10 The Endocrine System
... maintain homeostasis. Endocrine glands release chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones affect the functioning of target organs at other locations in the body. The activity of many endocrine glands is regulated by a negative feedback mechanism in which a gland's own hormone or ...
... maintain homeostasis. Endocrine glands release chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones affect the functioning of target organs at other locations in the body. The activity of many endocrine glands is regulated by a negative feedback mechanism in which a gland's own hormone or ...
The Endocrine System
... • Estrogen has psychological as well as biological effects. • Low levels of estrogen and progesterone are found in males. ...
... • Estrogen has psychological as well as biological effects. • Low levels of estrogen and progesterone are found in males. ...
endocrine system review – answer key
... Hormone receptors are only found on target cells b. If the hormone released in the diagram is ACTH, where in the human body would the target cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeosta ...
... Hormone receptors are only found on target cells b. If the hormone released in the diagram is ACTH, where in the human body would the target cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeosta ...
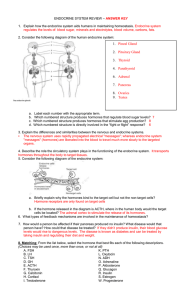
1. Pineal Gland 2. Pituitary Gland 3. Thyroid 4. Parathyroid 6
... Hormone receptors are only found on target cells b. If the hormone released in the diagram is ACTH, where in the human body would the target cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeosta ...
... Hormone receptors are only found on target cells b. If the hormone released in the diagram is ACTH, where in the human body would the target cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeosta ...
Ch 18 Lesson 1 - Aurora City Schools
... i. secretes hormones that aid the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates b. __________ __________- controlled by the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system i. secretes the hormone epinephrine(adrenaline) and norepinephrine ii. epinephrine increases heart rate and respiration, raises ...
... i. secretes hormones that aid the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates b. __________ __________- controlled by the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system i. secretes the hormone epinephrine(adrenaline) and norepinephrine ii. epinephrine increases heart rate and respiration, raises ...
Endocrine System
... for these hormones are found on the surface of the target cell and causes it to transmit a signal into the cell’s interior – can be used to turn on a protein kinase that phosphorylates certain proteins and changes their activity – or they can be used to release secondary messengers in the cell that ...
... for these hormones are found on the surface of the target cell and causes it to transmit a signal into the cell’s interior – can be used to turn on a protein kinase that phosphorylates certain proteins and changes their activity – or they can be used to release secondary messengers in the cell that ...
Some Practice Exam #6 Questions
... 19)Where are Sertoli cells found and what do they do? 20)How are ‘aromatase’ and ‘5-alpha-reductase’ different? In other words, what reaction does aromatase catalyze and what reaction does 5-alpha-reductase catalyze? 21)What pituitary gland hormone is directly involved with spermatogenesis? 22)What ...
... 19)Where are Sertoli cells found and what do they do? 20)How are ‘aromatase’ and ‘5-alpha-reductase’ different? In other words, what reaction does aromatase catalyze and what reaction does 5-alpha-reductase catalyze? 21)What pituitary gland hormone is directly involved with spermatogenesis? 22)What ...
Document
... The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master gland” because its secretions control, or regulate, the secretions of other endocrine glands. The thyroid secretes thyroxine when the body’s metabolic rate decreases. Thyroxine, the body’s major metabolic hormone, stimulates energy production i ...
... The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master gland” because its secretions control, or regulate, the secretions of other endocrine glands. The thyroid secretes thyroxine when the body’s metabolic rate decreases. Thyroxine, the body’s major metabolic hormone, stimulates energy production i ...
B1.2 Coordination and Control
... • Automatic responses important for survival • Similar response to a normal conscious action but involves a relay neuron in the spinal cord or unconscious area of the brain • It then travels to the conscious area so you know about the reflex - after it has happened Synapses Junctions between nerves ...
... • Automatic responses important for survival • Similar response to a normal conscious action but involves a relay neuron in the spinal cord or unconscious area of the brain • It then travels to the conscious area so you know about the reflex - after it has happened Synapses Junctions between nerves ...
Endocrine System 3 - Iowa State University
... 12. What are the two hormones that are stored in the posterior pituitary? ...
... 12. What are the two hormones that are stored in the posterior pituitary? ...
Hormones - Milan Area Schools
... –Hair growth, fat buildup, body development, and mensus cycles. ...
... –Hair growth, fat buildup, body development, and mensus cycles. ...
