UNIT 1 Atomic Structure
... Note electrons are usually shown as far apart as possible -they have the same charge and therefore repel each other. 3. The Noble gases (Group 0) have a stable electron configuration (s2p6) with 8 electrons filling the outer s and p orbitals. This stability comes from the low energy state of this c ...
... Note electrons are usually shown as far apart as possible -they have the same charge and therefore repel each other. 3. The Noble gases (Group 0) have a stable electron configuration (s2p6) with 8 electrons filling the outer s and p orbitals. This stability comes from the low energy state of this c ...
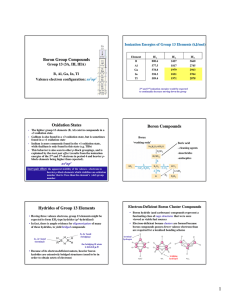
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier ...
... Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier ...
LBC1_Sec3_Unit01_Alchemy
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
Discussion Notes (cont.)
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
Chapter 18 Comparing Atoms Lab
... 22. What is the heaviest element with at least one isotope that is NOT radioactive? 23. On most periodic tables, a single atomic mass is listed instead of the mass numbers for all the stable isotopes. How is this mass related to the different isotopes? ...
... 22. What is the heaviest element with at least one isotope that is NOT radioactive? 23. On most periodic tables, a single atomic mass is listed instead of the mass numbers for all the stable isotopes. How is this mass related to the different isotopes? ...
Structure of an Atom
... protons and neutrons. These e particles are known as subatomic particles. Electrons: The negatively charged particles in an atom are called electrons. An electron has one unit negative charge. The mass of an electron is 1/1837 of the mass of hydrogen atom (lightest atom). Thus, electrons have a negl ...
... protons and neutrons. These e particles are known as subatomic particles. Electrons: The negatively charged particles in an atom are called electrons. An electron has one unit negative charge. The mass of an electron is 1/1837 of the mass of hydrogen atom (lightest atom). Thus, electrons have a negl ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
CHAPTER 2. THE ELEMENTS: BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF …
... • So helium has a filled electron shell making it a noble gas Helium is a nontoxic, odorless, tasteless, colorless gas with a very low density of only 0.164 g/L at 25C and 1 atm pressure Helium comes from some sources of natural gas containing up to 10% helium by volume • Helium was first observed ...
... • So helium has a filled electron shell making it a noble gas Helium is a nontoxic, odorless, tasteless, colorless gas with a very low density of only 0.164 g/L at 25C and 1 atm pressure Helium comes from some sources of natural gas containing up to 10% helium by volume • Helium was first observed ...
gp - fc2009goran
... • Iodine is one of the earliest elements whose radioisotopes were used in what is now called nuclear medicine. The most common, stable form of iodine has an atomic number of 53 (protons) and an atomic weight of 127 (53 protons plus 74 neutrons). Because its nucleus has the "correct" number of neutro ...
... • Iodine is one of the earliest elements whose radioisotopes were used in what is now called nuclear medicine. The most common, stable form of iodine has an atomic number of 53 (protons) and an atomic weight of 127 (53 protons plus 74 neutrons). Because its nucleus has the "correct" number of neutro ...
Chemistry Readings
... the nucleus). The shells are also called energy levels or orbitals. We will use the term shell. Chemists use letters to name the shells around a nucleus. They use the letters "k, l, m, n, o, p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold ...
... the nucleus). The shells are also called energy levels or orbitals. We will use the term shell. Chemists use letters to name the shells around a nucleus. They use the letters "k, l, m, n, o, p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold ...
Chemical Element
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element (that is, with the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus), but having different numbers of neutrons. Most naturally-occurring elements have more than one isotope. Thus, for example, there are three main isotopes of carbon. All carbon atoms have 6 proto ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element (that is, with the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus), but having different numbers of neutrons. Most naturally-occurring elements have more than one isotope. Thus, for example, there are three main isotopes of carbon. All carbon atoms have 6 proto ...
Atomic Theory
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
05_Lecture - HCC Learning Web
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Most elements occur naturally with varying numbers of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. • Isotopes have the same atomic number, but different mass numbe ...
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Most elements occur naturally with varying numbers of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. • Isotopes have the same atomic number, but different mass numbe ...
Atoms and Materials for Engineering
... entry. We only know that they are second-level p orbitals (2p). The number 4 after the p indicates that there are 4 electrons in 2p orbitals. It is expected that we already know there are a maximum of three p orbitals at level 2, two contain Figure 5 oxygen one electron each and the other has 2 elec ...
... entry. We only know that they are second-level p orbitals (2p). The number 4 after the p indicates that there are 4 electrons in 2p orbitals. It is expected that we already know there are a maximum of three p orbitals at level 2, two contain Figure 5 oxygen one electron each and the other has 2 elec ...
