Radioactive Decay Mechanisms
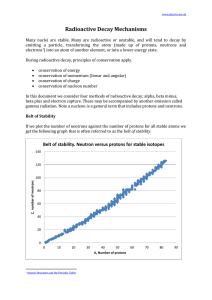
... Radioactive Decay Mechanisms Many nuclei are stable. Many are radioactive or unstable, and will tend to decay by emitting a particle, transforming the atom (made up of protons, neutrons and electrons1) into an atom of another element, or into a lower energy state. During radioactive decay, principle ...
... Radioactive Decay Mechanisms Many nuclei are stable. Many are radioactive or unstable, and will tend to decay by emitting a particle, transforming the atom (made up of protons, neutrons and electrons1) into an atom of another element, or into a lower energy state. During radioactive decay, principle ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
Structure of the Atom
... based partly on Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle the position and the momentum of a moving object cannot simultaneously be measured and known exactly there is an inherent limitation to knowing both where a particle is at a particular moment and how it is moving in order to predict where it wil ...
... based partly on Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle the position and the momentum of a moving object cannot simultaneously be measured and known exactly there is an inherent limitation to knowing both where a particle is at a particular moment and how it is moving in order to predict where it wil ...
Answer key
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
Using your periodic table ppt (9/26-10/11) File
... orbitals & number of valence e-, & to know that properties are similar for elements in a group • Describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations of protons, neutrons, and electrons • Identify that protons determine an elements identity and valence electrons d ...
... orbitals & number of valence e-, & to know that properties are similar for elements in a group • Describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations of protons, neutrons, and electrons • Identify that protons determine an elements identity and valence electrons d ...
File
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
Lesson Overview
... for example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. The weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes, in which the abundance of each isotope in nature is considered, is called its atomic mass. ...
... for example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. The weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes, in which the abundance of each isotope in nature is considered, is called its atomic mass. ...
Alpha Decay Alpha decay can most simply be described like this: 1
... 1. The nucleus of an atom splits into two parts. 2. One of these parts (the alpha particle) goes zooming off into space. 3. The nucleus left behind has its atomic number reduced by 2 and its mass number reduced by 4 (that is, by 2 protons and 2 neutrons). There are other points, but the three above ...
... 1. The nucleus of an atom splits into two parts. 2. One of these parts (the alpha particle) goes zooming off into space. 3. The nucleus left behind has its atomic number reduced by 2 and its mass number reduced by 4 (that is, by 2 protons and 2 neutrons). There are other points, but the three above ...
electron configurations of elements(ground state)
... sublevel paired with a half-full sublevel is more stable. Hence, an electron is taken from the 5s sublevel making it half-full and put with the 4d sublevel making it full. Thus, the electron configuration of silver is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d10 4p 6 5s1 4d10 . Copper(Cu) and gold(Au), the ot ...
... sublevel paired with a half-full sublevel is more stable. Hence, an electron is taken from the 5s sublevel making it half-full and put with the 4d sublevel making it full. Thus, the electron configuration of silver is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d10 4p 6 5s1 4d10 . Copper(Cu) and gold(Au), the ot ...
Isotopes File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... atoms (iodine-127) that are normally absorbed by the body from foods. Put another way, iodine supplied by nutrients becomes concentrated in the thyroid gland and its cells. Normally, this is a good thing since thyroid cells need iodine to manufacture chemicals that are vital to the body. ...
... atoms (iodine-127) that are normally absorbed by the body from foods. Put another way, iodine supplied by nutrients becomes concentrated in the thyroid gland and its cells. Normally, this is a good thing since thyroid cells need iodine to manufacture chemicals that are vital to the body. ...
Atoms - Peoria Public Schools
... • Dalton’s atomic theory has five points: – All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. – Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. – Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or dest ...
... • Dalton’s atomic theory has five points: – All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. – Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. – Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or dest ...
Test 4 Review
... Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass, and the chemical properties. He arranged the cards in order of increasing atomic mass and noticed a pattern: MENDELEEV'S PERIODIC LAW – When the elements are ...
... Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass, and the chemical properties. He arranged the cards in order of increasing atomic mass and noticed a pattern: MENDELEEV'S PERIODIC LAW – When the elements are ...
Definition - kcpe-kcse
... - lined up the cards in order of increasing mass, found a pattern - elements with similar properties were in the same column ...
