Endocrine System
... necessary hormone. When the hormone levels in the body reaches the required level, the hypothalamus is stimulated by a process called negative feedback; it then stimulates the pituitary to inhibit any further production of the hormone. Clare Hargreaves-Norris ...
... necessary hormone. When the hormone levels in the body reaches the required level, the hypothalamus is stimulated by a process called negative feedback; it then stimulates the pituitary to inhibit any further production of the hormone. Clare Hargreaves-Norris ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... • controls secretions of some hormones of adrenal cortex • release controlled by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus • produced by corticotropes What term would describe these two hormones that cause the secretion of other hormones in distant endocrine tissues? ...
... • controls secretions of some hormones of adrenal cortex • release controlled by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus • produced by corticotropes What term would describe these two hormones that cause the secretion of other hormones in distant endocrine tissues? ...
The Endocrine System
... control the activities of our body’s cells. This system is usually working closely with the Nervous System. ...
... control the activities of our body’s cells. This system is usually working closely with the Nervous System. ...
Lecture5
... Most of the hormones of this gland are steroids (lipids). These hormones fall into the two major groups viz: glucorticoids and mineralocorticoids. (i)Glucoritcoids: The most important members of this group are the cortisol and corticosterone. These hormones promote the conversion of fat and protein ...
... Most of the hormones of this gland are steroids (lipids). These hormones fall into the two major groups viz: glucorticoids and mineralocorticoids. (i)Glucoritcoids: The most important members of this group are the cortisol and corticosterone. These hormones promote the conversion of fat and protein ...
Midcycle OSCE
... Infection, excitation and movement, early hypoxia, infection, fetal heart arrhythmia and prematurity. ...
... Infection, excitation and movement, early hypoxia, infection, fetal heart arrhythmia and prematurity. ...
Endocrinology Features of Endocrine system:
... • Varies from person to person depending on height, weight, age, stress etc • It is important for growth and development (protein, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism of all tissues) • What happens when the hormone is over-secreted or undersecreted? ...
... • Varies from person to person depending on height, weight, age, stress etc • It is important for growth and development (protein, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism of all tissues) • What happens when the hormone is over-secreted or undersecreted? ...
IVA_ Endocrine_System_Chemical_Co_Ordination
... - Development and maintenance of female reproductive system - Maintenance of menstrual cycle - Development of secondary sexual characters - Estrogen promotes the protein synthesis and calcification and bone growth 2) Progesterone: It is synthesized and secreted by corpus luteum and placenta. Functio ...
... - Development and maintenance of female reproductive system - Maintenance of menstrual cycle - Development of secondary sexual characters - Estrogen promotes the protein synthesis and calcification and bone growth 2) Progesterone: It is synthesized and secreted by corpus luteum and placenta. Functio ...
Recombinant Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
... Lyophilized Thyroid Stimulating Hormone although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution TSH should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HS ...
... Lyophilized Thyroid Stimulating Hormone although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution TSH should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HS ...
S T U D Y G U I D E
... lular respiration. This produces hyperglycemia and forces cells to use fats for cellular respiration which _____________________________________________________________________________________________ results in acidosis. b. A new mother is informed that her baby has severe hypothyroidism. How would ...
... lular respiration. This produces hyperglycemia and forces cells to use fats for cellular respiration which _____________________________________________________________________________________________ results in acidosis. b. A new mother is informed that her baby has severe hypothyroidism. How would ...
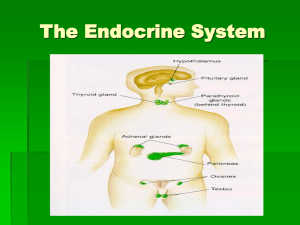
The Endocrine System
... This gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions… we’ll only cover the endocrine portion now (exocrine is for digestion) The endocrine portion of the gland contains three types of cells, each making a different hormone, arranged into groups called Islets of Langerhans ...
... This gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions… we’ll only cover the endocrine portion now (exocrine is for digestion) The endocrine portion of the gland contains three types of cells, each making a different hormone, arranged into groups called Islets of Langerhans ...
Dysmenorrhea - Scott Kramer MD
... There are two types of dysmenorrhea—primary or secondary. Primary dysmenorrhea is pelvic pain that comes from having your period and the natural production of prostaglandins. Often it begins soon after a pre-teen or teen starts having periods. In many cases, a woman’s periods become less painful as ...
... There are two types of dysmenorrhea—primary or secondary. Primary dysmenorrhea is pelvic pain that comes from having your period and the natural production of prostaglandins. Often it begins soon after a pre-teen or teen starts having periods. In many cases, a woman’s periods become less painful as ...
test review key - Hartland High School
... Matures female reproductive organs Helps prepare the uterus to receive a fertilized egg Helps maintain pregnancy Prepares the breasts to produce milk Produced by the corpus luteum Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Responsible f ...
... Matures female reproductive organs Helps prepare the uterus to receive a fertilized egg Helps maintain pregnancy Prepares the breasts to produce milk Produced by the corpus luteum Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Responsible f ...
Endocrine glands and their parts 1. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) 2
... Medulla of suprarenal gland (12) This is part of the adrenal gland; the hormones create the "fight or flight" reaction to stress situations by modifying metabolic rates and muscle tone. Neurohypophysis (3) That part of the pituitary gland that produces an antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Ovary (fe ...
... Medulla of suprarenal gland (12) This is part of the adrenal gland; the hormones create the "fight or flight" reaction to stress situations by modifying metabolic rates and muscle tone. Neurohypophysis (3) That part of the pituitary gland that produces an antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Ovary (fe ...
your guide Fertility Treatment with Reproductive Medicine Albury
... Fertility treatment is an intensive experience that requires a large emotional investment. We encourage you to visit us and to meet our fertility specialists. Sit and discuss your family aspirations and talk over your chances of achieving a pregnancy with Reproductive Medicine Albury. We take great ...
