Unit P: Endocrine System
... Too much thyroxine secreted leading to enlargement of gland People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, ...
... Too much thyroxine secreted leading to enlargement of gland People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, ...
The New Science of Anti-Aging Hormone Replacement Therapy
... The very interesting overview by Clemons and Goss and their presented studies substantiates the assumption that the continued increased burdening of the organism by supraphysiological doses of 17-ß-estradiol increases the proliferation pressure of the mammary glands, increases the radiological densi ...
... The very interesting overview by Clemons and Goss and their presented studies substantiates the assumption that the continued increased burdening of the organism by supraphysiological doses of 17-ß-estradiol increases the proliferation pressure of the mammary glands, increases the radiological densi ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... Hormones are produced by many different tissues of the body, as shown in 10th Martini Figure 18-1 (Organs and Tissues of the Endocrine System). Many of the most important hormones are part of what is often called the hypothalamic-pituitary axis (CTM Figure 18.1). This name reflects the fact that hyp ...
... Hormones are produced by many different tissues of the body, as shown in 10th Martini Figure 18-1 (Organs and Tissues of the Endocrine System). Many of the most important hormones are part of what is often called the hypothalamic-pituitary axis (CTM Figure 18.1). This name reflects the fact that hyp ...
Endocrine System
... •The bulk of hormone is cleared by the liver and kidneys •Only a small fraction is removed by target tissue – Steroid (and thyroid hormones) are degraded after hormonereceptor complex binds to DNA • action and elimination are slower (hours-days) – protein and amine hormones (non steroids) bind to re ...
... •The bulk of hormone is cleared by the liver and kidneys •Only a small fraction is removed by target tissue – Steroid (and thyroid hormones) are degraded after hormonereceptor complex binds to DNA • action and elimination are slower (hours-days) – protein and amine hormones (non steroids) bind to re ...
Instructions - Meridian Valley Lab
... IMPORTANT INFORMATION - read this before beginning collection 1. If on hormone replacement therapy (estrogens, testosterone, thyroids, etc), consult with prescribing physician as to whether these hormones should be taken during collection. It is generally recommended to continue hormone replacement ...
... IMPORTANT INFORMATION - read this before beginning collection 1. If on hormone replacement therapy (estrogens, testosterone, thyroids, etc), consult with prescribing physician as to whether these hormones should be taken during collection. It is generally recommended to continue hormone replacement ...
Endocrine System Endocrine vs. Exocrine
... aExocrine gland producing digestive enzymes and endocrine gland producing hormones aEndocrine portion called Islets of Langerhans ...
... aExocrine gland producing digestive enzymes and endocrine gland producing hormones aEndocrine portion called Islets of Langerhans ...
Jenny Yin Endocrine System Maintain homeostasis Local Hormones
... Lipid-soluble molecules are able to pass across membranes because they can mix with the phospholipids found in the membrane. Steroid hormones exert their action by: Being lipid soluble, steroid hormones can cross the plasma and nuclear membrane of a cell, where they may exert their effect on the exp ...
... Lipid-soluble molecules are able to pass across membranes because they can mix with the phospholipids found in the membrane. Steroid hormones exert their action by: Being lipid soluble, steroid hormones can cross the plasma and nuclear membrane of a cell, where they may exert their effect on the exp ...
IntrauterIne InsemInatIon (IuI)
... About this booklet This series of booklets has been developed and written with the support of leading fertility clinics across Australia, and AccessAustralia – a national organisation that provides numerous services for people having difficulty conceiving. We also acknowledge the many people who sp ...
... About this booklet This series of booklets has been developed and written with the support of leading fertility clinics across Australia, and AccessAustralia – a national organisation that provides numerous services for people having difficulty conceiving. We also acknowledge the many people who sp ...
Endocrine System
... Too much thyroxine secreted leading to enlargement of gland People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, ...
