Name: Period: ______ Ch 9: The Endocrine System Objectives
... developmennt of heavy bones and muscles, lowering of the voice, and stimulates male sex drive). It promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system. It is required for sperm cell production. Placenta The placenta is a remarkable oran formed temporatily in the uterus of pregnant women. In a ...
... developmennt of heavy bones and muscles, lowering of the voice, and stimulates male sex drive). It promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system. It is required for sperm cell production. Placenta The placenta is a remarkable oran formed temporatily in the uterus of pregnant women. In a ...
Complications presentation - TEACH | Training in Early Abortion for
... External/Low Cervical lac < 2 cm in length usually heal without leaving a defect and require no repair Pressure +/- vasopressin, silver nitrate, monsels Exception → brisk bleeding that continues → repair ...
... External/Low Cervical lac < 2 cm in length usually heal without leaving a defect and require no repair Pressure +/- vasopressin, silver nitrate, monsels Exception → brisk bleeding that continues → repair ...
The Endocrine System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... Testes in males, promotes testosterone secretion Hyposecretion – failure of sexual maturation ...
... Testes in males, promotes testosterone secretion Hyposecretion – failure of sexual maturation ...
File
... Peripheral vascular changes leading to decreased blood flow to the feet that can lead to sores and amputation ...
... Peripheral vascular changes leading to decreased blood flow to the feet that can lead to sores and amputation ...
endocrine system - Living Bhakti Studies
... Your endocrine system is a collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate your body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and transported to the tissues and organs throughout your body. ...
... Your endocrine system is a collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate your body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and transported to the tissues and organs throughout your body. ...
The Endocrine System
... secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system helps control the following processes and systems: Growth and development Homeostasis (the internal salt water balance of body systems) Metabolism (body energy levels) Reproduction Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) The End ...
... secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system helps control the following processes and systems: Growth and development Homeostasis (the internal salt water balance of body systems) Metabolism (body energy levels) Reproduction Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) The End ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
Endocrine System
... A. Considered to be part of animals communication system 1. Nervous system uses physical structures for communication 2. Endocrine system uses body fluids to transport messages (hormones) a. referred to as humeral versus neural control II. Hormones A. Classically, hormones are defined as chemical su ...
... A. Considered to be part of animals communication system 1. Nervous system uses physical structures for communication 2. Endocrine system uses body fluids to transport messages (hormones) a. referred to as humeral versus neural control II. Hormones A. Classically, hormones are defined as chemical su ...
Premenstrual syndrome Evidence-based treatment in family practice CME Sue Douglas,
... studied in a randomized controlled trial. One small trial involving 24 women found that women who consumed a carbohydrate-rich beverage daily during the late luteal phase reported fewer mood changes in the hours following consumption than women who consumed an isocaloric beverage.11 While the scient ...
... studied in a randomized controlled trial. One small trial involving 24 women found that women who consumed a carbohydrate-rich beverage daily during the late luteal phase reported fewer mood changes in the hours following consumption than women who consumed an isocaloric beverage.11 While the scient ...
Hormones Gone Wild KEY
... the thyroids are not producing enough hormones. This can lead to lethargy (being tired and sluggish) and weight gain, two of his symptoms. This is not really affecting a particular system as it is his entire body, as his cells are not getting the energy they need to sustain life and his body is prod ...
... the thyroids are not producing enough hormones. This can lead to lethargy (being tired and sluggish) and weight gain, two of his symptoms. This is not really affecting a particular system as it is his entire body, as his cells are not getting the energy they need to sustain life and his body is prod ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... So the hormone binds to the receptor, so what? How does that do anything? There are two major mechanisms, second-messenger mechanisms and direct gene activation, by which the hormone activates the target cell. Direct Gene Activation. Steroid hormones pass through plasma membrane (they’re lipid solub ...
... So the hormone binds to the receptor, so what? How does that do anything? There are two major mechanisms, second-messenger mechanisms and direct gene activation, by which the hormone activates the target cell. Direct Gene Activation. Steroid hormones pass through plasma membrane (they’re lipid solub ...
The Endocrine System
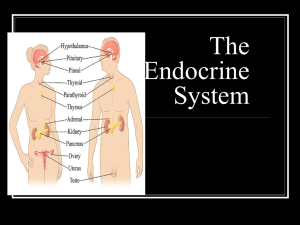
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
The Endocrine System and Hormone Function--An
... – Pituitary dwarfism results from hyposecretion of GH during childhood – Gigantism results from hypersecretion of GH during childhood – Acromegaly results from hypersecretion of GH during adulthood ...
