Test Review Answers File
... 8. Why are the Noble Gases considered “inert” gases? List all the elements in this group. -undergo fewest chemical reactions, low chemical reactivity -helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon 9. List which elements are chemically similar to Beryllium. Explain why. Magnesium, calcium, strontium, ba ...
... 8. Why are the Noble Gases considered “inert” gases? List all the elements in this group. -undergo fewest chemical reactions, low chemical reactivity -helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon 9. List which elements are chemically similar to Beryllium. Explain why. Magnesium, calcium, strontium, ba ...
Matter and Periodic Table Matter- anything that has mass and takes
... -If two atoms of the same element have different number of neutrons then it is an isotope. Atomic Mass = found on the periodic table = average of all isotopes masses ...
... -If two atoms of the same element have different number of neutrons then it is an isotope. Atomic Mass = found on the periodic table = average of all isotopes masses ...
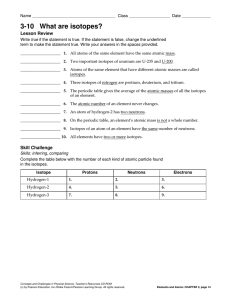
3-10 What are isotopes?
... 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true about the atomic numbers for all the isotopes of carbon? For all the isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen? _____________________________________________________________________ 7. One of thes ...
... 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true about the atomic numbers for all the isotopes of carbon? For all the isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen? _____________________________________________________________________ 7. One of thes ...
atoms
... atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. Atomic Symbol: The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are used ...
... atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. Atomic Symbol: The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are used ...
Chapter 5
... • Left blank spots in table which predicted properties of elements not yet discovered ...
... • Left blank spots in table which predicted properties of elements not yet discovered ...
Periodic Table Jeopardy
... Atomic Theory with evidence. He had four key postulates that he wanted everyone to know. ...
... Atomic Theory with evidence. He had four key postulates that he wanted everyone to know. ...
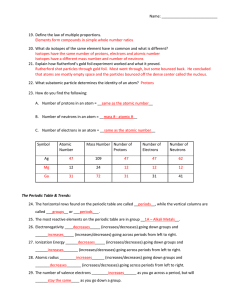
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. 5. The total number of nucleons (particles in the nucleus) in the atom make up the mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is ...
... 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. 5. The total number of nucleons (particles in the nucleus) in the atom make up the mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is ...
UNIT 6: PERIODICITY THE FOREST: Repeating (periodic) patterns
... Describe the locations in the periodic table and the general properties of the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals, the halogens, and the noble gases. Use the periodic table to predict the electron configurations of elements. Give examples of the relationship between an element’s electron confi ...
... Describe the locations in the periodic table and the general properties of the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals, the halogens, and the noble gases. Use the periodic table to predict the electron configurations of elements. Give examples of the relationship between an element’s electron confi ...
Looking for Patterns in Chemical Reactivity
... to the energy changes that take place when their atoms lose, gain, or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. Metals are elements that tend to lose their valence electrons relatively easily and this accounts for many of their physical and chemical properties. One important property of ...
... to the energy changes that take place when their atoms lose, gain, or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. Metals are elements that tend to lose their valence electrons relatively easily and this accounts for many of their physical and chemical properties. One important property of ...
19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of n ...
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of n ...
Matter
... A mixture in which particles of a material are dispersed throughout a liquid or gas but are large enough that they settle out. Particles are insoluble, so they DO NOT dissolve in the liquid or gas. Particles can be separated using a filter. ...
... A mixture in which particles of a material are dispersed throughout a liquid or gas but are large enough that they settle out. Particles are insoluble, so they DO NOT dissolve in the liquid or gas. Particles can be separated using a filter. ...
Atomic Structure
... Radioisotopes have the same chemical properties as other atoms of the same element. This means they will be used by cells to make compounds in the same way as non-radioactive isotopes. However, the radioactive isotopes are easily detected and this makes them useful as a “medical tracer”. They can be ...
... Radioisotopes have the same chemical properties as other atoms of the same element. This means they will be used by cells to make compounds in the same way as non-radioactive isotopes. However, the radioactive isotopes are easily detected and this makes them useful as a “medical tracer”. They can be ...
SL Topic 2 : Atomic structure
... energy level. III. The lines are due to electrons absorbing energy as they move from higher energy levels to lower energy levels. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III ...
... energy level. III. The lines are due to electrons absorbing energy as they move from higher energy levels to lower energy levels. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III ...
Document
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
Topic 13 – 14.1
... 14.1 How atoms of various elements are different The atoms of different elements contain different numbers of protons in the nucleus. Because the number of protons is so important, it is called the atomic number. ...
... 14.1 How atoms of various elements are different The atoms of different elements contain different numbers of protons in the nucleus. Because the number of protons is so important, it is called the atomic number. ...
Atomic Structure
... Decay (p. 841) According to the band of stability graph (Figure 18.1) this nuclide is neutron-poor, so it must do something to decrease the number of protons or increase the number of neutrons. ...
... Decay (p. 841) According to the band of stability graph (Figure 18.1) this nuclide is neutron-poor, so it must do something to decrease the number of protons or increase the number of neutrons. ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE abbr
... valence electron Reactivity increases from top to bottom of group. Francium would be the most reactive element in this group (if it didn’t radioactively decay so quickly). ...
... valence electron Reactivity increases from top to bottom of group. Francium would be the most reactive element in this group (if it didn’t radioactively decay so quickly). ...
Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
Document
... 4. Radioactive tracers are useful in ___________ _____________. 5. Both fusion and fission reactions produce __________________. 6. One type of radioactive device that indicates the intensity of radiation with a clicking sound that increases in frequency as more radiation is present is a(n) ________ ...
... 4. Radioactive tracers are useful in ___________ _____________. 5. Both fusion and fission reactions produce __________________. 6. One type of radioactive device that indicates the intensity of radiation with a clicking sound that increases in frequency as more radiation is present is a(n) ________ ...
pg156
... a. How do the first ionization energies of main-group elements vary across a period and down a group? ...
... a. How do the first ionization energies of main-group elements vary across a period and down a group? ...
200
... Winner of the coin toss decides the first question Each team will have 1 person compete at a time. If the team answers incorrectly the other team has a chance to answer • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the ...
... Winner of the coin toss decides the first question Each team will have 1 person compete at a time. If the team answers incorrectly the other team has a chance to answer • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the ...
Two valence electrons.
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
Jeopardy
... Winner of the coin toss decides the first question Each team will have 1 person compete at a time. If the team answers incorrectly the other team has a chance to answer • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the ...
... Winner of the coin toss decides the first question Each team will have 1 person compete at a time. If the team answers incorrectly the other team has a chance to answer • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the ...
c) C2 Glossary Topic 1
... The number of objects of a particular kind in a sample (shown as a percentage of the total number of objects) ...
... The number of objects of a particular kind in a sample (shown as a percentage of the total number of objects) ...