Universal Learning
... Frontal lobes of the cortex Responsible for planning and performing temporal activities. People with damaged frontal lobes have trouble performing the sequence of an activity even though they have no problem with the individual steps of the activity Frontal lobes are responsible for temporal r ...
... Frontal lobes of the cortex Responsible for planning and performing temporal activities. People with damaged frontal lobes have trouble performing the sequence of an activity even though they have no problem with the individual steps of the activity Frontal lobes are responsible for temporal r ...
NEURO PresentationWORKING students B
... Predictive and Timing Function of the Cerebellum • motion is a series of discrete sequential movement • the planning and timing of sequential movements is the function of the lateral cerebellar hemisphere • this area communicates with premotor and sensory cortex and corresponding area of the basal ...
... Predictive and Timing Function of the Cerebellum • motion is a series of discrete sequential movement • the planning and timing of sequential movements is the function of the lateral cerebellar hemisphere • this area communicates with premotor and sensory cortex and corresponding area of the basal ...
Reflex Facilitation During Eyeblink Conditioning and Subsequent
... recover after surgery before the commencement of the experimental procedures. On the first day, adaptation to the experimental situation was done by placing the animals in a Plexiglas restraining box in a soundproof conditioning chamber. The rabbits were divided in two groups: the unpaired (UP) grou ...
... recover after surgery before the commencement of the experimental procedures. On the first day, adaptation to the experimental situation was done by placing the animals in a Plexiglas restraining box in a soundproof conditioning chamber. The rabbits were divided in two groups: the unpaired (UP) grou ...
2004 - 21st Century Science Initiative, Palisades, New York
... • A persistent firing pattern in the rat hippocampus, known as theta-rhythm • Increased release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and other growth factors • Changes in gene regulation • Increased cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus ...
... • A persistent firing pattern in the rat hippocampus, known as theta-rhythm • Increased release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and other growth factors • Changes in gene regulation • Increased cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus ...
NEUROSCIENCE Review Questions CHOOSE THE LETTER THAT
... C. there is complete but temporary paralysis. D. there is a complete, but temporary, loss of reflexes below the damage. E. spinal reflexes become hyperactive. 14. Concerning primary motor cortex, area 4: A. lesions in area 4 result in apraxia. B. it has a map of the ipsilateral body with small disc ...
... C. there is complete but temporary paralysis. D. there is a complete, but temporary, loss of reflexes below the damage. E. spinal reflexes become hyperactive. 14. Concerning primary motor cortex, area 4: A. lesions in area 4 result in apraxia. B. it has a map of the ipsilateral body with small disc ...
LectureTest22011, the new questions
... D. In the gustatory (taste) pathways, the cell bodies of the third neurons are in the thalamus. (Hint: you can deduce this from the general rules that we gave.) E. In the visual pathway, the axons of the ganglion neurons are in the optic nerve and optic chiasma. C. 28. What is an example of somatoto ...
... D. In the gustatory (taste) pathways, the cell bodies of the third neurons are in the thalamus. (Hint: you can deduce this from the general rules that we gave.) E. In the visual pathway, the axons of the ganglion neurons are in the optic nerve and optic chiasma. C. 28. What is an example of somatoto ...
doc Chapter 6 Notes
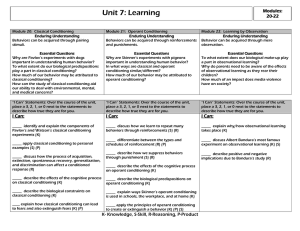
... • interval schedule: a schedule in which reinforcement is available after a specific unit of time • paid by the hour • Fixed and Variable Schedules • partial reinforcement can also be given a fixed or variable schedule • fixed schedule: a schedule in which reinforcement is consistently provided upon ...
... • interval schedule: a schedule in which reinforcement is available after a specific unit of time • paid by the hour • Fixed and Variable Schedules • partial reinforcement can also be given a fixed or variable schedule • fixed schedule: a schedule in which reinforcement is consistently provided upon ...
The Auditory Brain and Perceiving Auditory Scenes
... acoustic organization ◦ Belt area: A region of cortex, directly adjacent to A1, with inputs from A1, where neurons respond to more complex characteristics of sounds ◦ Parabelt area: A region of cortex, lateral and adjacent to the belt area, where neurons respond to more complex characteristics of so ...
... acoustic organization ◦ Belt area: A region of cortex, directly adjacent to A1, with inputs from A1, where neurons respond to more complex characteristics of sounds ◦ Parabelt area: A region of cortex, lateral and adjacent to the belt area, where neurons respond to more complex characteristics of so ...
Modules 20-22
... organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.11-12.5 Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. CC ...
... organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.11-12.5 Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. CC ...
Association Cortex, Consciousness, and other topics that Embarrass
... • The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite fashionable: • The phrenologist said that a given area of the brain increases in size, as does the overlying skull, when its function is exercised, and a good clinician ...
... • The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite fashionable: • The phrenologist said that a given area of the brain increases in size, as does the overlying skull, when its function is exercised, and a good clinician ...
Cerebellar control of visceral responses–possible mechanisms
... However, a closer look into the cerebellar neuronal connections may explain why this was not the case. During more widespread cortical stimulation some of the white matter is likely to be excited as well, due to extensive folding of the cerebellum. Therefore climbing and mossy fibers, which both sen ...
... However, a closer look into the cerebellar neuronal connections may explain why this was not the case. During more widespread cortical stimulation some of the white matter is likely to be excited as well, due to extensive folding of the cerebellum. Therefore climbing and mossy fibers, which both sen ...
