* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Navigation Methods
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
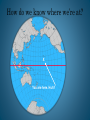
Navigation SAD JOKE • Dead ahead, through the pitch-black night, the captain sees a light on a collision course with his ship. He sends a signal: "Change your course ten degrees east." "Change yours ten degrees west," comes the reply. The captain responds, "I'm a United States Navy captain! Change your course, sir!" "I'm a seaman second class," the next message reads. "Change your course, sir." The captain is furious. "I'm a battleship! I'm not changing course!" "I'm a lighthouse. Your call." How do we know where we’re at? X You are here. Huh? When people first started going out in boats they tended to stay close to shore so they could use landmarks to guide them. As people ventured further (the Hawaiians 3000BC could travel over 1000km between islands) they needed to find other landmarks so they turned to the stars. 1. Celestial navigation • The pattern of stars and planets seen from Earth are constant in space. The celestial sphere. • It is useful to be able to precisely specify positions on the celestial sphere. Sextant • a device that measures the angle between two objects. It uses the position of stars to find it’s latitude, longitude. • The North Celestial Pole is the point on the celestial sphere directly above the Earth's North Pole. Similarly, the South Celestial Pole is directly above the Earth's South Pole. • The star Polaris, in the constellation Ursa Minor, is located very close to the North Celestial Pole. Polaris is therefore also called the North Star. Latitude and Longitude Globes, maps and charts have a system of North-South and East-West lines which make up the Earth’s Grid. This grid is the basis for locating points on Earth. Imagine a piece of graph paper covering the planet. The intersection of two lines determines the exact location of a point. Latitude The distance north or south of the earth's equator. 0 degrees latitude is the equator, the "belt" that goes around the "waist" of the earth. 90 degrees north is the North Pole and 90 degrees south is the South Pole. Longitude Longitude: Angular distance on the earth's surface, measured east or west from the prime meridian at Greenwich, England. Prime Meridian Equator Tools of the trade… • Sextant: measures the angle between celestial bodies and the Earth to determine position. • Compass: Point to magnetic North, so you can follow a course by knowing our position in relation to North. • Loran C: radio transmissions from set positions on the surface of the Earth, that triangulate to give you a position. • GPS: is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their ground stations. Compass Loran C (LOng RAnge Navigation) • LORAN-C was originally developed to provide radio-navigation service for U.S. coastal waters and was later expanded to include complete coverage of the continental U.S. as well as most of Alaska. Twenty-four U.S. LORAN-C stations work in partnership with Canadian and Russian stations to provide coverage in Canadian waters and in the Bering Sea. LORAN-C provides better than 0.25 nautical mile absolute accuracy for suitably equipped users within the published areas. What is Loran-C? • Loran-C is a low frequency/long wave electronic position fixing system using radio signals transmissions @ 100 KHz from 3 or more transmitters, linked in a chain. It gives a latitude and longitude readout position to marine, aero and land receivers. The Global Positioning System (GPS) • is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their ground stations. • GPS uses these "man-made stars" as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters. In fact, with advanced forms of GPS you can make measurements to better than a centimeter! • In a sense it's like giving every square meter on the planet a unique address. • GPS receivers have been miniaturized to just a few integrated circuits and so are becoming very economical. And that makes the technology accessible to virtually everyone. • These days GPS is finding its way into cars, boats, planes, construction equipment, movie making gear, farm machinery, even laptop computers. Coordinates given in Longitude, Latitude West East Longitude: 40 E Latitude: North South 65 N Mapping activity • http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/DE/k9mod/Mapskill/ mod3fl5.swf • http://www.globenav.com/ • Youtube video: Lost at Sea- the Search for Longitude (a NOVA program) What happens when you are not a good navigator!!!