise on the Summer Solstice) Ancient “Observatories” in the Americas! (Serving as “Calendars” & “Almanacs”…) The Sun’s apparent path through the Celestial Sphere goes along the “Ecliptic Plane”… TILTED by ~23.5 with respect to Earth’s Rotation (NP/SP) Axis! More Tilt with respect to the Sun => Stronger Seasons! 1 Year 365.2425 Days 365.25 Days (Need “Leap Day” Corrections!) Christopher Clavius Pope Gregory XIII The lunar crater Clavius, with peripheral craters “Solar Days” (= a day “by the Sun”) (= 24 hrs.) vs. “Sidereal Days” (= a day “by the Stars”) (= 23 hrs., 56 min.) => 1 Year 365.25 Solar Days 366.25 Sidereal Days “Precession” of Earth’s Axis, and the temporary nature of the “North Star” . . . . . . and the “Vernal Equinox”!