File
... Isotopes behave the same chemically because they still have the same number of protons and electrons ...
... Isotopes behave the same chemically because they still have the same number of protons and electrons ...
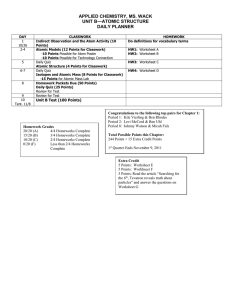
Review for Test
... 3. If Fred had two bar magnets, could he have placed them near the screen without causing any distortion in the image? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. If Fred had two bar magnets, could he have placed them near the screen without causing any distortion in the image? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
ATOMIC STRUacad test
... 14. Which of the following statements explains why chemists do not count atoms and molecules directly? A. Atoms and molecules are extremely small B. All of the relationships in a chemical reaction can be expressed as mass ratios C. Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction D. Re ...
... 14. Which of the following statements explains why chemists do not count atoms and molecules directly? A. Atoms and molecules are extremely small B. All of the relationships in a chemical reaction can be expressed as mass ratios C. Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction D. Re ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and the Periodic Table
... – English school teacher – widely supported due to supporting evidence – three parts • every element is made of tiny unique particles called atoms that cannot be subdivided • atoms of the same element are exactly alike • atoms of different elements can join to form molecules ...
... – English school teacher – widely supported due to supporting evidence – three parts • every element is made of tiny unique particles called atoms that cannot be subdivided • atoms of the same element are exactly alike • atoms of different elements can join to form molecules ...
Lesson 1 & 2 Periodic table trends and formation
... - arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass - some elements were out of order therefore modern table is arranged in Atomic Number Meyer recognised Mendeleev’s work and both where awarded The Davy medal for Chemistry in 1882. ...
... - arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass - some elements were out of order therefore modern table is arranged in Atomic Number Meyer recognised Mendeleev’s work and both where awarded The Davy medal for Chemistry in 1882. ...
Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Chapter 5
... radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
... radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table
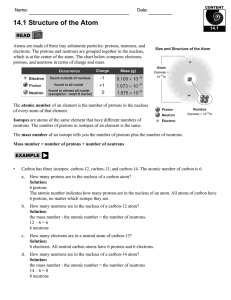
... or neutron). The majority of the atomic mass is contributed by the protons and neutrons. For any element in the periodic table, the number of electrons in an atom of that element always equals the number of protons in the nucleus. But this is not true for neutrons. Atoms of the same element can have ...
... or neutron). The majority of the atomic mass is contributed by the protons and neutrons. For any element in the periodic table, the number of electrons in an atom of that element always equals the number of protons in the nucleus. But this is not true for neutrons. Atoms of the same element can have ...
Lecture 4
... – The nucleus contains the protons and the neutrons – The electrons are constantly moving around in the electron cloud – In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
... – The nucleus contains the protons and the neutrons – The electrons are constantly moving around in the electron cloud – In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
14.1 Structure of the Atom
... Using dot diagrams to represent chemical reactivity Once you have a dot diagram for an element, you can predict how an atom will achieve a full valence shell. For instance, it is easy to see that chlorine has one empty space in its valence shell. It is likely that chlorine will try to gain one elect ...
... Using dot diagrams to represent chemical reactivity Once you have a dot diagram for an element, you can predict how an atom will achieve a full valence shell. For instance, it is easy to see that chlorine has one empty space in its valence shell. It is likely that chlorine will try to gain one elect ...
Activity 6 Atoms with More than One Electron
... difficulty with this if they have poor skills in making and reading graphs. Students also tend to mix up rows (periods) and columns (groups) on the periodic table, so while they are able to recognize the patterns, they may not be able to articulate correctly how these patterns are related to the org ...
... difficulty with this if they have poor skills in making and reading graphs. Students also tend to mix up rows (periods) and columns (groups) on the periodic table, so while they are able to recognize the patterns, they may not be able to articulate correctly how these patterns are related to the org ...
U1 Atoms, Elements and Ions
... – A tiny nucleus about 10-13 cm in diameter. – Electrons that move around the nucleus at an average distance of about 10-8 cm away. – Electrons and protons having equal and opposite charges while neutrons have no charge. – Protons and neutrons almost 2000 times more massive than electrons. ...
... – A tiny nucleus about 10-13 cm in diameter. – Electrons that move around the nucleus at an average distance of about 10-8 cm away. – Electrons and protons having equal and opposite charges while neutrons have no charge. – Protons and neutrons almost 2000 times more massive than electrons. ...
Valence Electrons - Warren County Public Schools
... •When organized elements into groups by similar chemical properties, he observed the periods increasing in atomic mass. (1869) • His organization system was successful at predicting undiscovered elements. •Do you observe any inconsistencies with his organization system? ...
... •When organized elements into groups by similar chemical properties, he observed the periods increasing in atomic mass. (1869) • His organization system was successful at predicting undiscovered elements. •Do you observe any inconsistencies with his organization system? ...
