Neural correlates of attention in primate visual cortex
... ventral pathway [which passes through areas V2 and V4 into inferior temporal visual cortex] and the dorsal pathway [which passes through the middletemporal area (MT) and the medial superior temporal area (MST) into the parietal cortex]. In the ventral pathway, attentional effects could be demonstrat ...
... ventral pathway [which passes through areas V2 and V4 into inferior temporal visual cortex] and the dorsal pathway [which passes through the middletemporal area (MT) and the medial superior temporal area (MST) into the parietal cortex]. In the ventral pathway, attentional effects could be demonstrat ...
Is neocortex essentially multisensory?
... the cat has a direct influence not only the integrative properties of superior collicular neurons [36], but can also influence orienting behavior. Cats typically show multisensory enhancement of orienting to congruent visual– auditory spatial targets when stimuli are near threshold. When the anterio ...
... the cat has a direct influence not only the integrative properties of superior collicular neurons [36], but can also influence orienting behavior. Cats typically show multisensory enhancement of orienting to congruent visual– auditory spatial targets when stimuli are near threshold. When the anterio ...
Morphological and Functional Types of Neurons
... recordings began, a bilateral pneumothorax was performed in order to minimize movements associated with respiration. Before an animal was placed into the stereotaxic frame, silastic cuffs containing bipolar silver wire electrodes were placed bilaterally on the intact median and sciatic nerves. The n ...
... recordings began, a bilateral pneumothorax was performed in order to minimize movements associated with respiration. Before an animal was placed into the stereotaxic frame, silastic cuffs containing bipolar silver wire electrodes were placed bilaterally on the intact median and sciatic nerves. The n ...
Temporal Plasticity Involved in Recovery from Manual Dexterity
... ments (Murata et al., 2008). We used rhesus macaques because, among nonhuman primate species, they are more comparable with humans with respect to the anatomical structures of the motor cortex and corticospinal tract than are other monkeys used in experimental research (e.g., squirrel monkeys and ma ...
... ments (Murata et al., 2008). We used rhesus macaques because, among nonhuman primate species, they are more comparable with humans with respect to the anatomical structures of the motor cortex and corticospinal tract than are other monkeys used in experimental research (e.g., squirrel monkeys and ma ...
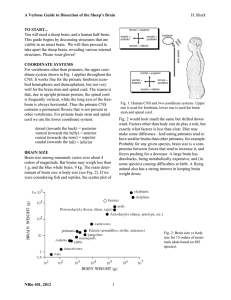
The Basal Ganglia
... • If the offset of an auditory stimulus predicts reward, none of the dopamine neurons that respond to other incentive stimuli respond to tone offset, though behavioural activation occurs. • Neuron responses are quite similar in A8, A9 and A10. Exceptions: the medial SNc and the VTA respond more freq ...
... • If the offset of an auditory stimulus predicts reward, none of the dopamine neurons that respond to other incentive stimuli respond to tone offset, though behavioural activation occurs. • Neuron responses are quite similar in A8, A9 and A10. Exceptions: the medial SNc and the VTA respond more freq ...
Central Lateral Line and Auditory Pathways: A Phylogenetic
... pressure transducers) coupled to the labyrinth (van Bergeijk, 1967). Inner ear auditory receptors were thought to be the last peripheral octavolateralis component to evolve, occurring during the rhipidistianamphibian transition with the appearance of a middle ear transmission apparatus and new recep ...
... pressure transducers) coupled to the labyrinth (van Bergeijk, 1967). Inner ear auditory receptors were thought to be the last peripheral octavolateralis component to evolve, occurring during the rhipidistianamphibian transition with the appearance of a middle ear transmission apparatus and new recep ...
HYPOTHALAMUS
... The mammillary part of the hypothalamus consists of the posterior hypothalamic nucleus and the prominent mammillary nuclei. The posterior nucleus is a large, ill-defined group of cells that may play a role in thermoregulation (see below). The mammillary nuclei are considered to be part of the hypoth ...
... The mammillary part of the hypothalamus consists of the posterior hypothalamic nucleus and the prominent mammillary nuclei. The posterior nucleus is a large, ill-defined group of cells that may play a role in thermoregulation (see below). The mammillary nuclei are considered to be part of the hypoth ...
Early Appearance of Inhibitory Input to the MNTB Supports Binaural
... immaturities that limit auditory processing in juvenile animals, they are able to lateralize sounds using binaural cues. This study explores a central mechanism that may compensate for these limitations during development. Interaural time and level difference processing by neurons in the superior ol ...