Isotopes - Net Texts
... inside the atom. So if a neutron or two is added or removed from the nucleus, then the chemical properties will not change. This means that such an atom would remain in the same place in the periodic table. For example, no matter how many neutrons we add or subtract from a nucleus with 6 protons, th ...
... inside the atom. So if a neutron or two is added or removed from the nucleus, then the chemical properties will not change. This means that such an atom would remain in the same place in the periodic table. For example, no matter how many neutrons we add or subtract from a nucleus with 6 protons, th ...
Chapter 2 - My Teacher Site
... All atoms of a particular element have a unique number of protons, known as the atomic number, in their nucleus • The atomic number is written as a subscript to the left of the symbol for that element – Ex) 2He = Helium (2 protons) ...
... All atoms of a particular element have a unique number of protons, known as the atomic number, in their nucleus • The atomic number is written as a subscript to the left of the symbol for that element – Ex) 2He = Helium (2 protons) ...
Elements
... Thomson’s Model of the Atom Thomson’s experiment showed that atoms have a structure and are divisible Thomson reasoned that electrons must be a fraction of the entire size of the atom since their mass is much smaller that the whole atom Thomson also reasoned since atoms are neutral, the electro ...
... Thomson’s Model of the Atom Thomson’s experiment showed that atoms have a structure and are divisible Thomson reasoned that electrons must be a fraction of the entire size of the atom since their mass is much smaller that the whole atom Thomson also reasoned since atoms are neutral, the electro ...
Science Focus 10 Unit 1 Energy and Matter in Chemical
... 2) surround it by dots that represent the atom’s valence electrons (use the group number to determine the number of valence electrons) 3) if an atom has more than 4 valence electrons, the additional electrons are paired. ...
... 2) surround it by dots that represent the atom’s valence electrons (use the group number to determine the number of valence electrons) 3) if an atom has more than 4 valence electrons, the additional electrons are paired. ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... • Elements gain or lose electrons to acquire the electron configuration of the noble gases. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
... • Elements gain or lose electrons to acquire the electron configuration of the noble gases. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
atoms. - Toolbox Pro
... • Fe has 4 orbitals • The first orbital closest to the nucleus contains 2 electrons. • The second contains 8. • The third contains 14. • The fourth contains 2 • Fe has 2 valence electrons (the # of electrons in the outermost shell) 2-8-14-2 is the Fe atom’s electron configuration ...
... • Fe has 4 orbitals • The first orbital closest to the nucleus contains 2 electrons. • The second contains 8. • The third contains 14. • The fourth contains 2 • Fe has 2 valence electrons (the # of electrons in the outermost shell) 2-8-14-2 is the Fe atom’s electron configuration ...
Christopher Warner Title: Element Project Educational Filters: The
... particle found in atoms. Walter Bothe and James Chadwick, who repeated Bothe’s work, found high energy particles with no charge and a similar mass as the proton. This particle is now known as neutrons (Smoot, 1987). J.J. Thomson also noticed two kinds of neon atoms that were exactly alike chemically ...
... particle found in atoms. Walter Bothe and James Chadwick, who repeated Bothe’s work, found high energy particles with no charge and a similar mass as the proton. This particle is now known as neutrons (Smoot, 1987). J.J. Thomson also noticed two kinds of neon atoms that were exactly alike chemically ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 27. What is the mass of 180.3 cm3 of lead if the density is 11.4 g/cm3? 28. What is the density of 325g of a substance with a volume of 492mL? 29. Define accuracy and precision. 30. Complete the following calculations with the correct number of significant figures: a. 1.23kg + 4.082kg b. 16.04s – 5 ...
... 27. What is the mass of 180.3 cm3 of lead if the density is 11.4 g/cm3? 28. What is the density of 325g of a substance with a volume of 492mL? 29. Define accuracy and precision. 30. Complete the following calculations with the correct number of significant figures: a. 1.23kg + 4.082kg b. 16.04s – 5 ...
Document
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... In the early 1800’s British scientist John Dalton proposed that each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Dalton stated that all of the atoms of a particular element are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements. Daltons theory also assumed that atoms could not be di ...
... In the early 1800’s British scientist John Dalton proposed that each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Dalton stated that all of the atoms of a particular element are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements. Daltons theory also assumed that atoms could not be di ...
Objectives - Warren County Public Schools
... •When organized elements into groups by similar chemical properties, he observed the periods increasing in atomic mass. (1869) • His organization system was successful at predicting undiscovered elements. •Do you observe any inconsistencies with his organization system? ...
... •When organized elements into groups by similar chemical properties, he observed the periods increasing in atomic mass. (1869) • His organization system was successful at predicting undiscovered elements. •Do you observe any inconsistencies with his organization system? ...