... - lined up the cards in order of increasing mass, found a pattern - elements with similar properties were in the same column ...
Unit 3 Notes only
... 2) You should have 6 total electrons for Carbon. 3) Only two electrons can fit in the 1st shell. 4) The 2nd shell can hold up to 8 electrons. 5) The 3rd shell can hold 18, but the elements in the first few periods only use 8 electrons. ...
... 2) You should have 6 total electrons for Carbon. 3) Only two electrons can fit in the 1st shell. 4) The 2nd shell can hold up to 8 electrons. 5) The 3rd shell can hold 18, but the elements in the first few periods only use 8 electrons. ...
Quantum Mechanics and Split Peas - EC Chemistry Lab 2015-16
... drop from a higher distance. Record the distance you dropped from. 5. Use the rules below to count how many peas are in each area of the target. Record your data on the accompanying data sheet. 6. After completing the counting of the first run, collect the peas and repeat steps 1 – 5 from a differen ...
... drop from a higher distance. Record the distance you dropped from. 5. Use the rules below to count how many peas are in each area of the target. Record your data on the accompanying data sheet. 6. After completing the counting of the first run, collect the peas and repeat steps 1 – 5 from a differen ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... Owing to their relatively low ionization energies, metals tend to form cations, and when they combine with nonmetals they form ionic substances. For example, when metals combine with oxygen they form ionic oxides. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3(s) Metal oxides tend to dissolve in water to form hydroxide i ...
... Owing to their relatively low ionization energies, metals tend to form cations, and when they combine with nonmetals they form ionic substances. For example, when metals combine with oxygen they form ionic oxides. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3(s) Metal oxides tend to dissolve in water to form hydroxide i ...
CHEMISTRY OLYMPICS 2nd 6 weeks What particles form the
... • A) that electrons orbit the nucleus • B) that atoms are made of positively and negatively charged particles • C) that most of an atom’s mass is concentrated in a relatively small portion of the atom’s entire volume • D) that all neutrons are located in the nucleus ...
... • A) that electrons orbit the nucleus • B) that atoms are made of positively and negatively charged particles • C) that most of an atom’s mass is concentrated in a relatively small portion of the atom’s entire volume • D) that all neutrons are located in the nucleus ...
PPT_Topic2
... number of an element and explain what they mean, and state that electrons are found in shells. We will do this by Analysing nuclide notation and drawing diagrams to show electron structure. We will have succeeded if We can draw a diagram and explain important atom numbers to another pupil. ...
... number of an element and explain what they mean, and state that electrons are found in shells. We will do this by Analysing nuclide notation and drawing diagrams to show electron structure. We will have succeeded if We can draw a diagram and explain important atom numbers to another pupil. ...
Ordering the elements in the Periodic Table
... very good straight line while that relating frequency to relative atomic mass is not so good. The relationship is actually quite complicated. In fact Moseley plotted the square root of the Xray frequency against atomic number, but do not let this detail obscure how important this result was. Notice ...
... very good straight line while that relating frequency to relative atomic mass is not so good. The relationship is actually quite complicated. In fact Moseley plotted the square root of the Xray frequency against atomic number, but do not let this detail obscure how important this result was. Notice ...
In 1869, Russia`s Dmitri Mendeleev and Germany`s Lothar Meyer
... Although their observations were identical, Mendeleev is given the credit because he predicted the existence of undiscovered elements and left spaces for them. Mendeleev ...
... Although their observations were identical, Mendeleev is given the credit because he predicted the existence of undiscovered elements and left spaces for them. Mendeleev ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... So why is Mendeleev called the “father of the modern periodic table” and not Meyer, or both? ...
... So why is Mendeleev called the “father of the modern periodic table” and not Meyer, or both? ...
Atomic Theory - Valhalla High School
... which causes electrons to fall back to a lower energy level or the Ground State ...
... which causes electrons to fall back to a lower energy level or the Ground State ...
Atoms - TeacherWeb
... nucleus are called valence electrons. These electrons form chemical bonds with other atoms and give elements their chemical properties. Atoms combine with other atoms to complete their outermost or last energy level, called the valence shell. ...
... nucleus are called valence electrons. These electrons form chemical bonds with other atoms and give elements their chemical properties. Atoms combine with other atoms to complete their outermost or last energy level, called the valence shell. ...