... immaturities that limit auditory processing in juvenile animals, they are able to lateralize sounds using binaural cues. This study explores a central mechanism that may compensate for these limitations during development. Interaural time and level difference processing by neurons in the superior ol ...
A non-invasive method to relate the timing of neural activity to white
... The neurophysiological basis of variability in the latency of evoked neural responses has been of interest for decades. We describe a method to identify white matter pathways that may contribute to inter-individual variability in the timing of neural activity. We investigated the relation of the lat ...
... The neurophysiological basis of variability in the latency of evoked neural responses has been of interest for decades. We describe a method to identify white matter pathways that may contribute to inter-individual variability in the timing of neural activity. We investigated the relation of the lat ...
A Verbose Guide to Dissection of the Sheep`s Brain H
... target of axons from olfactory bulb, which you can see travelling as a wide white bundle, the olfactory tract (see Figs. 5, 6, and 12A). The caudal part of piriform cortex, on the other hand, is non-olfactory, being connected to the hippocampus. (The hippocampus, another region of allocortex, is not ...
... target of axons from olfactory bulb, which you can see travelling as a wide white bundle, the olfactory tract (see Figs. 5, 6, and 12A). The caudal part of piriform cortex, on the other hand, is non-olfactory, being connected to the hippocampus. (The hippocampus, another region of allocortex, is not ...
Aberrant Localization of Synchronous Hemodynamic
... “resting state” has been demonstrated for healthy individuals in functionally similar cortical regions, such as primary motor, visual, language, or auditory cortex (Biswal et al 1995, 1997; Cordes et al 2001; Lowe et al 1998; Xiong et al 1999). Functional connectivity of, for example, the primary mo ...
... “resting state” has been demonstrated for healthy individuals in functionally similar cortical regions, such as primary motor, visual, language, or auditory cortex (Biswal et al 1995, 1997; Cordes et al 2001; Lowe et al 1998; Xiong et al 1999). Functional connectivity of, for example, the primary mo ...
The multisensory roles for auditory cortex in primate vocal
... great apes (including humans) (Hackett et al., 2001). These fields are delineated largely by their tonotopic organization and anatomical criteria. The reasons for why there are so many areas are not known, and how each of them, together or separately, relate to behavior is also somewhat of a mystery. ...
... great apes (including humans) (Hackett et al., 2001). These fields are delineated largely by their tonotopic organization and anatomical criteria. The reasons for why there are so many areas are not known, and how each of them, together or separately, relate to behavior is also somewhat of a mystery. ...
Harris KD. Neural signatures of cell assembly organization. Nat Rev
... Box 2 | Conditional independence and the virtual population In probability theory, the concept of independence has more than one definition. Two events, A and B, are said to be marginally independent if the probability for them both to occur is the product of their individual probabilities (P): P(A ...
... Box 2 | Conditional independence and the virtual population In probability theory, the concept of independence has more than one definition. Two events, A and B, are said to be marginally independent if the probability for them both to occur is the product of their individual probabilities (P): P(A ...
Flow of information for emotions through temporal and orbitofrontal pathways REVIEW
... eulaminate 1). The caudally adjacent areas, including areas 13, OPro and orbital area 25, are dysgranular in type, characterized by the presence of a thin and incipient granular layer 4 (Fig. 1B). The most caudally located orbitofrontal cortex lacks a granular layer 4, and is thus agranular in type ...
... eulaminate 1). The caudally adjacent areas, including areas 13, OPro and orbital area 25, are dysgranular in type, characterized by the presence of a thin and incipient granular layer 4 (Fig. 1B). The most caudally located orbitofrontal cortex lacks a granular layer 4, and is thus agranular in type ...
Transgenic Mice Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein under the
... melanocortin signaling. The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (Arc) has been established as a site of leptin action in the CNS. The Arc contains two counterpoised neuronal populations producing distinct melanocortins, i.e., ␣-MSH and AgRP (Broberger et al., 1998a; Elias et al., 1998). ␣-MSH and Ag ...
... melanocortin signaling. The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (Arc) has been established as a site of leptin action in the CNS. The Arc contains two counterpoised neuronal populations producing distinct melanocortins, i.e., ␣-MSH and AgRP (Broberger et al., 1998a; Elias et al., 1998). ␣-MSH and Ag ...
An Action Selection Calculus
... This paper also identifies where the factor theory mechanisms clearly differ and where they apparently differ, but can be explained as manifestations of a single type of mechanism and how these differences may be resolved into a single structured framework. It sheds light on why it has traditionally ...
