Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... Red Dwarfs and Barnard’s star. Their origin and significance to astronomy. What is a Red Dwarf? A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperatur ...
... Red Dwarfs and Barnard’s star. Their origin and significance to astronomy. What is a Red Dwarf? A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperatur ...
Astronomy Practice Test
... B. over the North Pole C. in the larger constellations D. inside other galaxies 10. Why does the air temperature rise in the summer? A. We are closer to the sun. B. The air becomes thicker and more dense. C. The sun’s rays are more direct and days are longer. D. The ratio of the hours of daylight to ...
... B. over the North Pole C. in the larger constellations D. inside other galaxies 10. Why does the air temperature rise in the summer? A. We are closer to the sun. B. The air becomes thicker and more dense. C. The sun’s rays are more direct and days are longer. D. The ratio of the hours of daylight to ...
I. Parallax
... _______________. Because of Earth’s orbit around the Sun, this happens when astronomers view a “nearby” star at ___ _________________________. C. An example of this is when you hold your finger ___________ ________________and view it first with ________ and then the _________. D. The term parallax i ...
... _______________. Because of Earth’s orbit around the Sun, this happens when astronomers view a “nearby” star at ___ _________________________. C. An example of this is when you hold your finger ___________ ________________and view it first with ________ and then the _________. D. The term parallax i ...
How Big is Big? Integrated Science 2 Name: Date: Pd: Select items
... used to describe topics in science, such as the age of the universe, the length of a galaxy, or number of stars in a galaxy. Before we begin to look at our Origins unit, which covers times and distances in the billions—and more, we want you to take a minute to just think about how big our universe i ...
... used to describe topics in science, such as the age of the universe, the length of a galaxy, or number of stars in a galaxy. Before we begin to look at our Origins unit, which covers times and distances in the billions—and more, we want you to take a minute to just think about how big our universe i ...
te acher`s guide te acher`s guide
... Stars asks the following five questions about our Sun and all of its shining counterparts. Space travelers Adi and Woops help viewers clearly answer each question using computer graphics and space footage. What are the signs of the zodiac? The signs of the zodiac are twelve different groups of stars ...
... Stars asks the following five questions about our Sun and all of its shining counterparts. Space travelers Adi and Woops help viewers clearly answer each question using computer graphics and space footage. What are the signs of the zodiac? The signs of the zodiac are twelve different groups of stars ...
Constellation Chart Activity
... a) Find 6h of Right Ascension at the bottom of the map. The date written right below it is _________________. That means that if you go outside at 8 PM local time on that date, that line would be YOUR Meridian. b) Find Orion and Gemini along that 6h RA line. On that date at that time, Orion will be ...
... a) Find 6h of Right Ascension at the bottom of the map. The date written right below it is _________________. That means that if you go outside at 8 PM local time on that date, that line would be YOUR Meridian. b) Find Orion and Gemini along that 6h RA line. On that date at that time, Orion will be ...
Semester #1 – GeoScience Review Guide – Final Exam Scale
... 1. What is a light-year? How big is it in kilometers? 2. In your scale model of the Solar System, the scale was 1 cm = 10,000,000,000 km. Jupiter is 778,000,000 km from the sun. On your scale model, how many cm was Jupiter from the sun? 3. Is this a true or false statement? 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 4 ...
... 1. What is a light-year? How big is it in kilometers? 2. In your scale model of the Solar System, the scale was 1 cm = 10,000,000,000 km. Jupiter is 778,000,000 km from the sun. On your scale model, how many cm was Jupiter from the sun? 3. Is this a true or false statement? 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 4 ...
File
... notation. This is 4.22 light years (4.22 ly). A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. (equaling 9.46 x 1012 km). Book analogy: If the Sun is a pinhead, the next star is another pinhead 35 miles away. This shows that the universe is made mostly of empty space. ...
... notation. This is 4.22 light years (4.22 ly). A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. (equaling 9.46 x 1012 km). Book analogy: If the Sun is a pinhead, the next star is another pinhead 35 miles away. This shows that the universe is made mostly of empty space. ...
