* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
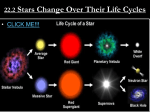
Name: _____________________________ Period: _____ The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram Background Information: For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R Diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types of stars. Just as infants, adolescents and adults are in different stages of the human life cycle, main sequence, red giants, super-giants and white dwarfs are stars in different stages of the life cycle of stars. Color the H-R Diagram below to show the temperature of the stars. 1. What information is plotted on the vertical axis of the diagram? 2. What information is plotted on the horizontal axis of the diagram? Pre-AP Astronomy 3. List the colors of the stars from the color of the hottest star to the color of the coolest star. 4. List the four categories of information you can determine about a star by using the H-R Diagram? 5. If you know a star’s color, what other information can you determine? 6. What is the relationship between the X and Y values for main sequence stars? 7. 90% of stars belong to which category? 8. Which star is the brightest white dwarf? 9. What star is the hottest super giant? 10. What is the temperature of Barnard’s Star? 11. Which star is the dimmest on this chart? 12. In which category will you find the hottest star on the chart? 13. What category of stars are hot but not very luminous? 14. Compare our Sun to Alpha Centauri A in terms of group, brightness, color and temperature. 15. Compare Zeta Eridani to Epsilon Eridani in terms of group, brightness, color and temperature. 16. Describe the ways in which Barnard’s Star and Antares are alike. 17. Place the following stars in order of increasing temperature: Alpha Centauri A, Betelgeuse, Rigel and Sirius B __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ 18. Place the following stars in order of increasing brightness: Rigel, Barnard’s Star, Sirius, and Procyon B __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ Pre-AP Astronomy