Section 3 The Periodic Table
... Electrons are placed in energy levels. Energy levels nearer the nucleus have lower energy than those levels that are farther away. ...
... Electrons are placed in energy levels. Energy levels nearer the nucleus have lower energy than those levels that are farther away. ...
What does an elements atomic mass tell us about the element?
... Atomic # = 19 Mass # = 39 K nucleus contains 19 protons 39 – 19 = 20 neutrons How many electrons? Same as # Protons (19) ...
... Atomic # = 19 Mass # = 39 K nucleus contains 19 protons 39 – 19 = 20 neutrons How many electrons? Same as # Protons (19) ...
UNIT 5 REVIEW PROBLEMS
... 8. Determine which element would have characteristics of both a metal and a nonmetal: a. b. c. d. ...
... 8. Determine which element would have characteristics of both a metal and a nonmetal: a. b. c. d. ...
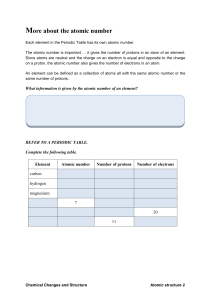
14 more about the atomic number
... The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of electrons in an atom. An element can be defined as a collection of ...
... The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of electrons in an atom. An element can be defined as a collection of ...
Isotopes Models
... called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It is radioactive. It is f ...
... called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It is radioactive. It is f ...
periodic table
... 3) element at the top Elements in the same group have: A. similar characteristic properties: bp/fp/sp heat B. same # electrons in the valence shell C. same oxidation #: charge after octet rule applied 4. Zig-zag line between B-Al and Po-At separates metals (80% chart) on the left from non-metals on ...
... 3) element at the top Elements in the same group have: A. similar characteristic properties: bp/fp/sp heat B. same # electrons in the valence shell C. same oxidation #: charge after octet rule applied 4. Zig-zag line between B-Al and Po-At separates metals (80% chart) on the left from non-metals on ...
Periodic Table notes
... b) more mass and is about the same in size c) more mass and is smaller in size d) none of the above ...
... b) more mass and is about the same in size c) more mass and is smaller in size d) none of the above ...
1H Atomic Theory Quiz Review
... What is the atomic mass of Copper with isotopes Cu-63 (mass of 63.0 amu and 69.2% abundance) and Cu-65 (mass 65.0 amu and 30.8% abundance)? Do the equation including units with sig figs. ...
... What is the atomic mass of Copper with isotopes Cu-63 (mass of 63.0 amu and 69.2% abundance) and Cu-65 (mass 65.0 amu and 30.8% abundance)? Do the equation including units with sig figs. ...
Chapter 3 notes
... • Orbital- or energy shell/level is a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. • Valence electron- an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom. So in Al valence 3. ...
... • Orbital- or energy shell/level is a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. • Valence electron- an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom. So in Al valence 3. ...
atoms of different elements differ in size, mass
... Most of the particles passed right through A few particles were deflected VERY FEW were greatly deflected ...
... Most of the particles passed right through A few particles were deflected VERY FEW were greatly deflected ...
T1 Final Study Guide - District 196 e
... *** This study guide is a place to get you started preparing for your final. The final is not limited to only things mentioned on this review, it can be anything we have done over the course of the trimester. We will also be having some review time during class as well. *** ...
... *** This study guide is a place to get you started preparing for your final. The final is not limited to only things mentioned on this review, it can be anything we have done over the course of the trimester. We will also be having some review time during class as well. *** ...
Atoms
... The mass of a proton is 1836 times that of an electron, and the mass of a neutron is 1839 times that of an electron. Thus the vast majority of the mass of an atom is in the nucleus. ...
... The mass of a proton is 1836 times that of an electron, and the mass of a neutron is 1839 times that of an electron. Thus the vast majority of the mass of an atom is in the nucleus. ...
cba #1 review - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... How can you determine valence electrons using the periodic table: Write the Electron configuration, short hand, Lewis dot, Bohr Model, Bohr electron configuration for the following elements: ...
