atomic number
... shell filled. You need to find another element that will take that electron away from you. When you lose that electron, you will you’ll have full shells. • Whenever an atom has full shells, we say it is "happy." Let's look at chlorine (Cl). Chlorine has seventeen electrons and only needs one more to ...
... shell filled. You need to find another element that will take that electron away from you. When you lose that electron, you will you’ll have full shells. • Whenever an atom has full shells, we say it is "happy." Let's look at chlorine (Cl). Chlorine has seventeen electrons and only needs one more to ...
Chemistry B2A Chapter 18 Oxidation
... In some reactions, it is not easy to see the electron loss and gain, so chemists developed another definition of oxidation and reduction: Oxidation is the gain of oxygen atoms and/or the loss of hydrogen atoms. Reduction is the loss of oxygen atoms and/or the gain of hydrogen atoms. CH4(g) + 2O2(g) ...
... In some reactions, it is not easy to see the electron loss and gain, so chemists developed another definition of oxidation and reduction: Oxidation is the gain of oxygen atoms and/or the loss of hydrogen atoms. Reduction is the loss of oxygen atoms and/or the gain of hydrogen atoms. CH4(g) + 2O2(g) ...
Summary of lesson
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
Education TI - Texas Instruments
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
only that they did. democritus, an early greek philosopher, even had
... Being asked what animal you'd like to be is a trick question; you're already an animal. Doug Coupland ...
... Being asked what animal you'd like to be is a trick question; you're already an animal. Doug Coupland ...
Physical Properties
... Mendeleev and Meyer • Published nearly identical schemes for classifying elements • Arranged elements by ______________________ • Mendeleev generally given more credit – Published first – More successful at demonstrating value of table – Predicted discovery of new elements, properties of new elemen ...
... Mendeleev and Meyer • Published nearly identical schemes for classifying elements • Arranged elements by ______________________ • Mendeleev generally given more credit – Published first – More successful at demonstrating value of table – Predicted discovery of new elements, properties of new elemen ...
File
... X and Z because they have the same atomic number but different masses. 15. Atoms W, X, Y, and Z have the following nuclear compositions. Which two are isotopes? How do you know? ...
... X and Z because they have the same atomic number but different masses. 15. Atoms W, X, Y, and Z have the following nuclear compositions. Which two are isotopes? How do you know? ...
Atomic Structure-PRACTICE TEST
... a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _D__ 56) The atomic mass of an element depends on the _______. a. Mass of each electron in that ...
... a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _D__ 56) The atomic mass of an element depends on the _______. a. Mass of each electron in that ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... usually have more significant periodic trends than do periods and blocks, which are explained below. Modern quantum mechanical theories of atomic structure explain group trends by proposing that elements in the same group generally have the same electron configurations in their valence (or outermost ...
... usually have more significant periodic trends than do periods and blocks, which are explained below. Modern quantum mechanical theories of atomic structure explain group trends by proposing that elements in the same group generally have the same electron configurations in their valence (or outermost ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
ISN III: Building Atoms and Organizing Matter
... many neutrons as protons; heavy elements apparently need more neutrons than protons in order to stick together. Atoms with a few too many neutrons, or not quite enough, can sometimes exist for a while, but they're unstable Question 3: I'm not sure what you mean by "unstable." Do atoms just fall apar ...
... many neutrons as protons; heavy elements apparently need more neutrons than protons in order to stick together. Atoms with a few too many neutrons, or not quite enough, can sometimes exist for a while, but they're unstable Question 3: I'm not sure what you mean by "unstable." Do atoms just fall apar ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
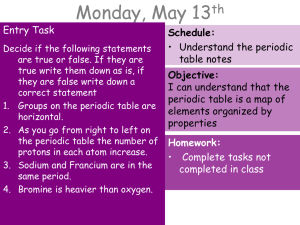
Entry Task
... 2. As you go from right to left on the periodic table the number of protons in each atom increase. 3. Sodium and Francium are in the same period. 4. Bromine is heavier than oxygen. ...
... 2. As you go from right to left on the periodic table the number of protons in each atom increase. 3. Sodium and Francium are in the same period. 4. Bromine is heavier than oxygen. ...