... Fertility treatment is an intensive experience that requires a large emotional investment. We encourage you to visit us and to meet our fertility specialists. Sit and discuss your family aspirations and talk over your chances of achieving a pregnancy with Reproductive Medicine Albury. We take great ...
flotub - LSHTM.
... Unlikely that a new regimen will demonstrate superiority Interest lies with showing whether a new regimen is not inferior Non-inferiority design is an excellent choice for current TB sensitive drug development (A. Nunn et al, Tuberculosis(2008)) ...
... Unlikely that a new regimen will demonstrate superiority Interest lies with showing whether a new regimen is not inferior Non-inferiority design is an excellent choice for current TB sensitive drug development (A. Nunn et al, Tuberculosis(2008)) ...
Chemical messengers - Our eclass community
... 5. Change the way in which cells function 6. Act over the long-term – days, weeks, months ...
... 5. Change the way in which cells function 6. Act over the long-term – days, weeks, months ...
GONAL-f® (follitropin alfa for injection)
... lagged behind FSH serum concentration. Of the three pharmacodynamic parameters, serum inhibin levels responded with the least delay and declined rapidly after discontinuation of Gonal-f®. Follicular growth was most delayed and continued even after discontinuation of Gonal-f® administration, and afte ...
... lagged behind FSH serum concentration. Of the three pharmacodynamic parameters, serum inhibin levels responded with the least delay and declined rapidly after discontinuation of Gonal-f®. Follicular growth was most delayed and continued even after discontinuation of Gonal-f® administration, and afte ...
1 Chapter 11: The Endocrine System • Exocrine glands will produce
... a specific or target cell or gland Characteristics of the Endocrine System o Coordinates and integrates with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis o Utilizes hormones secreted from endocrine glands to target precisely a specific structure. The process and communication of the endocrine system m ...
... a specific or target cell or gland Characteristics of the Endocrine System o Coordinates and integrates with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis o Utilizes hormones secreted from endocrine glands to target precisely a specific structure. The process and communication of the endocrine system m ...
Biochemistry of hormones derived from amino acids and proteins
... hCG is synthesized in the syncytiotrophoblast cells of the placenta; increases in blood and urine shortly after implantation; its detection is the basis of many pregnancy tests hCG- β subunit ...
... hCG is synthesized in the syncytiotrophoblast cells of the placenta; increases in blood and urine shortly after implantation; its detection is the basis of many pregnancy tests hCG- β subunit ...
Copyright (c) 2009, Radiological Society of North America, Inc
... Copyright (c) 2009, Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (RSNA) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED This file is part of the "RSNA Radiology Reporting Templates." The "RSNA Radiology Reporting Templates" are licensed without charge under the RSNA's license agreement (the "License"); you may not use this file ...
... Copyright (c) 2009, Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (RSNA) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED This file is part of the "RSNA Radiology Reporting Templates." The "RSNA Radiology Reporting Templates" are licensed without charge under the RSNA's license agreement (the "License"); you may not use this file ...
view article
... posterior pituitary and has important primary functions. Hormone Oxytocin plays a part during and after childbirth in contracting the uterus. Oxytocin has a significant role in social development and behavior. Studies have shown that autistic individuals, lack Oxytocin. The photograph seen on page 4 ...
... posterior pituitary and has important primary functions. Hormone Oxytocin plays a part during and after childbirth in contracting the uterus. Oxytocin has a significant role in social development and behavior. Studies have shown that autistic individuals, lack Oxytocin. The photograph seen on page 4 ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... Describe the nature and location of intracellular receptors for hormones that pass easily through cell membranes. Explain how their role compares to the signal-transduction pathway noted above, and describe the changes they are likely to trigger within the target cell. ...
... Describe the nature and location of intracellular receptors for hormones that pass easily through cell membranes. Explain how their role compares to the signal-transduction pathway noted above, and describe the changes they are likely to trigger within the target cell. ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Stephen G
... 6. How do hormones bring about their effects on cells? What are five ways a hormone may produce a change? 7. There are two major mechanisms by which hormone-receptor binding places intracellular machinery into action. One uses G-proteins and ________________, and the other involves steroid hormones ...
... 6. How do hormones bring about their effects on cells? What are five ways a hormone may produce a change? 7. There are two major mechanisms by which hormone-receptor binding places intracellular machinery into action. One uses G-proteins and ________________, and the other involves steroid hormones ...
PrDIANE®-35
... for cyproterone acetate. One in vivo consequence of cyproterone acetate treatment was the increased incidence of focal, possibly pre-neoplastic, liver lesions in which cellular enzymes were altered in female rats. The relevance of these findings does not appear to be clinically significant based on ...
... for cyproterone acetate. One in vivo consequence of cyproterone acetate treatment was the increased incidence of focal, possibly pre-neoplastic, liver lesions in which cellular enzymes were altered in female rats. The relevance of these findings does not appear to be clinically significant based on ...
Pr CLIMARA® 25 Pr CLIMARA® 50 Pr CLIMARA® 75 Pr
... Serious Warnings and Precautions The Women=s Health Initiative (WHI) trial examined the health benefits and risks of oral combined estrogen plus progestin therapy (n=16,608) and oral estrogen-alone therapy (n=10,739) in postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 years.1-3 The estrogen plus progestin arm of ...
... Serious Warnings and Precautions The Women=s Health Initiative (WHI) trial examined the health benefits and risks of oral combined estrogen plus progestin therapy (n=16,608) and oral estrogen-alone therapy (n=10,739) in postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 years.1-3 The estrogen plus progestin arm of ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.