File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... In the Bohr model of the atom, the nucleus contains the majority of the mass of the atom in its protons and neutrons. In most cases, electrons fill the lower energy levels first, followed by the next higher energy orbital until it is full, and so on until all electrons have been placed. Atoms tend t ...
... In the Bohr model of the atom, the nucleus contains the majority of the mass of the atom in its protons and neutrons. In most cases, electrons fill the lower energy levels first, followed by the next higher energy orbital until it is full, and so on until all electrons have been placed. Atoms tend t ...
The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]
... elements as X-A where the X is the element symbol and the A is the atomic mass of that element. ...
... elements as X-A where the X is the element symbol and the A is the atomic mass of that element. ...
Synthesis of elements by helium and oxygen building blocks Bohr
... repulsive Coulomb force and come within the short-range of the attractive strong nuclear force. The processes described above produce only nuclei of the elements: In the infernal heat of about 107 K atoms cannot have electron shells, neutrons would decay into protons and electrons. The elements cann ...
... repulsive Coulomb force and come within the short-range of the attractive strong nuclear force. The processes described above produce only nuclei of the elements: In the infernal heat of about 107 K atoms cannot have electron shells, neutrons would decay into protons and electrons. The elements cann ...
mack atoms - McClymonds Chemistry
... • The idea was not warmly received and did not gain traction for 2000 years ...
... • The idea was not warmly received and did not gain traction for 2000 years ...
Directed Reading
... ______ 27. When scientists study the interactions of atoms, what can they predict? a. how long it takes for chemical bonds to form b. how subatomic particles will split apart to form other atoms c. which kinds of atoms will form chemical bonds together d. the weather ______ 28. How many valence elec ...
... ______ 27. When scientists study the interactions of atoms, what can they predict? a. how long it takes for chemical bonds to form b. how subatomic particles will split apart to form other atoms c. which kinds of atoms will form chemical bonds together d. the weather ______ 28. How many valence elec ...
Chapter 10 - MrsDoughertys
... I will post a pdf of the overhead notes on the wiki this afternoon. For now, make sure you copy what I write so that if you have questions you can come see me. ...
... I will post a pdf of the overhead notes on the wiki this afternoon. For now, make sure you copy what I write so that if you have questions you can come see me. ...
periodic table
... • Mendeleev had to leave blank spaces in his periodic table to keep the elements properly lined up according to their chemical properties. • He looked at the properties and atomic masses of the elements surrounding these blank spaces. ...
... • Mendeleev had to leave blank spaces in his periodic table to keep the elements properly lined up according to their chemical properties. • He looked at the properties and atomic masses of the elements surrounding these blank spaces. ...
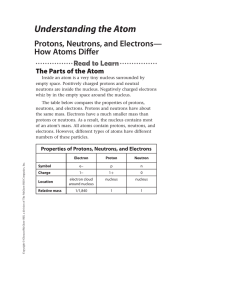
Understanding the Atom
... of the mineral appeared on the plate. One day, Becquerel left the mineral in a drawer next to a wrapped, unexposed plate. Later, he unwrapped the plate and found that it contained an image of the mineral. The mineral spontaneously emitted energy, even in the dark! What was this energy? ...
... of the mineral appeared on the plate. One day, Becquerel left the mineral in a drawer next to a wrapped, unexposed plate. Later, he unwrapped the plate and found that it contained an image of the mineral. The mineral spontaneously emitted energy, even in the dark! What was this energy? ...
The Periodic Table
... e. Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. ...
... e. Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. ...
8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... The chemistry of bromine will be similar to the chemistry of chlorine and iodine. An enormous number of possible chemical reactions could be discussed. For example: all three elements form –1 anions. The binary hydrogen compounds of all three (i.e. HCl, HBr, HI) are acidic. Döbereiner’s system was i ...
... The chemistry of bromine will be similar to the chemistry of chlorine and iodine. An enormous number of possible chemical reactions could be discussed. For example: all three elements form –1 anions. The binary hydrogen compounds of all three (i.e. HCl, HBr, HI) are acidic. Döbereiner’s system was i ...