... How can you determine valence electrons using the periodic table: Write the Electron configuration, short hand, Lewis dot, Bohr Model, Bohr electron configuration for the following elements: ...
ch 4 notes
... • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
... • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
CP3
... of an isotope in amu’s is simply the Mass number Most elements have several common isotopes Mass on periodic table must reflect this, that is why there are decimals Weighted average calculation (like grades) ...
... of an isotope in amu’s is simply the Mass number Most elements have several common isotopes Mass on periodic table must reflect this, that is why there are decimals Weighted average calculation (like grades) ...
Ch. 2. Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
... Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. *Isotopes are identified by including the mass number with the element name. Ex: Carbon 14, Carbon 12 Average Atomic Mass: An estimate of the mass of an element’s a ...
... Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. *Isotopes are identified by including the mass number with the element name. Ex: Carbon 14, Carbon 12 Average Atomic Mass: An estimate of the mass of an element’s a ...
The Atom
... Dates (some may not have dates) Important Peoples Names What they found/discovered/believed to be true The experiment they did Picture of the model they developed (if there is one) ...
... Dates (some may not have dates) Important Peoples Names What they found/discovered/believed to be true The experiment they did Picture of the model they developed (if there is one) ...
Nuclear Physics Rutherford`s model of the atom
... Beta decay is a process which allows the atom to obtain the optimal ratio of protons and neutrons. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus (β−), while in the case of a positron emission ...
... Beta decay is a process which allows the atom to obtain the optimal ratio of protons and neutrons. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus (β−), while in the case of a positron emission ...
Six Weeks Review PPT
... Democritus, 460 BC – proposes particles so small they can not be destroyed or divided, and describes them as “atomos” (uncuttable) John Dalton, early 1800’s - first to use “atom”; proposes that atoms of the same element are identical, and atoms of different elements have different weights/masses; So ...
... Democritus, 460 BC – proposes particles so small they can not be destroyed or divided, and describes them as “atomos” (uncuttable) John Dalton, early 1800’s - first to use “atom”; proposes that atoms of the same element are identical, and atoms of different elements have different weights/masses; So ...
Phys Sci I, Quiz #3 - Electriciy and Magnetism, Atomic and Nuclear
... B) quark C) electromagnetic D) gravitational ...
... B) quark C) electromagnetic D) gravitational ...
Atomic Structure - Peoria Public Schools
... Henri Becquerel: Discovery of radioactivity 1900's Robert Millikan: Charge and mass of the electron Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and trans-uranium elements ...
... Henri Becquerel: Discovery of radioactivity 1900's Robert Millikan: Charge and mass of the electron Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and trans-uranium elements ...
COS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
... • region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons ...
... • region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons ...
1 - M*W
... d) Have the same number of electrons 23) To draw a Lewis structure you do not need to know a) The number of valence electrons for each atom b) The types of atoms in the molecule c) The number of atoms in the molecule d) Bond energies 24) Neils Bohr’s contribution to modern atomic theory was the prop ...
... d) Have the same number of electrons 23) To draw a Lewis structure you do not need to know a) The number of valence electrons for each atom b) The types of atoms in the molecule c) The number of atoms in the molecule d) Bond energies 24) Neils Bohr’s contribution to modern atomic theory was the prop ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... _________ 16. Of the following particles, those not found in the nucleus of an atom are a. protons. b. neutrons. c. electrons. d. protons and neutrons. _________ 17. Different atoms of the same element may have different a. numbers of protons. b. atomic numbers. c. atomic masses. d. numbers of elect ...
... _________ 16. Of the following particles, those not found in the nucleus of an atom are a. protons. b. neutrons. c. electrons. d. protons and neutrons. _________ 17. Different atoms of the same element may have different a. numbers of protons. b. atomic numbers. c. atomic masses. d. numbers of elect ...
Notetaking Workshee
... arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. 3. In 1913, the work of Henry G.J. ___________________, an English scientist made an arrangement of elements based on their increasing _________________________________________ instead of masses. 4. The current ...
... arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. 3. In 1913, the work of Henry G.J. ___________________, an English scientist made an arrangement of elements based on their increasing _________________________________________ instead of masses. 4. The current ...