... Too much thyroxine secreted leading to enlargement of gland People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, ...
in the - Fertility Lifelines
... The ovulatory phase begins when the level of luteinizing hormone (LH), also released by the pituitary gland, drastically increases or surges. LH causes the follicle to break open and release the mature egg into the fallopian tube. During her reproductive years, a woman usually releases a single matu ...
... The ovulatory phase begins when the level of luteinizing hormone (LH), also released by the pituitary gland, drastically increases or surges. LH causes the follicle to break open and release the mature egg into the fallopian tube. During her reproductive years, a woman usually releases a single matu ...
- ePrints@Bangalore University
... the physical and psychological symptoms of PMS. The most common dietary recommendations are to restrict sugar and increase consumption of complex carbohydrates 15. Women who consume a carbohydraterich beverage daily during the late luteal phase experienced mood changes when compared with the women w ...
... the physical and psychological symptoms of PMS. The most common dietary recommendations are to restrict sugar and increase consumption of complex carbohydrates 15. Women who consume a carbohydraterich beverage daily during the late luteal phase experienced mood changes when compared with the women w ...
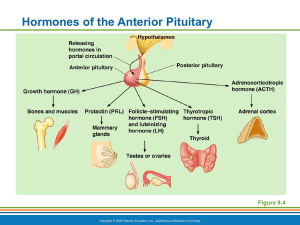
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary 6 Anterior Pituitary Hormones
... Characteristics of all anterior pituitary hormones Proteins (or peptides) ...
... Characteristics of all anterior pituitary hormones Proteins (or peptides) ...
Chapter 20: Endocrine System
... produces insulin but the body cells do not respond. Both types lead to long-term serious complications. ...
... produces insulin but the body cells do not respond. Both types lead to long-term serious complications. ...
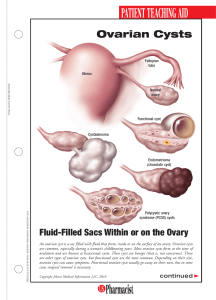
PDF - US Pharmacist
... This serious situation requires immediate medical attention. Sudden and severe pelvic or abdominal pain; fever and chills; vomiting; or weakness, dizziness, and rapid breathing all signal a twisted or ruptured ovarian cyst. Functional cysts do not affect fertility. Ovarian cysts that occur as part o ...
... This serious situation requires immediate medical attention. Sudden and severe pelvic or abdominal pain; fever and chills; vomiting; or weakness, dizziness, and rapid breathing all signal a twisted or ruptured ovarian cyst. Functional cysts do not affect fertility. Ovarian cysts that occur as part o ...
BSC 2086 Class Notes Chapter 16 – Part 1 Summer 2010
... Glucocorticoids keep blood sugar levels relatively constant and maintain blood pressure by increasing the action of ________________________. ...
... Glucocorticoids keep blood sugar levels relatively constant and maintain blood pressure by increasing the action of ________________________. ...
Endocrine System Study Questions with answers
... 7. What are the three ways that endocrine glands are regulated? neural control ( nervous system stimulates the release of hormones), hormonal control ( another hormone stimulates the release of a hormone) , and humoral control (stimulated by a change in an ion or chemical) ...
... 7. What are the three ways that endocrine glands are regulated? neural control ( nervous system stimulates the release of hormones), hormonal control ( another hormone stimulates the release of a hormone) , and humoral control (stimulated by a change in an ion or chemical) ...
presentation source
... THYROID HORMONE SYNTHESIS DEPENDENT ON IODINE (IODINE PUMP CONCENTRATES IODINE IN CELLS) DEPENDENT ON TYROSINE PARTIALLY SYNTHESIZED (THYROGLOBULIN) EXTRACELLULARLY AT LUMINAL SURFACE OF FOLLICULAR CELLS AND STORED IN FOLLICULAR LUMEN ...