File
... Electrons Lost = Electrons Gained Both sodium chloride and magnesium oxide are simple ionic compounds. ...
... Electrons Lost = Electrons Gained Both sodium chloride and magnesium oxide are simple ionic compounds. ...
Unit 1 Notes
... mercury, iron) – each was associated with a symbol of a different celestial body. e.g. gold - sun, copper – Venus, lead – Saturn, etc. Early 1800’s - alchemists had discovered new elements and needed new symbols to represent them. 1814, Swedish chemist Jons Jacob Berzelius used letters as symbol ...
... mercury, iron) – each was associated with a symbol of a different celestial body. e.g. gold - sun, copper – Venus, lead – Saturn, etc. Early 1800’s - alchemists had discovered new elements and needed new symbols to represent them. 1814, Swedish chemist Jons Jacob Berzelius used letters as symbol ...
(a) Atoms - Warren County Public Schools
... first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
... first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions - Science Take-Out
... 1. Use the information on the periodic table to make a model of a hydrogen atom. Then make a hydrogen ion by removing the electron (blue chip) from the model. Draw your ion model. Use a “+” sign for each proton, an “n” for each neutron and a “–” sign for each electron. ...
... 1. Use the information on the periodic table to make a model of a hydrogen atom. Then make a hydrogen ion by removing the electron (blue chip) from the model. Draw your ion model. Use a “+” sign for each proton, an “n” for each neutron and a “–” sign for each electron. ...
An understanding of the nature of matter has developed
... reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 98 elements exist naturally although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature.[n 1] Elements with atomic numbers from 99 to 118 have only b ...
... reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 98 elements exist naturally although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature.[n 1] Elements with atomic numbers from 99 to 118 have only b ...
Nontes Unit 3 pdf
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
Notes Unit 3
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
Atomic Theory
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
Atoms and Elements
... • Each element has a _________________________number of protons in its nucleus. All carbon atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei. The ______________________in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. ________is the short-hand designation for the________________________. Because each ...
... • Each element has a _________________________number of protons in its nucleus. All carbon atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei. The ______________________in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. ________is the short-hand designation for the________________________. Because each ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 15. Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. b. Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. The mass of a ...
... ____ 15. Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. b. Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. The mass of a ...
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table
... Note: It is often confusing for students to see the terms “atom” and “element” used interchangeably as if they are the same thing. Explain to students that an atom is the smallest particle or “building block” of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same type of atom. For instan ...
... Note: It is often confusing for students to see the terms “atom” and “element” used interchangeably as if they are the same thing. Explain to students that an atom is the smallest particle or “building block” of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same type of atom. For instan ...
File
... B) atomic masses B) In the third shell, an electron has more energy C) atomic radii D) atomic numbers and is farther from the nucleus. 33. Elements on the modern Periodic Table are arranged in C) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is order of increasing closer to the nucleus. A) ato ...
... B) atomic masses B) In the third shell, an electron has more energy C) atomic radii D) atomic numbers and is farther from the nucleus. 33. Elements on the modern Periodic Table are arranged in C) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is order of increasing closer to the nucleus. A) ato ...
Accelerated Chemistry Chapter 4 Student Notes
... between levels), the e- disappears from one shell and reappears in ...
... between levels), the e- disappears from one shell and reappears in ...
chapter 11: modern atomic theory
... Werner Heisenberg (1927); Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle – For very small particles (e.g. proton, neutrons, electrons), there is an inherent uncertainty in the particles’ position and motion. → It is impossible to determine both the particle’s position and its momentum. → It is impossible to dete ...
... Werner Heisenberg (1927); Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle – For very small particles (e.g. proton, neutrons, electrons), there is an inherent uncertainty in the particles’ position and motion. → It is impossible to determine both the particle’s position and its momentum. → It is impossible to dete ...

![The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016109524_1-1437871a54cd24e5ee13c27e98f0719d-300x300.png)