... This paper also identifies where the factor theory mechanisms clearly differ and where they apparently differ, but can be explained as manifestations of a single type of mechanism and how these differences may be resolved into a single structured framework. It sheds light on why it has traditionally ...
CHAPTER 12: THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE 12.1
... Possible pathway for information transferred by conduction of an action potential from one region of brain to another (Figure 12.8): 1. Action potential originates in gray matter 2. Action potential is sent to another area of gray matter by projection fibers 3. Second (new) action potential is gener ...
... Possible pathway for information transferred by conduction of an action potential from one region of brain to another (Figure 12.8): 1. Action potential originates in gray matter 2. Action potential is sent to another area of gray matter by projection fibers 3. Second (new) action potential is gener ...
The Relationship Between Synchronization Among Neuronal
... random noisy input was provided to all units in one of the two areas (area 1). In some simulations, the mean interarea delay was increased to 8 ms to mimic a greater separation between the areas. In other simulations, excitatory NMDA synaptic channels were incorporated. These NMDA channels were used ...
... random noisy input was provided to all units in one of the two areas (area 1). In some simulations, the mean interarea delay was increased to 8 ms to mimic a greater separation between the areas. In other simulations, excitatory NMDA synaptic channels were incorporated. These NMDA channels were used ...
Encoding of Rules by Neurons in the Human Dorsolateral Prefrontal
... was applied to filter out the majority of the low-voltage background activity. Classification of action potentials was performed using template matching and principal component analysis. Putative neurons were required to separate clearly from any channel noise, to demonstrate waveform morphology consi ...
... was applied to filter out the majority of the low-voltage background activity. Classification of action potentials was performed using template matching and principal component analysis. Putative neurons were required to separate clearly from any channel noise, to demonstrate waveform morphology consi ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes in the ‘traditional’ reward circuit of the brain, psychostimulant drugs also produce alterations in other areas associate ...
... 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes in the ‘traditional’ reward circuit of the brain, psychostimulant drugs also produce alterations in other areas associate ...
Functional differences between dorsal and ventral hippocampus
... in the dorsal region in basal condition. The parcellation of hippocampus into dorsal and ventral zones has been considered by other authors, which found morphological and functional differences that could explain the reported results (Moser et al., 1993; Jung et al., 1994). Thus, from a behavioral p ...
... in the dorsal region in basal condition. The parcellation of hippocampus into dorsal and ventral zones has been considered by other authors, which found morphological and functional differences that could explain the reported results (Moser et al., 1993; Jung et al., 1994). Thus, from a behavioral p ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes in the ‘traditional’ reward circuit of the brain, psychostimulant drugs also produce alterations in other areas associate ...
... 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes in the ‘traditional’ reward circuit of the brain, psychostimulant drugs also produce alterations in other areas associate ...
Parallel contributions of distinct human memory systems during
... is plausible that there may be interactions between the hippocampus, midbrain DA areas, and more dorsal regions of the striatum, via a ventromedial to dorsolateral movement of information through these spiral loops. To expand upon these interactions, it has been proposed that dopamine's role in rewa ...
... is plausible that there may be interactions between the hippocampus, midbrain DA areas, and more dorsal regions of the striatum, via a ventromedial to dorsolateral movement of information through these spiral loops. To expand upon these interactions, it has been proposed that dopamine's role in rewa ...
Bridging Cytoarchitectonics and Connectomics in Human Cerebral
... Materials and Methods Von Economo and Koskinas cytoarchitectonic metrics Cytoarchitectonic mappings of the human cortex were taken from the 1925 Von Economo and Koskinas work Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des erwachsenen Menschen (Von Economo and Koskinas, 1925) [translated Cytoarchitectonics ...
... Materials and Methods Von Economo and Koskinas cytoarchitectonic metrics Cytoarchitectonic mappings of the human cortex were taken from the 1925 Von Economo and Koskinas work Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des erwachsenen Menschen (Von Economo and Koskinas, 1925) [translated Cytoarchitectonics ...
The Influence of Classical Conditioning Procedures on Subsequent
... not yet become strong enough to result in contingency awareness. In effect, attention to the CS in a novel context would be a form of hypothesis testing, a testing of an association that is not yet strong enough to have created contingency awareness. The hypothesis that associative learning in the a ...
... not yet become strong enough to result in contingency awareness. In effect, attention to the CS in a novel context would be a form of hypothesis testing, a testing of an association that is not yet strong enough to have created contingency awareness. The hypothesis that associative learning in the a ...