14_creationism
... The origin of life. This is such an extraordinary event and “achievement”. Perhaps life is so complex that the origin of life is a lot less likely than we think. This is testable. As we search the universe we may be unlikely to find even primitive life. The origin of intelligence. Perhaps primitive ...
... The origin of life. This is such an extraordinary event and “achievement”. Perhaps life is so complex that the origin of life is a lot less likely than we think. This is testable. As we search the universe we may be unlikely to find even primitive life. The origin of intelligence. Perhaps primitive ...
Earth_Universe04
... Properties of stars Binary stars and stellar mass • Binary stars • Two stars orbiting one another • Stars are held together by mutual gravitation • Both orbit around a common center of mass • More than 50% of the stars in the universe are binary stars ...
... Properties of stars Binary stars and stellar mass • Binary stars • Two stars orbiting one another • Stars are held together by mutual gravitation • Both orbit around a common center of mass • More than 50% of the stars in the universe are binary stars ...
Denton ISD
... determine the elements in the star by studying the pattern of dark lines in the absorption spectrum. What instrument should she use to identify the elements in the star? A electron microscope B telescope C spectroscope D gas chromatograph http://academics.wellesley.edu/Chemistry/Chem105manual/Chem10 ...
... determine the elements in the star by studying the pattern of dark lines in the absorption spectrum. What instrument should she use to identify the elements in the star? A electron microscope B telescope C spectroscope D gas chromatograph http://academics.wellesley.edu/Chemistry/Chem105manual/Chem10 ...
The Warrumbungle Observer The Warrumbungle Observer
... constellation Capricorn which looks like the letter ‘D’ in the eastern evening sky. Careful observations of Jupiter’s position each night will show Jupiter moving compared to the other stars in Capricorn and appearing to be moving up the left side of ‘the letter D’ Four of Jupiter’s moons are easily ...
... constellation Capricorn which looks like the letter ‘D’ in the eastern evening sky. Careful observations of Jupiter’s position each night will show Jupiter moving compared to the other stars in Capricorn and appearing to be moving up the left side of ‘the letter D’ Four of Jupiter’s moons are easily ...
File - greenscapes4you
... All stars form in a cloud of dust and gas called a nebula. They begin their life with roughly the same composition. Star’s mass at birth: about 75% hydrogen about 25% helium; less than 2% heavier elements During most of star’s life, rate at which it generates energy depends on balance between inward ...
... All stars form in a cloud of dust and gas called a nebula. They begin their life with roughly the same composition. Star’s mass at birth: about 75% hydrogen about 25% helium; less than 2% heavier elements During most of star’s life, rate at which it generates energy depends on balance between inward ...
File
... The explosion called a supernova occurs after a large star has become a red supergiant. When the star stops expanding because it can no longer create enough energy to support its own mass, it collapses completely and makes a giant explosion. A supernova is brighter than all the stars in the galaxy c ...
... The explosion called a supernova occurs after a large star has become a red supergiant. When the star stops expanding because it can no longer create enough energy to support its own mass, it collapses completely and makes a giant explosion. A supernova is brighter than all the stars in the galaxy c ...
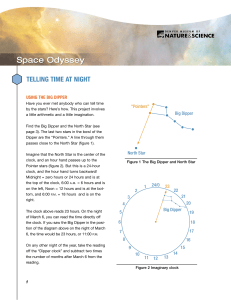
telling time at night
... up about one-third* of the way from horizon to zenith, the top of the sky. The North Star is fairly bright (second magnitude) and visible from the city, but not as bright as the brightest stars (first magnitude). The Big Dipper rotates around the North Star through the night and throughout the seaso ...
... up about one-third* of the way from horizon to zenith, the top of the sky. The North Star is fairly bright (second magnitude) and visible from the city, but not as bright as the brightest stars (first magnitude). The Big Dipper rotates around the North Star through the night and throughout the seaso ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.