Assessing endocrine function
... Example of a pituitary function test The ACTH response to a bolus injection of CRH is measured The grey shaded area shows the range of responses measured in control subjects In hypopituitarism there is no response ...
... Example of a pituitary function test The ACTH response to a bolus injection of CRH is measured The grey shaded area shows the range of responses measured in control subjects In hypopituitarism there is no response ...
Hormones and Behavior 1
... WHAT EXACTLY ARE HORMONES? • Organic molecules produced and released into blood by endocrine (ductless) glands and tissues • Carried by blood to target tissues • Specific hormones only affect certain cells and hormones affect different cells in different ways – Target cells possess receptors for spe ...
... WHAT EXACTLY ARE HORMONES? • Organic molecules produced and released into blood by endocrine (ductless) glands and tissues • Carried by blood to target tissues • Specific hormones only affect certain cells and hormones affect different cells in different ways – Target cells possess receptors for spe ...
Chapter22 Lecture Outline
... Outline how ovarian function is hormonally controlled, starting with the hypothalamus to the final target organs (i.e. uterus, and 2o sex organs). Then discuss the hormones named above in terms of the female reproductive cycle that occurs each month (i.e. list each hormone, name the (specific) organ ...
... Outline how ovarian function is hormonally controlled, starting with the hypothalamus to the final target organs (i.e. uterus, and 2o sex organs). Then discuss the hormones named above in terms of the female reproductive cycle that occurs each month (i.e. list each hormone, name the (specific) organ ...
TABLE OF CONTENTS - Wake Forest Baptist Health
... with a very high estrogen level. When eggs are aspirated from the ovary, as they will be in IVF cycles, hyperstimulation is rare. When it does occur, it consists of rapid enlargement of the ovaries during the latter part of the cycle which is accompanied by pain, fluid loss into the abdomen, and alt ...
... with a very high estrogen level. When eggs are aspirated from the ovary, as they will be in IVF cycles, hyperstimulation is rare. When it does occur, it consists of rapid enlargement of the ovaries during the latter part of the cycle which is accompanied by pain, fluid loss into the abdomen, and alt ...
Postpartum Thyroiditis FAQ - American Thyroid Association
... What is the clinical course of postpartum thyroiditis? The classic description of postpartum thyroiditis includes thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism. The thyrotoxic phase usually lasts for 1-3 months and is associated with symptoms including anxiety, insomnia, palpitations (fast heart rate), ...
... What is the clinical course of postpartum thyroiditis? The classic description of postpartum thyroiditis includes thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism. The thyrotoxic phase usually lasts for 1-3 months and is associated with symptoms including anxiety, insomnia, palpitations (fast heart rate), ...
The Endocrine System
... Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen in females, and stimulates the production of sperm in the male. 6. Luteinizing hormone Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen and the formation of the corpus luteum after ovulation, w ...
... Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen in females, and stimulates the production of sperm in the male. 6. Luteinizing hormone Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen and the formation of the corpus luteum after ovulation, w ...
The Endocrine System
... Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen in females, and stimulates the production of sperm in the male. 6. Luteinizing hormone Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen and the formation of the corpus luteum after ovulation, w ...
... Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen in females, and stimulates the production of sperm in the male. 6. Luteinizing hormone Stimulates the growth of the graafian follicle and the production of estrogen and the formation of the corpus luteum after ovulation, w ...
Pathogenesis-of-diseases-of-the-Pituitary-Pineal-Thyroid
... encapsulated- invasion of capsule and blood vessels distinguishes it from follicular adenoma ...
... encapsulated- invasion of capsule and blood vessels distinguishes it from follicular adenoma ...
Endocrine System - Practicum-Health-II-2011-2012
... – Results from hyposecretion of the growth hormone of the pituitary gland, which has been caused by a tumor, infection, genetic factors, or trauma ...
... – Results from hyposecretion of the growth hormone of the pituitary gland, which has been caused by a tumor, infection, genetic factors, or trauma ...
ocumento de información de fecundación in vitro o microinyección
... The economic cost of maintaining the cryopreserved materials (oocytes, sperm or embryos) shall be borne by patients, as long as these are deposited in the Medical Centre. 4.- Obligation renewal of consent regarding cryopreserved embryos At least every two years the parenting woman or partner will be ...
... The economic cost of maintaining the cryopreserved materials (oocytes, sperm or embryos) shall be borne by patients, as long as these are deposited in the Medical Centre. 4.- Obligation renewal of consent regarding cryopreserved embryos At least every two years the parenting woman or partner will be ...
The Endocrine System
... The thyroid gland regulates the body’s metabolism and has no effect on calcium levels while parathyroid glands regulate calcium levels and have no effect on metabolism. Calcium is the element that allows the normal conduction of electrical currents along nerves--its how our nervous system works and ...
... The thyroid gland regulates the body’s metabolism and has no effect on calcium levels while parathyroid glands regulate calcium levels and have no effect on metabolism. Calcium is the element that allows the normal conduction of electrical currents along nerves--its how our nervous system works and ...
The Master Gland/Pituitary Endocrine glands and hormones
... Thyroid gland Hormones Thyroid Stimulating Hormones (TSH)** ...
