* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine glands and their parts 1. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
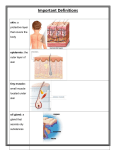
Endocrine glands and their parts 1. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) 2. Adenohypophysis 3. Neurohypophysis 4. Infundibulum 5. Thyroid gland 6. Lateral lobe of the thyroid 7. Isthmus of the thyroid 8. Parathyroid gland 9. Suprarenal or adrenal gland 10. Capsule of suprarenal gland 11. Cortex of suprarenal gland 12. Medulla of suprarenal gland 13. 'Pancreatic islets of Langerhans 14. Alpha cells of pancreatic islets 15. Beta cells of pancreatic islets 16. Testis or testicle (male) 17. Seminiferous tubules 18. Epididymis 19. Ductus deferens 20. Ovary (female) 21. Blood vessels to ovary 22. Medulla or inner portion of ovary 23. Developing follicles 24. Corpus luteum * Body organs and structures closely associated with endocrine glands 25. Diencephalon (interbrain) 26. Trachea (windpipe) 27. Carotid artery 28. Arch of aorta 29. Heart 30. Kidney 31. Pancreas 32. Uterus (womb) 33. Oviduct (fallopian tube) -9- GLOSSARY Adenohypophysis (2) That part of the pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal glands and thyroid gland, produces the growth hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Alpha cells of pancreatic islets (14) The cells of the islets of Langehans that secrete glucagon. Beta cells of pancreatic islets (15) The cells of the islets of Langehans that secrete insulin. Capsule of suprarenal gland (10) The tissue surrounding the adrenal glands. Corpus luteum (24) The ruptured follicle following release of the ovum. Cortex of suprarenal gland (11) This is part of the adrehaf gland; the hormones affect potassium ion reabsorption, water retention, glucose production increase, and release of antibodies, among others. Developing follicles (23) Clusters of cells surrounding a single ovum which is being prepared to be released as a mature ovum. Ductus deferens (19) Tubules which transport mature sperm from the testis to the abdominal cavity, where it is mixed with other fluids to form semen. Epididymis, (18) Structure in the testicle where sperm is collected from the seminiferous tubules, and stored until it is fully mature. Infundibulum (4) The pituitary stalk; connects the pituitary gland to the brain. Islets of Langerhans Patches of pancreas that secrete insulin. Isthmus of the thyroid (7) Tissue connecting the thyroid lobes. Lateral lobe of the thyroid (6) One of the lobes of the thyroid. Medulla of suprarenal gland (12) This is part of the adrenal gland; the hormones create the "fight or flight" reaction to stress situations by modifying metabolic rates and muscle tone. Neurohypophysis (3) That part of the pituitary gland that produces an antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Ovary (female) (20) Produce the hormones estrogen, which controls prenatal sexual differentiation, development of female sex characteristics at puberty, and breast development; and progesterone, which maintains hypertrophy of uterine endometrium. Pancreatic islets of Langerhans (13) These cell masses are imbedded in the pancreas. They produce the hormones insulin, which lowers blood glucose levels, and glucagon, which stimulates glycogen release by the liver. Parathyroid gland (8) Located on the posterior surface of the thyroid, these four glands secrete a hormone which increases concentration of calcium ions in the plasma. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) (1) Located at the base of the brain; made up of two areas, the adenohypophysis and the neurohypophysis. Seminiferous tubules (17) A mass of compact tubules responsible for the production of sperm. The compact mass is the testicle. Suprarenal or adrenal gland (9) These glands are located atop the kidneys. Testis or testicle (male) (16) Produce the hormone testosterone, which controls prenatal sexual differentiation, the development of male sex characteristics at puberty, and the normal development of sperm. Thyroid gland (5) This gland, found surrounding the larynx in the throat, decreases the concentration of calcium ions in plasma and increases general metabolism, nutrient metabolism, and energy production. -10-