... – Pituitary dwarfism results from hyposecretion of GH during childhood – Gigantism results from hypersecretion of GH during childhood – Acromegaly results from hypersecretion of GH during adulthood ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... act within an org., in cells adjacent to where they are produced ...
... act within an org., in cells adjacent to where they are produced ...
Hormone - WordPress.com
... corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian estrogen production; stimulates sperm production and androgen-binding protein LH has a role in ovulation and the growth of the corpus luteum; stimulates androgen secretion by interstitial cells in testes ...
... corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian estrogen production; stimulates sperm production and androgen-binding protein LH has a role in ovulation and the growth of the corpus luteum; stimulates androgen secretion by interstitial cells in testes ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. However, a given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells, which are called target cells. A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone. ...
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. However, a given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells, which are called target cells. A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone. ...
Chapter 30
... Protein synthesis is induced. In this case, the protein produced is a receptor for another steroid protein, progesterone. ...
... Protein synthesis is induced. In this case, the protein produced is a receptor for another steroid protein, progesterone. ...
Name ____ hr ____ January 2009 Unit 6: Hormones Monday
... 8. Explain how the hypothalamus controls body functions through its action on the pituitary gland. How does control on the anterior and posterior pituitary gland differ? ...
... 8. Explain how the hypothalamus controls body functions through its action on the pituitary gland. How does control on the anterior and posterior pituitary gland differ? ...
chapter 16-the endocrine system
... a. Somatotrophic Hormone (STH)-regulates the growth of the skeleton. It is regulated by the hypothalamus via Growth Hormone Releasing. Factor and Growth Hormone Inhibiting Factor. This is also known as Human Growth Hormone. 1) What is gigantism? 2) What is acromegaly? 3) What is pituitary dwarfism? ...
... a. Somatotrophic Hormone (STH)-regulates the growth of the skeleton. It is regulated by the hypothalamus via Growth Hormone Releasing. Factor and Growth Hormone Inhibiting Factor. This is also known as Human Growth Hormone. 1) What is gigantism? 2) What is acromegaly? 3) What is pituitary dwarfism? ...
Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH Human)
... thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid gland. TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). TSH production is controlled by a Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone, (TRH), which is manufactur ...
... thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid gland. TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). TSH production is controlled by a Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone, (TRH), which is manufactur ...
Lecture 5: Endocrine System
... A regulatory system that produces hormones. The endocrine system is not truly a distinct system (though it does have specific organs that are identified as “endocrine players”) because it plays a role in everything. 1. Hormone: a substance secreted by a gland (or single cell) into the blood that ac ...
... A regulatory system that produces hormones. The endocrine system is not truly a distinct system (though it does have specific organs that are identified as “endocrine players”) because it plays a role in everything. 1. Hormone: a substance secreted by a gland (or single cell) into the blood that ac ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Target cells are any cells that have receptors for a given type of signaling molecule (hormone) and that may alter their behavior in response to it. 1. Oxytoxin (hypothalamus/pituitary gland)—its role is in childbirth and milk production 2. Estrogen (ovaries)—its role is to maintain primary sex orga ...
... Target cells are any cells that have receptors for a given type of signaling molecule (hormone) and that may alter their behavior in response to it. 1. Oxytoxin (hypothalamus/pituitary gland)—its role is in childbirth and milk production 2. Estrogen (ovaries)—its role is to maintain primary sex orga ...
Thymus Pineal Thyroid Parathyroid
... • Type of depression • Related to changes in seasons • May occur due to drops in serotonin (reduced sunlight) and affect melatonin (sleep patterns, mood) • Begins and ends about the same time each year ...
... • Type of depression • Related to changes in seasons • May occur due to drops in serotonin (reduced sunlight) and affect melatonin (sleep patterns, mood) • Begins and ends about the same time each year ...
The Management of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
... more effective than hormonal treatment. However, there are rare hormonal conditions that cause abnormal uterine bleeding in ovulatory cycles. The most common one is midcycle bleeding due to abrupt fall in estrogen levels just before the ovulation which is called as ‘estrogen withdrawal bleeding’. An ...
... more effective than hormonal treatment. However, there are rare hormonal conditions that cause abnormal uterine bleeding in ovulatory cycles. The most common one is midcycle bleeding due to abrupt fall in estrogen levels just before the ovulation which is called as ‘estrogen withdrawal bleeding’. An ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.