... Thyroid gland Hormones Thyroid Stimulating Hormones (TSH)** ...
Chapter 10 - Delmar Cengage Learning
... • Decreases uterine activity when a female is in estrus or pregnant • Progestins (a group of compounds similar in effect to progesterone) are used in dogs to block estrus • Progestins are used in cattle to synchronize breeding and birth cycles • Progestins may be used to treat behavior problems and ...
... • Decreases uterine activity when a female is in estrus or pregnant • Progestins (a group of compounds similar in effect to progesterone) are used in dogs to block estrus • Progestins are used in cattle to synchronize breeding and birth cycles • Progestins may be used to treat behavior problems and ...
Slide 1
... • The half-life of hormones circulating in the blood ranges from minutes to hours. – Most hormones are removed from the blood by the liver. These are usually water-soluble and are considered “free” hormones – Thyroid hormone circulates for several days. They are attached to plasma proteins in the bl ...
... • The half-life of hormones circulating in the blood ranges from minutes to hours. – Most hormones are removed from the blood by the liver. These are usually water-soluble and are considered “free” hormones – Thyroid hormone circulates for several days. They are attached to plasma proteins in the bl ...
X-Plain Hysteroscopy Reference Summary
... and the ovaries are working correctly, the endometrium and the egg are discharged to the outside of the body. This is called the menstrual period. As menopause approaches, menstrual periods become irregular and eventually stop. Menopause occurs when the ovaries quit producing hormones and releasing ...
... and the ovaries are working correctly, the endometrium and the egg are discharged to the outside of the body. This is called the menstrual period. As menopause approaches, menstrual periods become irregular and eventually stop. Menopause occurs when the ovaries quit producing hormones and releasing ...
Typical disorders of the endocrine system 1. Choose the correct
... + a) acromegaly; + b) gigantism; + c) hypercortisolism; d) secondary aldosteronism; e) primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insuffi ...
... + a) acromegaly; + b) gigantism; + c) hypercortisolism; d) secondary aldosteronism; e) primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insuffi ...
The Endocrine System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... Testes in males, promotes testosterone secretion Hyposecretion – failure of sexual maturation ...
... Testes in males, promotes testosterone secretion Hyposecretion – failure of sexual maturation ...
Progesterone 1.08
... 4. Progesterone may cause drowsiness therefore is usually taken in the evening or at bedtime. Some women become very drowsy and/or dizzy after taking progesterone. In a small percentage of these women, these effects may be increased including blurred vision, difficulty speaking, difficulty walking a ...
... 4. Progesterone may cause drowsiness therefore is usually taken in the evening or at bedtime. Some women become very drowsy and/or dizzy after taking progesterone. In a small percentage of these women, these effects may be increased including blurred vision, difficulty speaking, difficulty walking a ...
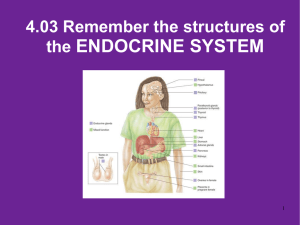
4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the
... emergency situation or when the body is under stress. Norepinephrine- Opposite of epinephrine. ...
... emergency situation or when the body is under stress. Norepinephrine- Opposite of epinephrine. ...
16 - Brazosport College
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
Question 1
... treatment to induce ovulation. It is usually given in a dose of 50mg per day for 5 days (usually days 5-9 after a period has occurred spontaneously or been induced). Higher doses can be given if ovulation does not occur following treatment with this dose, and sometimes mid-cycle hCG (which mimics th ...
... treatment to induce ovulation. It is usually given in a dose of 50mg per day for 5 days (usually days 5-9 after a period has occurred spontaneously or been induced). Higher doses can be given if ovulation does not occur following treatment with this dose, and sometimes mid-cycle hCG (which mimics th ...
Chapter 16 - apsubiology.org
... glandular secretions Homeostasis during normal and emergency conditions Some immune system activities Coordinated, sequential growth, development, and maturation Reproduction by regulating: gamete production fertilization nourishment of the embryo and fetus labor and delivery lactati ...
... glandular secretions Homeostasis during normal and emergency conditions Some immune system activities Coordinated, sequential growth, development, and maturation Reproduction by regulating: gamete production fertilization nourishment of the embryo and fetus labor and delivery lactati ...
19 Cardiovascular System: BLOOD
... The responsiveness of a target cell to a hormone depends on the hormone's concentration, the abundance of the target cell's hormone receptors, and influences exerted by other hormones. ______________________________________________ Control of Hormone Secretions: 1. Most hormones are released in sho ...
... The responsiveness of a target cell to a hormone depends on the hormone's concentration, the abundance of the target cell's hormone receptors, and influences exerted by other hormones. ______________________________________________ Control of Hormone Secretions: 1. Most hormones are released in sho ...
File
... • The endocrine system carries out its functions based upon messages received from the Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus monitors the blood and sends hormones from glands into the blood when needed • Organs await the arrival of hormones • In general, hormonal control regulates the metabolic functions ...
... • The endocrine system carries out its functions based upon messages received from the Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus monitors the blood and sends hormones from glands into the blood when needed • Organs await the arrival of hormones • In general, hormonal control regulates the metabolic functions ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.