Endocrine/Reproduction/Genetics Study Guide
... Be able to label both male and female reproductive system structures AND describe their functions. What is the proper term for sperm production? Egg production? What type of cell division is necessary to achieve the correct amount of DNA? ...
... Be able to label both male and female reproductive system structures AND describe their functions. What is the proper term for sperm production? Egg production? What type of cell division is necessary to achieve the correct amount of DNA? ...
Conference Audio Order Form
... Wendy Rashidi, MD: A Holistic Approach to Balancing Hormones; James Wilson, ND, DC, PhD: A Comprehensive Introduction to Detoxification; The Role of the Endocrine System in Autoimmunity; George Gillson, MD, PhD: The Relevance of Transmethylation; The Role of Growth Hormone in the Metabolic Web; David ...
... Wendy Rashidi, MD: A Holistic Approach to Balancing Hormones; James Wilson, ND, DC, PhD: A Comprehensive Introduction to Detoxification; The Role of the Endocrine System in Autoimmunity; George Gillson, MD, PhD: The Relevance of Transmethylation; The Role of Growth Hormone in the Metabolic Web; David ...
AMA 176 powerpoint
... AMA 176 - Anatomy & Physiology/Medical Terminology/Pathology 7 Endocrine System ...
... AMA 176 - Anatomy & Physiology/Medical Terminology/Pathology 7 Endocrine System ...
The Endocrine System
... • The endocrine system releases chemical hormones into the blood • This system is slower in producing its effect than the nervous system, however, the effect lasts longer • It helps to maintain homeostasis by monitoring changes in organs or tissues of the body. ...
... • The endocrine system releases chemical hormones into the blood • This system is slower in producing its effect than the nervous system, however, the effect lasts longer • It helps to maintain homeostasis by monitoring changes in organs or tissues of the body. ...
Name_____________________________________________
... essential for the immune system to work properly. The thymus is present at birth, develops during childhood and then gradually disappears during adulthood. ...
... essential for the immune system to work properly. The thymus is present at birth, develops during childhood and then gradually disappears during adulthood. ...
Chapter 16 – Endocrine Test Review
... 7. Which endocrine gland is known as the “master gland”? 8. What type of regulatory mechanism controls hormone secretion? Which hormone is controlled by a different mechanism? 9. Compare/contrast T3 and T4. Which is the “principle thyroid hormone”? 10. What is the main mineralcorticoid in the human ...
... 7. Which endocrine gland is known as the “master gland”? 8. What type of regulatory mechanism controls hormone secretion? Which hormone is controlled by a different mechanism? 9. Compare/contrast T3 and T4. Which is the “principle thyroid hormone”? 10. What is the main mineralcorticoid in the human ...
Hormones and puberty
... Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites in the body, stimulating a ...
... Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites in the body, stimulating a ...
The Endocrine System - Mediapolis Community School
... Posterior Pituitary Hormones • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)- diuretics are chemicals that increase urine production, so antidiuretics decrease urine production. • Oxytosin (OT)- deals mostly with uterine wall contractions for childbirth, but also functions as an antidiuretic. ...
... Posterior Pituitary Hormones • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)- diuretics are chemicals that increase urine production, so antidiuretics decrease urine production. • Oxytosin (OT)- deals mostly with uterine wall contractions for childbirth, but also functions as an antidiuretic. ...
Hormones
... the body § What it does: controls the rate of metabolic processes (how energy is used) in the body and influences physical development § People may not produce enough of this hormone and get a condition known as hypothyroidism. They can take thyroxine to treat this condition. ...
... the body § What it does: controls the rate of metabolic processes (how energy is used) in the body and influences physical development § People may not produce enough of this hormone and get a condition known as hypothyroidism. They can take thyroxine to treat this condition. ...
Endocrine syste
... Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) – speed up cells release of energy from foods, stimulate cellular metabolism Calcitonin – maintains homeostasis of blood calcium, decreases the amount of calcium in the blood, act on bone to inhibit its breakdown, therefore calcium does not move out of bone. ...
... Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) – speed up cells release of energy from foods, stimulate cellular metabolism Calcitonin – maintains homeostasis of blood calcium, decreases the amount of calcium in the blood, act on bone to inhibit its breakdown, therefore calcium does not move out of bone. ...
endocrine glands
... thyroid to release ______________. ___________ causes Ca+ to be absorbed by the bone. When blood levels of Ca+ return to normal, hypothalamus tells the pituitary to stop producing ______. ...
... thyroid to release ______________. ___________ causes Ca+ to be absorbed by the bone. When blood levels of Ca+ return to normal, hypothalamus tells the pituitary to stop producing ______. ...