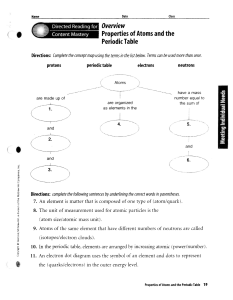
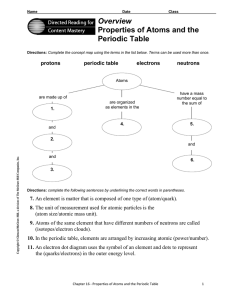
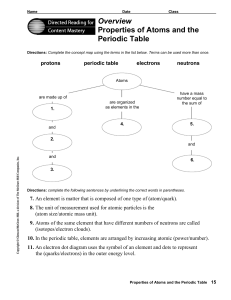
Identify which of the three subatomic particles (p+, n, e–): is the
... To distinguish atoms of different elements elements you find the amount of protons or electrons and you are able to find out what number element it is on the periodic table. 7 . Use an example to identify the smallest unit of an element. the smallest unit in an element is an electron. ...
... To distinguish atoms of different elements elements you find the amount of protons or electrons and you are able to find out what number element it is on the periodic table. 7 . Use an example to identify the smallest unit of an element. the smallest unit in an element is an electron. ...
Chem 200 Dr. Saidane
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
Goal 1 Study Guide and Practice Problems Fill in the following table
... c. Sodium-24 has a half-life of 15 hours. How much sodium-24 will remain in an 18.0 g sample after 60 hours? M = 1.125 g 19. How are radioactive decay, fission, and fusion different? ...
... c. Sodium-24 has a half-life of 15 hours. How much sodium-24 will remain in an 18.0 g sample after 60 hours? M = 1.125 g 19. How are radioactive decay, fission, and fusion different? ...
ps-5-1-and-5-2-ws
... Moving across the periodic table from left to right, one finds, in order, metals, then gases, then nonmetals. ...
... Moving across the periodic table from left to right, one finds, in order, metals, then gases, then nonmetals. ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... where some substances spontaneously emit radiation. When radioactive substances emit radiation, they can transmutate: change into a different element. Why do atoms emit radiation? Because their nuclei are unstable, so they emit energy and undergo radioactive decay. Types of Radiation: ...
... where some substances spontaneously emit radiation. When radioactive substances emit radiation, they can transmutate: change into a different element. Why do atoms emit radiation? Because their nuclei are unstable, so they emit energy and undergo radioactive decay. Types of Radiation: ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. electron cloud six number electrons isotopes six protons neutron(s) proton(s) mass quarks The electron has vcry little mass compared to the 1. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. electron cloud six number electrons isotopes six protons neutron(s) proton(s) mass quarks The electron has vcry little mass compared to the 1. ...
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
05 Chemistry Basics with Flips 2011
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
isotopes
... What do the numbers used when writing isotopes represent? • The mass number • total number of protons and neutrons in a specific nucleus of an atom. • The atomic number • always refers to the total number of protons in an atom. ...
... What do the numbers used when writing isotopes represent? • The mass number • total number of protons and neutrons in a specific nucleus of an atom. • The atomic number • always refers to the total number of protons in an atom. ...
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
Atomic structure unit powerpoint
... other. In making such alignments Mendeleev was able to determine that several, as yet unidentified, elements should exist (the elements with masses 44, 68 and 72 are examples). He went on to make predictions about the properties of these missing elements which aided in their discovery. The discovery ...
... other. In making such alignments Mendeleev was able to determine that several, as yet unidentified, elements should exist (the elements with masses 44, 68 and 72 are examples). He went on to make predictions about the properties of these missing elements which aided in their discovery. The discovery ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... form new substances • Ion – a charged atom (positive or negative). • Ionization – the process of removing electrons to form ions. • The energy needed is called ionization energy. • Electron affinity – the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. • Polyatomic ion – when two elements bond first coval ...
... form new substances • Ion – a charged atom (positive or negative). • Ionization – the process of removing electrons to form ions. • The energy needed is called ionization energy. • Electron affinity – the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. • Polyatomic ion – when two elements bond first coval ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... d. gained electrons e. gained protons ...
... d. gained electrons e. gained protons ...
Ch 1.1 ppt
... • Certain chemical properties were repeated regularly. • These properties were related to the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. ...
... • Certain chemical properties were repeated regularly. • These properties were related to the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. ...
Chemistry 30A Chapter 2- Atoms and the Periodic Table Laney
... The Schrödinger equation which assumes that the electron behaves like a wave, or even like a twanging guitar string, can be solved exactly for only one atom, the hydrogen atom. But the results are applicable to all of the atoms of the Periodic Table. The hydrogen atom consists of one proton and one ...
... The Schrödinger equation which assumes that the electron behaves like a wave, or even like a twanging guitar string, can be solved exactly for only one atom, the hydrogen atom. But the results are applicable to all of the atoms of the Periodic Table. The hydrogen atom consists of one proton and one ...
The Atom - Mrs. Ellis` Science Class!
... ____________ the ________________ in specific and ______________ paths o However, an electron’s _____________ location _________________ be determined o Electrons exist in energy levels called ________________________ o The number of ____________ orbitals depends on how many _________________ an ato ...
... ____________ the ________________ in specific and ______________ paths o However, an electron’s _____________ location _________________ be determined o Electrons exist in energy levels called ________________________ o The number of ____________ orbitals depends on how many _________________ an ato ...
Define:
... 43. Express the sum of 8.67 m and 5.2 m to the correct number of significant figures. 44. Express the product of 5.5 mm and 2.00 mm to the correct number of significant figures. 45. List the metric prefixes and their decimal equivalents. Ex: centi .01 46. Make the following conversions: a. 8961 m to ...
... 43. Express the sum of 8.67 m and 5.2 m to the correct number of significant figures. 44. Express the product of 5.5 mm and 2.00 mm to the correct number of significant figures. 45. List the metric prefixes and their decimal equivalents. Ex: centi .01 46. Make the following conversions: a. 8961 m to ...
Atomic Theory & the Periodic Table
... valence e- absorb that packet of energy & become unstable. In order to return to stability (lower their energy) they “spit out” that energy in the form of a photon that has a frequency in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can ...
... valence e- absorb that packet of energy & become unstable. In order to return to stability (lower their energy) they “spit out” that energy in the form of a photon that has a frequency in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can ...
Chapter 03
... ►Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in each atom of an element. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. ►Atoms are neutral overall and have no net charge because the number of positively charged protons and the number of negatively charged electrons a ...
... ►Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in each atom of an element. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. ►Atoms are neutral overall and have no net charge because the number of positively charged protons and the number of negatively charged electrons a ...
Unit #3 - Wikispaces
... e) Your text book makes this analogy: It would be like firing a 15" artillery shell at a piece of tissue paper and having it bounce back at you. f) The rays were deflected when they had direct hits on the nucleus of an atom. Subatomic Particles. 10) Electron- negatively charged particle (equal to -1 ...
... e) Your text book makes this analogy: It would be like firing a 15" artillery shell at a piece of tissue paper and having it bounce back at you. f) The rays were deflected when they had direct hits on the nucleus of an atom. Subatomic Particles. 10) Electron- negatively charged particle (equal to -1 ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
Measuring the Atom
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...