Click here to get the file
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
Interactions between Motivation, Emotion and Attention: From
... complex motivations need not be present initially. Stimulus selection can be carried out by assigning an emotional value to each stimulus depending on how well it satisfies each motivation. The development of this ability in children has only recently come into focus (Hajcak and Dennis, 2009), but i ...
... complex motivations need not be present initially. Stimulus selection can be carried out by assigning an emotional value to each stimulus depending on how well it satisfies each motivation. The development of this ability in children has only recently come into focus (Hajcak and Dennis, 2009), but i ...
Interactions between Motivation, Emotion and Attention: From
... complex motivations need not be present initially. Stimulus selection can be carried out by assigning an emotional value to each stimulus depending on how well it satisfies each motivation. The development of this ability in children has only recently come into focus (Hajcak and Dennis, 2009), but i ...
... complex motivations need not be present initially. Stimulus selection can be carried out by assigning an emotional value to each stimulus depending on how well it satisfies each motivation. The development of this ability in children has only recently come into focus (Hajcak and Dennis, 2009), but i ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repo ...
... becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repo ...
Classical vs Operant Conditioning The Differences Between
... Even if you are not a psychology student, you have probably at least heard about Pavlov's dogs. In his famous experiment, Ivan Pavlov5 noticed dogs began to salivate in response to a tone after the sound had been repeatedly paired with the presentation of food. Pavlov quickly realized that this was ...
... Even if you are not a psychology student, you have probably at least heard about Pavlov's dogs. In his famous experiment, Ivan Pavlov5 noticed dogs began to salivate in response to a tone after the sound had been repeatedly paired with the presentation of food. Pavlov quickly realized that this was ...
Chapter 8
... When the axon has many branches and controls many muscle fibers, gross motor movement is possible. ...
... When the axon has many branches and controls many muscle fibers, gross motor movement is possible. ...
The Output Signal of Purkinje Cells of the Cerebellum and Circadian
... However, in acute sagittal cerebellar slices the average spike rate of randomly selected Purkinje cells did not exhibit significant circadian variations, irrespective of their specific firing pattern. Also, frequency and amplitude of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents and the amplitude of ...
... However, in acute sagittal cerebellar slices the average spike rate of randomly selected Purkinje cells did not exhibit significant circadian variations, irrespective of their specific firing pattern. Also, frequency and amplitude of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents and the amplitude of ...
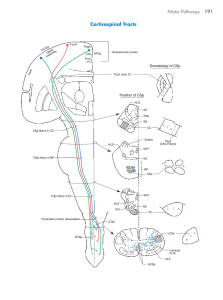
Lecture 3 Figure 1
... although projections to cervical levels clearly predominate. Cells in dorsomedial regions of the red nucleus receive input from upper extremity areas of the motor cortex and project to cervical cord, but those in ventrolateral areas of the nucleus receive some fibers from lower extremity areas of the ...
... although projections to cervical levels clearly predominate. Cells in dorsomedial regions of the red nucleus receive input from upper extremity areas of the motor cortex and project to cervical cord, but those in ventrolateral areas of the nucleus receive some fibers from lower extremity areas of the ...
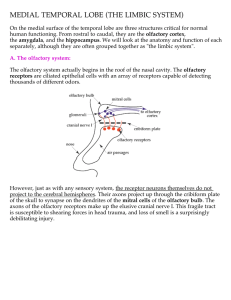
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... sensory stimulus (man in ski mask in alley = danger) to an adaptive response (fight or flight). On the basis of this information, you should be able to guess the primary inputs to and outputs from the amygdala. Inputs: the amygdala must get sensory input, and it must be fairly highly processed input ...
... sensory stimulus (man in ski mask in alley = danger) to an adaptive response (fight or flight). On the basis of this information, you should be able to guess the primary inputs to and outputs from the amygdala. Inputs: the amygdala must get sensory input, and it must be fairly highly processed input ...
Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3
... 2. Layers II and III are the recipients of most callosal (contralateral hemisphere) and association (corticocortical) inputs. 3. Layer IV receives most sensory afferents from __________. 4. Besides the sensory, association, and callosal afferents providing inputs to neocortex, there are several non- ...
... 2. Layers II and III are the recipients of most callosal (contralateral hemisphere) and association (corticocortical) inputs. 3. Layer IV receives most sensory afferents from __________. 4. Besides the sensory, association, and callosal afferents providing inputs to neocortex, there are several non- ...
5. Discussion - UvA-DARE - University of Amsterdam
... The last chapter revolved around the question of how a change in brain state, i.e. the difference between wakefulness and being under anesthesia, alters activity patterns of neurons in the primary visual cortex that emerge spontaneously and in response to visual stimuli. Using two-photon calcium ima ...
... The last chapter revolved around the question of how a change in brain state, i.e. the difference between wakefulness and being under anesthesia, alters activity patterns of neurons in the primary visual cortex that emerge spontaneously and in response to visual stimuli. Using two-photon calcium ima ...
Brain 1
... The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the synapse occur that result in increased firing to the same stimulus. These changes in the ...
... The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the synapse occur that result in increased firing to the same stimulus. These changes in the ...
Learning program
... Acquisition: the organism learns to associate the two events, for this to occur there are some important– factors to consider Extinction the gradual decrease in the strength or frequency of a response that has been conditioned when the UCS is no longer presented Association Association of two stimu ...
... Acquisition: the organism learns to associate the two events, for this to occur there are some important– factors to consider Extinction the gradual decrease in the strength or frequency of a response that has been conditioned when the UCS is no longer presented Association Association of two stimu ...