General Concepts
... If you are not given this symbol with the mass number, you can still determine the mass number for the most abundant isotopic form for that atom. For example, if you look on the periodic table for Carbon, you will see a value underneath its symbol - the RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS of 12.011. This mass is ...
... If you are not given this symbol with the mass number, you can still determine the mass number for the most abundant isotopic form for that atom. For example, if you look on the periodic table for Carbon, you will see a value underneath its symbol - the RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS of 12.011. This mass is ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT AP Chemistry is a
... 9. How many Energy levels do strontium and iodine have? ________ 10. Which element is located in Period 4, group 2? ________________ 11. Name an element that has similar properties to sodium. __________ 12. State a property of cobalt._______________________________________ 13. Cobalt has a total of ...
... 9. How many Energy levels do strontium and iodine have? ________ 10. Which element is located in Period 4, group 2? ________________ 11. Name an element that has similar properties to sodium. __________ 12. State a property of cobalt._______________________________________ 13. Cobalt has a total of ...
chem 1 TIFF new.indd
... For example, the smallest element is hydrogen. It has an atomic number of 1, which means it has only one proton. It also has only one electron, since the number of protons equals the number of electrons. Though atoms are very small, each one has a weight, called the atomic weight. For most atoms the ...
... For example, the smallest element is hydrogen. It has an atomic number of 1, which means it has only one proton. It also has only one electron, since the number of protons equals the number of electrons. Though atoms are very small, each one has a weight, called the atomic weight. For most atoms the ...
Year 9 Science revison _15-16_ end of year CHEM
... it has 1 electron in the outer shell. It loses that electron (in a chemical reaction) to have a full outer shell and become “stable” like the noble gases. You know that it loses 1 electron…..because it’s in group 1. ii) what is the charge on a rubidium ion ? ...
... it has 1 electron in the outer shell. It loses that electron (in a chemical reaction) to have a full outer shell and become “stable” like the noble gases. You know that it loses 1 electron…..because it’s in group 1. ii) what is the charge on a rubidium ion ? ...
Periodic Law
... The groups in the periodic table have "A" and "B" designations. The elements in the A groups, which appear in two parts—two at the beginning and six at the end of the table—are known as the main group elements. Those in the B groups, which are in between the two A group divisions, are called transit ...
... The groups in the periodic table have "A" and "B" designations. The elements in the A groups, which appear in two parts—two at the beginning and six at the end of the table—are known as the main group elements. Those in the B groups, which are in between the two A group divisions, are called transit ...
Electron Proton Neutron
... The first orbit (i.e., for n = 1) is represented by letter K. Similarly, for n = 2, it is L − shell, for n = 3, it is M − shell and for n = 4, it is N − shell. These orbits or shells are also called energy levels. ...
... The first orbit (i.e., for n = 1) is represented by letter K. Similarly, for n = 2, it is L − shell, for n = 3, it is M − shell and for n = 4, it is N − shell. These orbits or shells are also called energy levels. ...
15.2 Electrons and Chemical Bonds
... Example dot Carbon has four dots and hydrogen has one. One carbon atom bonds diagrams with four hydrogen atoms because this allows the carbon atom to have eight valence electrons (8 dots)—four of its own and four shared from the hydrogen atoms. The picture above shows dot diagrams for carbon dioxide ...
... Example dot Carbon has four dots and hydrogen has one. One carbon atom bonds diagrams with four hydrogen atoms because this allows the carbon atom to have eight valence electrons (8 dots)—four of its own and four shared from the hydrogen atoms. The picture above shows dot diagrams for carbon dioxide ...
Document
... don't consider processes that affect the nucleus to be chemical processes. The postulate is still useful. A slightly more restrictive wording is "Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or transformed into other atoms in a chemical change". ...
... don't consider processes that affect the nucleus to be chemical processes. The postulate is still useful. A slightly more restrictive wording is "Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or transformed into other atoms in a chemical change". ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that _D__ 56) The atomic mass of an element depends on the _______. a. Mass of each electron in that element b. Mass of ...
... a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that _D__ 56) The atomic mass of an element depends on the _______. a. Mass of each electron in that element b. Mass of ...