Protons and Electrons
... The energy levels are in groups that depend on their distance from the nucleus. Electrons in an energy level close to the nucleus are lower in energy than electrons in an energy level further from the nucleus. Each energy level can also contain a maximum number of electrons. For example, the first e ...
... The energy levels are in groups that depend on their distance from the nucleus. Electrons in an energy level close to the nucleus are lower in energy than electrons in an energy level further from the nucleus. Each energy level can also contain a maximum number of electrons. For example, the first e ...
Catalyst
... The mass number or atomic mass: This number tells the mass of one atom, which is approximately the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, since each proton and each neutron has a mass equal to one mass unit, and the electrons ...
... The mass number or atomic mass: This number tells the mass of one atom, which is approximately the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, since each proton and each neutron has a mass equal to one mass unit, and the electrons ...
File
... Station 4: Beanium Review Period 1 and 4: Take time now to make sure your data table is complete for your Beanium activity we completed on Friday. If you did not get mass make sure to get that information from a classmate now. Check your calculations. Based on the lab activity answer the following ...
... Station 4: Beanium Review Period 1 and 4: Take time now to make sure your data table is complete for your Beanium activity we completed on Friday. If you did not get mass make sure to get that information from a classmate now. Check your calculations. Based on the lab activity answer the following ...
Chapter 8. The Periodic Table
... relative atomic masses of atoms of the elements, chemists were seeking for relationships between atomic mass and chemical and physical properties. Numerous Nineteenth Century chemists speculated about families of elements having similar chemical properties. For example, lithium, sodium and potassium ...
... relative atomic masses of atoms of the elements, chemists were seeking for relationships between atomic mass and chemical and physical properties. Numerous Nineteenth Century chemists speculated about families of elements having similar chemical properties. For example, lithium, sodium and potassium ...
Henry Moseley, the Atomic Number, and Synthesis
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
Henry Moseley, the Atomic Number, and Synthesis
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
Chapter 2
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
Flavors of the Atom
... Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that can enter into a chemical reaction. Protons and neutrons make up the dense, positive nucleus. Electrons occupy the empty space outside the nucleus. A neutral atom contains the same number of electrons and protons. ...
... Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that can enter into a chemical reaction. Protons and neutrons make up the dense, positive nucleus. Electrons occupy the empty space outside the nucleus. A neutral atom contains the same number of electrons and protons. ...
Atomic structure and periodic table review questions What is an
... 3. Another name for the two sub-atomic particles found in the nucleus is ____________. 4. What are the sub-atomic particles found outside of the nucleus? 5. Which particle has a positive charge? 6. Which particle has a neutral charge? 7. Which particle has a negative charge? 8. An element’s atomic n ...
... 3. Another name for the two sub-atomic particles found in the nucleus is ____________. 4. What are the sub-atomic particles found outside of the nucleus? 5. Which particle has a positive charge? 6. Which particle has a neutral charge? 7. Which particle has a negative charge? 8. An element’s atomic n ...
Chapter 5
... elements in that group are alkali metals. The alkali metals all have one valence electron. That similarity is what makes them behave the same chemically. They are very reactive. Reactivity is highest on the outer edges of the table and elements get less reactive the closer they are to the center ...
... elements in that group are alkali metals. The alkali metals all have one valence electron. That similarity is what makes them behave the same chemically. They are very reactive. Reactivity is highest on the outer edges of the table and elements get less reactive the closer they are to the center ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... *1. MASS of an ELECTRON is 1,860 times LESS than a PROTON or NEUTRON *2. (e.g.) lithium [Li]: protons = 3+; electrons = 3-; neutrons = 4 = 7 u (or 7 amu) ...
... *1. MASS of an ELECTRON is 1,860 times LESS than a PROTON or NEUTRON *2. (e.g.) lithium [Li]: protons = 3+; electrons = 3-; neutrons = 4 = 7 u (or 7 amu) ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed
... biological molecules it generally has a valence of 5, forming three single covalent bonds and one double bond. Covalent bonds can form between atoms of the same element or atoms of different elements. o Although both types are molecules, the latter are also compounds. o Water (H2O) is a compound in ...
... biological molecules it generally has a valence of 5, forming three single covalent bonds and one double bond. Covalent bonds can form between atoms of the same element or atoms of different elements. o Although both types are molecules, the latter are also compounds. o Water (H2O) is a compound in ...
Atomic Theory
... 1. Electrons and protons have electrical charges that are identical in magnitude but opposite in sign. Relative charges of 1 and +1 are assigned to the electron and proton, respectively. 2. Neutrons have approximately the same mass as protons but no charge—they are electrically neutral. 3. The mass ...
... 1. Electrons and protons have electrical charges that are identical in magnitude but opposite in sign. Relative charges of 1 and +1 are assigned to the electron and proton, respectively. 2. Neutrons have approximately the same mass as protons but no charge—they are electrically neutral. 3. The mass ...