C H A P T E R 2
... "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper asterism would have been circumpolar, while today only one of the seven bright stars forming the Bi ...
... "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper asterism would have been circumpolar, while today only one of the seven bright stars forming the Bi ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
FREE Sample Here
... "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper asterism would have been circumpolar, while today only one of the seven bright stars forming the Bi ...
... "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper asterism would have been circumpolar, while today only one of the seven bright stars forming the Bi ...
9ol.ASTRONOMY 1 ... Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each =...
... 28. .Radioactive dating techniques have revealed that our Earth and Moon are approximately how old? 29. According to our theory of solar system formation, what three major changes occurred in the solar nebula as it shrank in size? 30. According to our present theory of solar system formation, why w ...
... 28. .Radioactive dating techniques have revealed that our Earth and Moon are approximately how old? 29. According to our theory of solar system formation, what three major changes occurred in the solar nebula as it shrank in size? 30. According to our present theory of solar system formation, why w ...
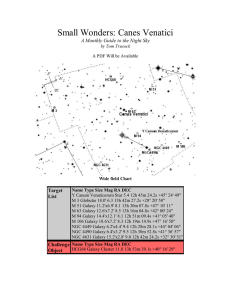
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
Chapter 15 Stars, Galaxies
... brighter or not as bright as Star X if both were to be seen from the same distance. 14. true 15. a. The star’s apparent brightness b. The star’s distance from Earth 16. false 17. A light-year is the distance that light travels through space in one year. 18. 9.5 million million 19. false 20. Parallax ...
... brighter or not as bright as Star X if both were to be seen from the same distance. 14. true 15. a. The star’s apparent brightness b. The star’s distance from Earth 16. false 17. A light-year is the distance that light travels through space in one year. 18. 9.5 million million 19. false 20. Parallax ...
VISIT TO NORMAN LOCKYER OBSERVATORY IN SIDMOUTH
... Held steady, binoculars should enable you to see Saturn's brightest moon, Titan, at magnitude 8.2. A small telescope will show the rings with magnifications of x25 or more and one of 6-8 inches aperture with a magnification of ~x200 coupled with a night of good "seeing" (when the atmosphere is calm) ...
... Held steady, binoculars should enable you to see Saturn's brightest moon, Titan, at magnitude 8.2. A small telescope will show the rings with magnifications of x25 or more and one of 6-8 inches aperture with a magnification of ~x200 coupled with a night of good "seeing" (when the atmosphere is calm) ...
Can We Make A Star?
... move so that the gasses will react with each other • Then we just sit way back and wait until the gasses explode into a fireball ...
... move so that the gasses will react with each other • Then we just sit way back and wait until the gasses explode into a fireball ...
Stars & Galaxies
... energy output rises and the body of the star swells into a “red giant” 6. Star’s core will eventually collapse in an explosion (star blows up)- supernova Every chemical element that made the planets, stars, oceans, and organisms is made up of star dust. ...
... energy output rises and the body of the star swells into a “red giant” 6. Star’s core will eventually collapse in an explosion (star blows up)- supernova Every chemical element that made the planets, stars, oceans, and organisms is made up of star dust. ...
Sermon Notes
... a type of Christ and Scorpio is a type of Satan. When Taurus rises Scorpio falls below the horizon. When Jesus comes again then Satan will descend into the bottomless pit. Isaiah 34:7 – And the unicorns shall come down with them, and the bullocks with the bulls; and their land shall be soaked with b ...
... a type of Christ and Scorpio is a type of Satan. When Taurus rises Scorpio falls below the horizon. When Jesus comes again then Satan will descend into the bottomless pit. Isaiah 34:7 – And the unicorns shall come down with them, and the bullocks with the bulls; and their land shall be soaked with b ...
homework assignment 3
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
Supernova’s
... leading to its collapse • Becomes Red Giant Star • Turns into a White Dwarf Star ...
... leading to its collapse • Becomes Red Giant Star • Turns into a White Dwarf Star ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... Patterns of stars: Constellations Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations. Constellations: Patterns of stars in the night sky ...
... Patterns of stars: Constellations Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations. Constellations: Patterns of stars in the night sky ...
2016-0620-Mountain-Skies
... study Greek mythology without hearing of the labors of Hercules and many of these stories are illustrated among the constellations in the sky. Hercules is pictured upside down as we view him from the northern hemisphere. Thus, the lower two stars in the letter “H” mark his shoulders, the middle two ...
... study Greek mythology without hearing of the labors of Hercules and many of these stories are illustrated among the constellations in the sky. Hercules is pictured upside down as we view him from the northern hemisphere. Thus, the lower two stars in the letter “H” mark his shoulders, the middle two ...
Earth and Space - Sun, Moon and Stars
... Create a model of the sun, moon and earth systems (e.g., using a globe/sphere and a light source, StarLab, etc.). Demonstrate how the earth revolves around the sun. Identify the sun as the brightest star and is located in the center of our solar system. Investigate and record the direction o ...
... Create a model of the sun, moon and earth systems (e.g., using a globe/sphere and a light source, StarLab, etc.). Demonstrate how the earth revolves around the sun. Identify the sun as the brightest star and is located in the center of our solar system. Investigate and record the direction o ...
Introduction to Astronomy - Northumberland Astronomical Society
... Every point on the sky can be specified by two numbers: Declination an angle measured north or south of the celestial equator. The North Celestial Pole is at +90◦ and the South Celestial Pole at −90◦ . Right Ascension an angle measured from a zero line (the First Point of Aries) to the object line. ...
... Every point on the sky can be specified by two numbers: Declination an angle measured north or south of the celestial equator. The North Celestial Pole is at +90◦ and the South Celestial Pole at −90◦ . Right Ascension an angle measured from a zero line (the First Point of Aries) to the object line. ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part I - Naples Free-Net
... With a calendar, you can have reliable agriculture, which is the basis of civilization. Take your star chart and look for the constellation Hercules, just for an example. You will note that the constellation Hercules as drawn does not look much like a man; constellations only occasionally look like ...
... With a calendar, you can have reliable agriculture, which is the basis of civilization. Take your star chart and look for the constellation Hercules, just for an example. You will note that the constellation Hercules as drawn does not look much like a man; constellations only occasionally look like ...
Astronomy Chap 1
... 3. Are celestial objects like stars and planets in the daytime sky? 4. What is the relationship between latitude and the angular height of the Sun? 5. Explain how angular height of the Sun in different parts of the country correlate with sunburns. What is the critical angle? 6. Review the Solar Moti ...
... 3. Are celestial objects like stars and planets in the daytime sky? 4. What is the relationship between latitude and the angular height of the Sun? 5. Explain how angular height of the Sun in different parts of the country correlate with sunburns. What is the critical angle? 6. Review the Solar Moti ...
Notes
... E. _________________________ holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the ____________________ that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between ____________. 3. The more _________ an object has the ________ its gravitational pull. a. ...
... E. _________________________ holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the ____________________ that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between ____________. 3. The more _________ an object has the ________ its gravitational pull. a. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.