* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download overview - Butlins
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
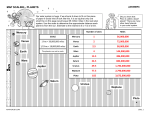
OVERVIEW This week we’re looking at space – something you probably vaguely remember learning back when you were in school. The below is a fun way for you and your children to really get to know the solar system we live in. Space exploration has allowed us a greater understanding of the universe, what it is made up of and our place on Earth within the solar sytem. A discovery in space could lead to something that changes life on Earth. For example, if scientists can understand what happens outside of Earth’s atmosphere in the stars and galaxies, they might be able to stop global warming or they might be able to harness a new form of energy! It’s impossible to have a full understanding of the universe but having a knowledge of basic terminology and the planets is a good place to start for any homework questions that might be fired your way over the coming school year. PlaneT Actual distance from Sun (million km) Mercury 56 Venus 111 Earth 153 Mars 234 Jupiter 777 Saturn 1500 Uranus 2800 Neptune 4500 1 GREAT RED SPOT - a large colourful swirl of gases that spin anticlockwise on Jupiter ATMOSPHERE – the air that surrounds the Earth BLACK HOLE – an object that has gravity strong enough to suck everything into it, even light LIGHT YEAR - the distance light travels in a vacuum in a year CELESTIAL BODIES - natural objects that are visible in the sky planets, stars, meteoroids, asteroids, moons etc Meteor (shooting star / falling star) - a bright streak of light in the sky caused by a meteoroid or a small icy particle as it burns up entering Earth's atmosphere. Very big, bright meteors are called fireballs and bolides HALEY’S COMET - a huge snowball of ice and dust that revolves around the Sun. When it gets close to the Sun the ice melts and looks like a tail. Haley's comet is one of the most famous comets. Meteoroid - a small rock METEORITE - a piece of a meteoroid found on Earth Constellation - a collection of stars that make a shape normally named aer mythological characters, people, animals and things – Ursa Major, Orion, the Northern Cross etc ORBIT - the path that one object takes to moves around another object or point. e.g the Earth orbits the Sun ECLIPSE - this is when a celestial body cuts off the light of another – we sometimes see the moon cover the Sun for a brief moment – this happened on 20th March this year! PLANET – an object bigger than an asteroid that orbits a star. Our solar system has eight planets within it GALAXY - a large collection of stars. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, includes the Sun Satellite - an object that moves around a larger body. The moon is a satellite of Earth. Manmade satellites orbit the Earth and the Sun to transmit pictures, TV channels and phone signals back to us GRAVITY – the natural force of araction that pulls objects together - this keeps our feet on the ground 2 SOLAR SYSTEM – includes the Sun, the eight planets and any other bodies that orbit the Sun STAR - a celestial body that is visible at night from Earth SOLAR WIND – a thin flow of gas-charged particles that stream from the Sun. These blow throughout the solar system at speeds of hundreds of kilometres per second UNIVERSE - all the maer and energy in space - this includes the Earth, galaxies, solar systems and you WHITE DWARF - the 'remains' of a star aer it collapses. It is white (because it's so hot) and extremely dense SPEED OF LIGHT - 299,792,458 meters/second (186,000 miles/second.) Einstein's Theory of Relativity states that nothing can move faster than the speed of light You will need: One pea One blueberry Two cherry tomatoes One watermelon One large grapefruit One large apple One small orange List of planets (Earth, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, Neptune, Saturn, Uranus, Venus) Scissors 3 METHOD: 1. Cut out the names of the planets to produce eight labels Mercury 2. Try and hazard a guess which pieces of fruit and veg represent each planet based on their size – without looking at the table provided below! 3. Match the fruit and veg to the labels, then place them in order from the closest to the Sun to the planet that is furthest from the sun Planets in order from the Sun Planets in order from the Sun Mercury Pea Venus Cherry Tomato Earth Cherry Tomato Mars Blueberry Jupiter Watermelon Saturn Large grapefruit Uranus Large apple Neptune Small orange 4