NOTES: The structure of an atom
... -Electrons are found outside of the nucleus and are particles with a negative charge. -electrons are so small and fast that scientists can’t tell exactly where they are at any one time. -the electron cloud is the region around the nucleus where electrons are found ...
... -Electrons are found outside of the nucleus and are particles with a negative charge. -electrons are so small and fast that scientists can’t tell exactly where they are at any one time. -the electron cloud is the region around the nucleus where electrons are found ...
10-2 Intensive Chemistry Review for Chapters 3
... 16. You are NOT responsible for knowing or using the equation on p. 95 for the energy of electrons. 17. What is meant by the statement that each electron has a unique 4-part quantum address around a nucleus? (You do NOT need to memorize table 3-4 on p. 97) 18. The principle quantum number (n level) ...
... 16. You are NOT responsible for knowing or using the equation on p. 95 for the energy of electrons. 17. What is meant by the statement that each electron has a unique 4-part quantum address around a nucleus? (You do NOT need to memorize table 3-4 on p. 97) 18. The principle quantum number (n level) ...
C2 Topic 1 Atomic structure and the periodic table PP
... Using the periodic table • Atomic number (proton number): is the number of protons in an atom - The elements are arranged in the Periodic Table in ascending order of atomic number • Mass number: is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom • Relative atomic mass (Ar): is the average mass ...
... Using the periodic table • Atomic number (proton number): is the number of protons in an atom - The elements are arranged in the Periodic Table in ascending order of atomic number • Mass number: is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom • Relative atomic mass (Ar): is the average mass ...
Fall Semester Review Packet
... 13. Explain how atoms of the same element may differ. Include all of the following terms in your explanation. Isotopes, ions, cations, anions, neutrons, electrons, and protons. 14. Explain the rules and describe the differences in nomenclature for molecular and ionic compounds. Give several examples ...
... 13. Explain how atoms of the same element may differ. Include all of the following terms in your explanation. Isotopes, ions, cations, anions, neutrons, electrons, and protons. 14. Explain the rules and describe the differences in nomenclature for molecular and ionic compounds. Give several examples ...
AlBr3 E IO Ionic FU C O Cov Molec C IO Cov Molec Sn E N/A N/A
... old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
... old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
3. atomic structure
... For example, the moon has an orbit about the earth Electrons do not follow a particular path around the nucleus Instead, an orbital describes the areas around the nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
... For example, the moon has an orbit about the earth Electrons do not follow a particular path around the nucleus Instead, an orbital describes the areas around the nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
Elements and Atoms
... • To make molecules, you must have elements. • Elements are made of atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
... • To make molecules, you must have elements. • Elements are made of atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
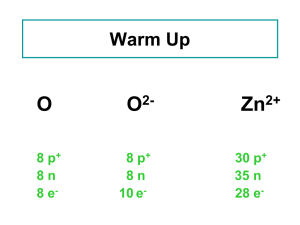
Zn 8 p + 8 p + 30 p + 8 n 8 n 35 n 8 e
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
Atomic Structure
... the atomic number. The number of electrons is usually the same as the atomic number. To find the number of neutrons: take the atomic mass, rounded to the nearest whole number, and subtract the atomic number. ...
... the atomic number. The number of electrons is usually the same as the atomic number. To find the number of neutrons: take the atomic mass, rounded to the nearest whole number, and subtract the atomic number. ...
Chapter 2: The Composition and Structure of the Atom • 2.1 Matter
... o Energy is released as the electron travels back to lower levels. Relaxation. o Orbit – what Bohr called the fixed energy levels. o Ground state – the lowest possible energy state an electron can occupy. o The orbits are also identified using “quantum numbers”: 1, 2, 3, … o When the electron relaxe ...
... o Energy is released as the electron travels back to lower levels. Relaxation. o Orbit – what Bohr called the fixed energy levels. o Ground state – the lowest possible energy state an electron can occupy. o The orbits are also identified using “quantum numbers”: 1, 2, 3, … o When the electron relaxe ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... • Average atomic mass – the average mass of the element’s isotopes, weighted according to the abundance of each isotope • For example: even though Carbon has mass numbers 12, 13, and 14 there’s more Carbon-12 on Earth, about 99% is Carbon-12 ...
... • Average atomic mass – the average mass of the element’s isotopes, weighted according to the abundance of each isotope • For example: even though Carbon has mass numbers 12, 13, and 14 there’s more Carbon-12 on Earth, about 99% is Carbon-12 ...
Unit 7: The Nature of Matter Essential Questions:
... 2. How do we identify different materials? ...
... 2. How do we identify different materials? ...
Chapter 3
... 2. All atoms of a given element have identical properties that differ from those of other elements. 3. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or transformed into atoms of another element. 4. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with one another in small wholenumber ratios. 5. T ...
... 2. All atoms of a given element have identical properties that differ from those of other elements. 3. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or transformed into atoms of another element. 4. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with one another in small wholenumber ratios. 5. T ...
Name
... Atoms of different elements can _________________mix together or ___________________ combine. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are__________________, _________________, or _________________________. ...
... Atoms of different elements can _________________mix together or ___________________ combine. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are__________________, _________________, or _________________________. ...
Ch 11 Atoms etc GNC
... What particles make up an atom in the electron cloud model, and what electrical charges do they have? Electrons—negatively charged; protons—positively charged; neutrons—electrically neutral Section 2 The Simplest Matter A. Elements—materials that cannot be broken down into simpler materials 1. There ...
... What particles make up an atom in the electron cloud model, and what electrical charges do they have? Electrons—negatively charged; protons—positively charged; neutrons—electrically neutral Section 2 The Simplest Matter A. Elements—materials that cannot be broken down into simpler materials 1. There ...
Atoms
... History of Atomic Theory Thomson – (discovering the electron) Proposed that atoms were made up of smaller particles. Theory that smaller negatively charged particles are spread evenly around a positively charged nucleus. His model was called the plum-pudding model. ...
... History of Atomic Theory Thomson – (discovering the electron) Proposed that atoms were made up of smaller particles. Theory that smaller negatively charged particles are spread evenly around a positively charged nucleus. His model was called the plum-pudding model. ...
matter crct/final exam review
... 16. What information does the atomic number give you about an element? 17. What determines an element’s placement on the Periodic Table? 18. Who organized the very first Periodic Table? 19. Why is it called the Periodic Table? 20. How is the Periodic Table arranged? 21. What is the most reactive fam ...
... 16. What information does the atomic number give you about an element? 17. What determines an element’s placement on the Periodic Table? 18. Who organized the very first Periodic Table? 19. Why is it called the Periodic Table? 20. How is the Periodic Table arranged? 21. What is the most reactive fam ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 51. Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as ______ as possible. 52. In an electron configuration, a superscript indicates… ...
... 51. Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as ______ as possible. 52. In an electron configuration, a superscript indicates… ...
Isotopes-Chemistry
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...