Another Old Final
... (b) Estimate the distance to this supernova and the lookback time (how long ago we are observing it). (c) Type-Ia supernovae reach peak luminosities of 109 L . Estimate the peak apparent brightness of this supernova. Would it have been visible to the naked eye on a clear night? ...
... (b) Estimate the distance to this supernova and the lookback time (how long ago we are observing it). (c) Type-Ia supernovae reach peak luminosities of 109 L . Estimate the peak apparent brightness of this supernova. Would it have been visible to the naked eye on a clear night? ...
Study Guide 4 Part A Outline
... The expansion started at some definite time in the past (the Big Bang)Universe expands away from every galaxy. Every galaxy would see its own version of the Hubble Law. Quasars & Active Galactic Nuclei o Quasars and other active galaxies emit large amounts of energy from relatively small regions n ...
... The expansion started at some definite time in the past (the Big Bang)Universe expands away from every galaxy. Every galaxy would see its own version of the Hubble Law. Quasars & Active Galactic Nuclei o Quasars and other active galaxies emit large amounts of energy from relatively small regions n ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... medium are called nebulae • Dark nebulae are so dense that they are opaque • They appear as dark blots against a background of distant stars • Emission nebulae, or H II regions, are glowing, ionized clouds of gas • Emission nebulae are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot st ...
... medium are called nebulae • Dark nebulae are so dense that they are opaque • They appear as dark blots against a background of distant stars • Emission nebulae, or H II regions, are glowing, ionized clouds of gas • Emission nebulae are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot st ...
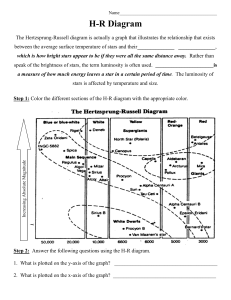
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determine how many times more or less massive your star is compared to the Sun. You may i ...
... comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determine how many times more or less massive your star is compared to the Sun. You may i ...
Study Guide: Chapters 32-‐34 FROSH CHAPTER 32 1. What is
... e. Extreme temperatures due to no atmosphere and location to the sun _________________________ f. Seen as blue due to frozen methane in atmosphere and rotates top to bottom __________________ g. Largest pl ...
... e. Extreme temperatures due to no atmosphere and location to the sun _________________________ f. Seen as blue due to frozen methane in atmosphere and rotates top to bottom __________________ g. Largest pl ...
File
... Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
... Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
PowerPoint file - Northwest Creation Network
... The popular theory is that stars form from vast clouds of gas and dust through gravitational contraction. ...
... The popular theory is that stars form from vast clouds of gas and dust through gravitational contraction. ...
Amie Bickert - ColonialAcademyScience
... White dwarf: blue-white core of the star that is left behind cools forms this. Supernovas: an explosion of a suergiant Neutron star: the remains of high-mass stars. Black holes- an object with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Guided Practice: T. and Ss. read se ...
... White dwarf: blue-white core of the star that is left behind cools forms this. Supernovas: an explosion of a suergiant Neutron star: the remains of high-mass stars. Black holes- an object with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Guided Practice: T. and Ss. read se ...
Space Exam Review
... large chunks of ice, dust and rock that orbit the Sun (the orbit can take a few years to a hundred thousand years) (nicknamed “Dirty Snowballs”) can be 100m to 40 km in diameter o Short-period comets: originate from just beyond Neptune and orbit the Sun in less than 200 years (for example, Halle ...
... large chunks of ice, dust and rock that orbit the Sun (the orbit can take a few years to a hundred thousand years) (nicknamed “Dirty Snowballs”) can be 100m to 40 km in diameter o Short-period comets: originate from just beyond Neptune and orbit the Sun in less than 200 years (for example, Halle ...
15 - Edmodo
... Activity B – Our Solar System 3. The Composition of our Solar System After the Sun formed, the leftover dust, gases, and other debris in the nebula continued to spin, creating a disk around the new star. Small bodies began to form, growing into the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets that make up ...
... Activity B – Our Solar System 3. The Composition of our Solar System After the Sun formed, the leftover dust, gases, and other debris in the nebula continued to spin, creating a disk around the new star. Small bodies began to form, growing into the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets that make up ...
Practice Homework 2: Properties of Stars 1. Star A is 100 times more
... have discovered it? 6. The Light in sun is created in the interior of the sun which is extremely hot and dense while the outer layers are relatively colder. What kind of spectrum it should produce? Helium in the sun causes absorption at certain frequencies, in which regions of sun do you think this ...
... have discovered it? 6. The Light in sun is created in the interior of the sun which is extremely hot and dense while the outer layers are relatively colder. What kind of spectrum it should produce? Helium in the sun causes absorption at certain frequencies, in which regions of sun do you think this ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... What do scientists use to calculate distance to stars? • Because stars are so far away, astronomers use light years to measure the distance from Earth to the stars. • A light year is the distance that light travels in one year, or 186,282 miles per second, or 5.88 trillion miles**** This quasar is ...
... What do scientists use to calculate distance to stars? • Because stars are so far away, astronomers use light years to measure the distance from Earth to the stars. • A light year is the distance that light travels in one year, or 186,282 miles per second, or 5.88 trillion miles**** This quasar is ...
B. protostar - University of Maryland Astronomy
... 23. A gigantic outburst of energy and particles occurred on the Sun this morning. Mrs. Deming was excited and told her ASTR 101 class to look for A. a full moon tonight. B. an eclipse. C. a meteor shower if it is clear. D. an aurora if it is clear. E. dangerous cosmic rays. 24. Which of the followi ...
... 23. A gigantic outburst of energy and particles occurred on the Sun this morning. Mrs. Deming was excited and told her ASTR 101 class to look for A. a full moon tonight. B. an eclipse. C. a meteor shower if it is clear. D. an aurora if it is clear. E. dangerous cosmic rays. 24. Which of the followi ...
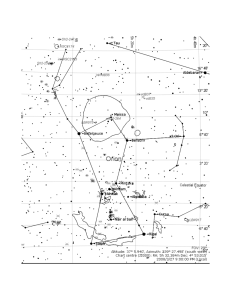
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.







![Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010793453_1-3f96ef5ee7d4646c2142d92e4dc3c3f6-300x300.png)