... THYROID HORMONE SYNTHESIS DEPENDENT ON IODINE (IODINE PUMP CONCENTRATES IODINE IN CELLS) DEPENDENT ON TYROSINE PARTIALLY SYNTHESIZED (THYROGLOBULIN) EXTRACELLULARLY AT LUMINAL SURFACE OF FOLLICULAR CELLS AND STORED IN FOLLICULAR LUMEN ...
Endocrine Notes
... • Hormone levels are regulated through a process called ________________________________ 1. When not the brain detects an inappropriate level of a certain hormone, it will do things to fix the problem. 2. When the problem is solved, the brain stops trying to fix it. EXAMPLE: • When insufficient leve ...
... • Hormone levels are regulated through a process called ________________________________ 1. When not the brain detects an inappropriate level of a certain hormone, it will do things to fix the problem. 2. When the problem is solved, the brain stops trying to fix it. EXAMPLE: • When insufficient leve ...
MCCQE Review: Gynecology
... Dysgenetic Gonads (Abnormal chromosome complement) - Turner’s Syndrome ...
... Dysgenetic Gonads (Abnormal chromosome complement) - Turner’s Syndrome ...
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
... pressure, and gall stones are just some of the diseases of humans that to some significant extent are caused by being overweight. It is likely that in many overweight patients with PCOS, the PCOS is substantially or even exclusively caused by the obesity. In other words, it is likely that in some ob ...
... pressure, and gall stones are just some of the diseases of humans that to some significant extent are caused by being overweight. It is likely that in many overweight patients with PCOS, the PCOS is substantially or even exclusively caused by the obesity. In other words, it is likely that in some ob ...
The Endocrine/Reproductive System
... hormones into tissue fluids and into the bloodstream. Hormones act as messengers that act to regulate organs in other parts of the body. Hormones are designed to act only on specific tissues within the body, creating a physiologic response by the receptor organ. Hormones are regulated by a negative ...
... hormones into tissue fluids and into the bloodstream. Hormones act as messengers that act to regulate organs in other parts of the body. Hormones are designed to act only on specific tissues within the body, creating a physiologic response by the receptor organ. Hormones are regulated by a negative ...
Chapter 20 - mwsu-wiki
... 1. Recognize and bind with high affinity to their particular hormones 2. Initiate a signal to appropriate intracellular effectors - Binding with receptors general stimulates 3 general types of responses by: 1. Acting on pre-existing channel forming proteins to alter membrane channel permeability 2. ...
... 1. Recognize and bind with high affinity to their particular hormones 2. Initiate a signal to appropriate intracellular effectors - Binding with receptors general stimulates 3 general types of responses by: 1. Acting on pre-existing channel forming proteins to alter membrane channel permeability 2. ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... Cartilages and bones are the main tissues of hGH action Increased deposition of protein by the chondrocytic and osteogenic cells that cause bone growth Increased rate if reproduction of these cells Specific effect of converting chondrocytes into osteogenic cells (causing specific deposition of ...
... Cartilages and bones are the main tissues of hGH action Increased deposition of protein by the chondrocytic and osteogenic cells that cause bone growth Increased rate if reproduction of these cells Specific effect of converting chondrocytes into osteogenic cells (causing specific deposition of ...
The Endocrine System
... hormones into the primary capillary plexus. 2 Hypothalamic hormones travel through portal veins to the anterior pituitary where they stimulate or inhibit release of hormones made in the anterior pituitary. 3 In response to releasing ...
... hormones into the primary capillary plexus. 2 Hypothalamic hormones travel through portal veins to the anterior pituitary where they stimulate or inhibit release of hormones made in the anterior pituitary. 3 In response to releasing ...
Chapter 45 - sharpesystems2012
... fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning Endocrine System - The internal system of communication involving hormones, the ductless glands that secrete hormones, and the molecular receptors on or in target cells that respond to hormones Target Cel ...
... fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning Endocrine System - The internal system of communication involving hormones, the ductless glands that secrete hormones, and the molecular receptors on or in target cells that respond to hormones Target Cel ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.