Exam 3 Study Guide
... The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ solar masses. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the ________________. Leavitt’s Law relates the ___________ of a Cepheid to its _____________. Hubble’s Law relates ___________ of a g ...
... The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ solar masses. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the ________________. Leavitt’s Law relates the ___________ of a Cepheid to its _____________. Hubble’s Law relates ___________ of a g ...
LEO - nina`s Senior project
... size, occupying an area of 947 square degrees. • It is located in the second quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ2) and can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -65°. ...
... size, occupying an area of 947 square degrees. • It is located in the second quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ2) and can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -65°. ...
Scientists Observe Star Triplets Being Born : Space
... having two mechanisms that can form multiple star systems fragmentations of circumstellar disks like the one just observed, or the fragmentation of the larger clouds of gas and dust, many of which young stars are from. The forming system is called L1448 IRS3B and it's relatively near - just 750 ligh ...
... having two mechanisms that can form multiple star systems fragmentations of circumstellar disks like the one just observed, or the fragmentation of the larger clouds of gas and dust, many of which young stars are from. The forming system is called L1448 IRS3B and it's relatively near - just 750 ligh ...
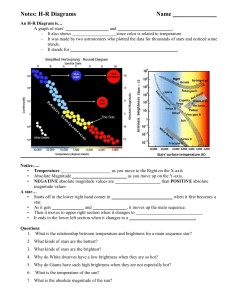
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... – Curved line sloping from top left to lower right of HR diagram. ...
... – Curved line sloping from top left to lower right of HR diagram. ...
Animals in Estonian Folk Astronomy
... to the Olevik newspaper and printed using the wood engraving technique. This map (Grenzstein 1886) can be considered a true pseudomythological sky map. The names of 55 objects in the sky have been included on the map following the NationalRomantic spirit of the 19th century. Some of these names hav ...
... to the Olevik newspaper and printed using the wood engraving technique. This map (Grenzstein 1886) can be considered a true pseudomythological sky map. The names of 55 objects in the sky have been included on the map following the NationalRomantic spirit of the 19th century. Some of these names hav ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... Extra Credit Questions for the Stars and the Universe Test 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away fro ...
... Extra Credit Questions for the Stars and the Universe Test 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away fro ...
Stars
... star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
... star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
The Heliocentric Model of the Solar System
... kilometers). It is called 1 AU (astronomical unit) and serves as a big unit to measure intermediate distances. • One AU is travelled by light in 8.3 ...
... kilometers). It is called 1 AU (astronomical unit) and serves as a big unit to measure intermediate distances. • One AU is travelled by light in 8.3 ...
Astrophysics - Florence
... Irregular galaxies have no specific structure. The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, the nearest galaxies Image to the right is known as the Bird Galaxy ...
... Irregular galaxies have no specific structure. The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, the nearest galaxies Image to the right is known as the Bird Galaxy ...
1. Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning sidereal
... A. The celestial spheres do not have just one common centre. B. The motions of the Sun are not its motions, but the motion of Earth. C. The Earth follow an elliptical orbit in its revolution around the Sun D. What appears to us as retrograde and forward motion of the planets is not their own, but th ...
... A. The celestial spheres do not have just one common centre. B. The motions of the Sun are not its motions, but the motion of Earth. C. The Earth follow an elliptical orbit in its revolution around the Sun D. What appears to us as retrograde and forward motion of the planets is not their own, but th ...
Extra Questions Stellar properties
... 1.A certain type of variable star is known to have an absolute magnitude of 0.0. Such stars are observed in a particular star cluster to have an average magnitude of +16.0 What is the distance to that star cluster. 2 The star Procyon in Canis Major is a prominent star in the winter sky because its a ...
... 1.A certain type of variable star is known to have an absolute magnitude of 0.0. Such stars are observed in a particular star cluster to have an average magnitude of +16.0 What is the distance to that star cluster. 2 The star Procyon in Canis Major is a prominent star in the winter sky because its a ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... 2 Com ds (6.0, 7.5) separation 3.6". Use high power when seeing is good. 24 Com ds. (5.0,6.5) separation 20.3" Wide contrasting yellow and blue pair. 35 Com ds. (5.1,7,2) separation 1.2”. Yellow and purple (deep blue). Coma is a fine hunting ground for galaxies plus a very fine globular cluster. Sta ...
... 2 Com ds (6.0, 7.5) separation 3.6". Use high power when seeing is good. 24 Com ds. (5.0,6.5) separation 20.3" Wide contrasting yellow and blue pair. 35 Com ds. (5.1,7,2) separation 1.2”. Yellow and purple (deep blue). Coma is a fine hunting ground for galaxies plus a very fine globular cluster. Sta ...
Pretest
... measures how far light travels through space in one year. 12. The distance that a star so far away would appear to move when seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit would be too small to measure accurately. 13. A star is born when nuclear fusion begins. 14. Most star formation takes place in the s ...
... measures how far light travels through space in one year. 12. The distance that a star so far away would appear to move when seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit would be too small to measure accurately. 13. A star is born when nuclear fusion begins. 14. Most star formation takes place in the s ...
Day-6
... The Milky Way probably formed by the merger of many smaller protogalaxies. Several of these are still orbiting the Milky Way as satellite galaxies. These can contain significant amounts of gas. The gas delivered by the protogalaxies was a significant source of star formation. Evidence for ...
... The Milky Way probably formed by the merger of many smaller protogalaxies. Several of these are still orbiting the Milky Way as satellite galaxies. These can contain significant amounts of gas. The gas delivered by the protogalaxies was a significant source of star formation. Evidence for ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
... • The main sequence is a narrow band of stars on the H-R diagram that runs diagonally from the upper left ( bright, hot stars) to the lower right ( dim, cool stars). About 90 percent of stars are on the main sequence, including the Sun. • A star’s position on the main sequence is determined by its i ...
... • The main sequence is a narrow band of stars on the H-R diagram that runs diagonally from the upper left ( bright, hot stars) to the lower right ( dim, cool stars). About 90 percent of stars are on the main sequence, including the Sun. • A star’s position on the main sequence is determined by its i ...
Branches of Earth Science Tools Used to Study Stars Constellations
... Galaxy is a huge collection of stars bound by gravity o Contain various star groups Billions of galaxies in the universe 3 types of galaxies o Spiral o Elliptical o Irregular ...
... Galaxy is a huge collection of stars bound by gravity o Contain various star groups Billions of galaxies in the universe 3 types of galaxies o Spiral o Elliptical o Irregular ...
doc - UWM
... planets, asteroids, comets, meteoroids (small debris traveling through the solar system), radiation, etc. In Milwaukee there are stars we can see all year round. TRUE. Some we can see include the stars of the Big Dipper, and Polaris the circumpolar North Star. ...
... planets, asteroids, comets, meteoroids (small debris traveling through the solar system), radiation, etc. In Milwaukee there are stars we can see all year round. TRUE. Some we can see include the stars of the Big Dipper, and Polaris the circumpolar North Star. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.