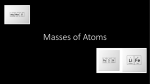* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Isotopes File - Northwest ISD Moodle
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Einsteinium wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Isotope analysis wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
An atom has 13 protons, 13 neutrons, and 13 electrons. Another atom has 13 protons, 14 neutrons, and 13 electrons . Analyze and explain how these two atoms are related. Explain what happens to an atom when protons are added or removed from its nucleus. C. Johannesson Isotopes • Dalton’s Atomic theory was changed. • Atoms of the same element can be different, called isotopes. Student Exploration How can isotopes of a given element be identified? What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic number? C. Johannesson Let’s Discuss How are the atoms of the isotopes of a given element similar? How are the atoms of the isotopes of a given element different? How are the atoms of the three isotopes of hydrogen similar? How are the atoms of the three isotopes of hydrogen different? By what reasoning would you conclude that the masses of different isotopes of the same element would differ? Applying Parts of the Atom When it comes to fighting cancer, doctors face two questions. Where has the cancer spread? And how can it be treated? In the case of one type of cancer, the answer to both questions may involve the isotope iodine-131. Iodine-131 is an artificial isotope of iodine. This isotope releases radiation that can kill cancer cells, especially those that originated in the thyroid gland. Why does iodine-131 target these particular cells? One job of the thyroid gland is to produce a substance that helps the body regulate some of its activities. Molecules of this substance contain natural iodine atoms (iodine-127) that are normally absorbed by the body from foods. Put another way, iodine supplied by nutrients becomes concentrated in the thyroid gland and its cells. Normally, this is a good thing since thyroid cells need iodine to manufacture chemicals that are vital to the body. Isotope An isotope is an atom with the same number of protons and electrons, but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes with more neutrons would have a greater mass. Isotopes Atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. Nuclear symbol: Mass # Atomic # 12 6 Hyphen notation: carbon-12 C Isotopes Chlorine-37 • atomic #: 17 • mass #: 37 • # of protons: 17 • # of electrons: 17 • # of neutrons: 20 37 17 Cl Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope Protons Electrons Neutrons Hydrogen–1 (protium) 1 1 0 Hydrogen-2 (deuterium) 1 1 1 Hydrogen-3 (tritium) 1 1 2 Nucleus Symbols if an element has an atomic number of 34 and a mass number of 78 what is the –number of protons –number of neutrons –number of electrons –Complete symbol Symbols if an element has 91 protons and 140 neutrons what is the –Atomic number –Mass number –number of electrons –Complete symbol Symbols if an element has 78 electrons and 117 neutrons what is the –Atomic number –Mass number –number of protons –Complete symbol Average Atomic Mass carbon-12 standard for average atomic mass (perfect 12 amu) Based on abundance of each element in nature. Mass found on the periodic table. Average Atomic Mass weighted average of all isotopes round to 2 decimal places Avg. Atomic Mass (mass)(% ) (mass)(% ) Average Atomic Mass EX: Calculate the avg. atomic mass of oxygen if its abundance in nature is 99.76% 16O, 0.04% 17O, and 0.20% 18O. Avg. (16)(.9976 ) (17)(.0004 ) (18)(0.002 0) 16.00 Atomic amu Mass Average Atomic Mass EX: Find chlorine’s average atomic mass if approximately 8 of every 10 atoms are chlorine-35 and 2 are chlorine-37. Avg. Atomic Mass (35)(.8) (37)(.2) 35.40 amu Sample Problem - Average Atomic Mass Naturally occurring lead is found to have natural percentage abundances of: 1.48% 204Pb, 23.6% 206Pb, 22.6% 207Pb, 52.3% 208Pb. Calculate the average atomic mass of lead. Lab Activity How can the average atomic mass for an element be determined given the masses of its isotopes and their relative abundance? Ions an atom with a charge, which means protons are not equal to the electrons. positive ions are called cations In a positive ion, the protons are greater than the electrons. negative ions are called anions. In a negative ion, the electrons are greater than the protons. Ions To determine the charge, subtract the electrons from the protons. Equation: Charge = protons – electrons The charge is shown as a superscript to the right of the symbol. Ions Ex: Magnesium has 12 protons and 12 electrons in the neutral state. (How do we know this? Answer this question.) If Magnesium has 12 protons, but only 10 electrons (which is usually the case when Mg forms an ion), is Mg more negative or more positive? Answer: More positive because Mg now has 2 more positive protons than negative electrons and makes the atom positively charged. Ion is written as.... Mg 2+ IONS Protons Neutrons Electrons Atomic # Mass # Name