Eye Movement Control by the Cerebral Cortex Charles Pierrot
... • Function: involved in motor programmes comprising of saccade with a body movement or successive saccades. ...
... • Function: involved in motor programmes comprising of saccade with a body movement or successive saccades. ...
Cre-Mediated Recombination in Rhombic Lip Derivatives
... CRE or FLP, under the control of cell type-specific promoters have been useful for studies of cell lineage (Lewandoski, 2001). When they are crossed to a mouse line that carries a recombination-dependent reporter gene, they mediate activation of the reporter gene in a celltype-specific manner. Once ...
... CRE or FLP, under the control of cell type-specific promoters have been useful for studies of cell lineage (Lewandoski, 2001). When they are crossed to a mouse line that carries a recombination-dependent reporter gene, they mediate activation of the reporter gene in a celltype-specific manner. Once ...
Auditory Cortex (1)
... the cerebral cortex of the cat. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 71: 315-344, 1942. 2. Evans EF, Ross HF and Whitfield IC. The spatial distribution of unit characteristic frequency in the primary auditory cortex of the cat. J Physiol 179: 238-247., 1965. 3. Goldstein MH, Abeles M, Daly RL and ...
... the cerebral cortex of the cat. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 71: 315-344, 1942. 2. Evans EF, Ross HF and Whitfield IC. The spatial distribution of unit characteristic frequency in the primary auditory cortex of the cat. J Physiol 179: 238-247., 1965. 3. Goldstein MH, Abeles M, Daly RL and ...
Cerebral Cortex
... The dorsal stream (parietal) begins with V1, goes through visual area V2, then to visual area V3, visual area MT (also known as V5) and to the inferior parietal lobule. The dorsal stream, sometimes called the “Where Pathway” is associated with representation of object location, and direction of moti ...
... The dorsal stream (parietal) begins with V1, goes through visual area V2, then to visual area V3, visual area MT (also known as V5) and to the inferior parietal lobule. The dorsal stream, sometimes called the “Where Pathway” is associated with representation of object location, and direction of moti ...
Pavlovian Conditioning
... Tone (CS)-elicits-Salivation (CR) Pavlov believed that conditioned responses were identical to unconditioned responses. That is usually not the case. For example, conditioned responses may be less pronounced (weaker) or a bit more lethargic than unconditioned responses. Several phenomena turn up in ...
... Tone (CS)-elicits-Salivation (CR) Pavlov believed that conditioned responses were identical to unconditioned responses. That is usually not the case. For example, conditioned responses may be less pronounced (weaker) or a bit more lethargic than unconditioned responses. Several phenomena turn up in ...
Lecture Test 2 2010
... E. The pyramidal tract descends through the midbrain and pons and beyond. B 32. Where does the cerebellum’s cortex send most of its output information on how to make our movements smooth and coordinated? A. cerebellar axons project all the way to the muscle fibers in our skeletal muscles B. to the p ...
... E. The pyramidal tract descends through the midbrain and pons and beyond. B 32. Where does the cerebellum’s cortex send most of its output information on how to make our movements smooth and coordinated? A. cerebellar axons project all the way to the muscle fibers in our skeletal muscles B. to the p ...
Conference Outline 1
... 5. Subdivisions of the cerebral hemispheres: the lobes The cerebral hemispheres can be divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). Some scientists though have added a fifth lobe that is the grouping of several medial structures that are involved in memory and emotions. This ...
... 5. Subdivisions of the cerebral hemispheres: the lobes The cerebral hemispheres can be divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). Some scientists though have added a fifth lobe that is the grouping of several medial structures that are involved in memory and emotions. This ...
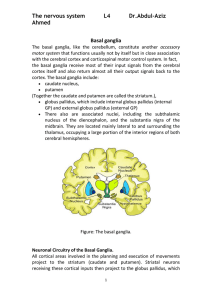
1.In the direct pathway
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
The Brain - Personal
... • Receive inputs from multiple sensory areas • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
... • Receive inputs from multiple sensory areas • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
Major lobes - Ohio University
... Parietal cortex: learns slowly, creates extensive, overlapping representations in a densely connected network. Dynamic PC states are short-term memory, mainly of spatial relations, quickly yielding to disorder and disintegration. Frontal cortex: learns slowly, stores isolated representations, activa ...
... Parietal cortex: learns slowly, creates extensive, overlapping representations in a densely connected network. Dynamic PC states are short-term memory, mainly of spatial relations, quickly yielding to disorder and disintegration. Frontal cortex: learns slowly, stores isolated representations, activa ...
PowerPoint
... • In Hebbian networks, all neurons can fire at the same time • Competitive learning means that only a single neuron from each group fires at each time step • Output units compete with one another. • These are winner takes all units (grandmother cells) ...
... • In Hebbian networks, all neurons can fire at the same time • Competitive learning means that only a single neuron from each group fires at each time step • Output units compete with one another. • These are winner takes all units (grandmother cells) ...
PowerPoint
... • In Hebbian networks, all neurons can fire at the same time • Competitive learning means that only a single neuron from each group fires at each time step • Output units compete with one another. • These are winner takes all units (grandmother cells) ...
... • In Hebbian networks, all neurons can fire at the same time • Competitive learning means that only a single neuron from each group fires at each time step • Output units compete with one another. • These are winner takes all units (grandmother cells) ...
Signals and circuits in the Purkinje neuron NEURAL CIRCUITS Ze’ev R. Abrams
... To demonstrate the power and utility of the combination of both time and frequency domain representations of the PN output signal, we utilize some signal processing techniques on a segment of PN signal recording: a 20 s segment of recording is displayed and analyzed in Figure 2 (segment was taken at ...
... To demonstrate the power and utility of the combination of both time and frequency domain representations of the PN output signal, we utilize some signal processing techniques on a segment of PN signal recording: a 20 s segment of recording is displayed and analyzed in Figure 2 (segment was taken at ...
The visual system
... 1) preparation and composition of the graft tissue - prolonged cold storage and use of solid grafts are not as good 2) selection of patients - older patients do not tend to benefit as much as young patients due to less confined damage and reduced ability to accept to graft 3) pre-graft medication – ...
... 1) preparation and composition of the graft tissue - prolonged cold storage and use of solid grafts are not as good 2) selection of patients - older patients do not tend to benefit as much as young patients due to less confined damage and reduced ability to accept to graft 3) pre-graft medication – ...
ling411-19-Learning - OWL-Space
... Probability of adjacent areas being connected: >70% • But if we count by columns instead of cells the figure is probably higher, maybe close to 100% Probability of distant areas being connected: 15-30% • Distant areas: at least one intervening area • In Macaque monkey, most areas have links to 1 ...
... Probability of adjacent areas being connected: >70% • But if we count by columns instead of cells the figure is probably higher, maybe close to 100% Probability of distant areas being connected: 15-30% • Distant areas: at least one intervening area • In Macaque monkey, most areas have links to 1 ...
Isabella E - BDoughertyAmSchool
... Behaviorism and the learning perspective are composed of many fields, but Pavlov´s discovery led to a branch of behaviorism in psychology. These psychologists believe that every single reaction, action, and emotion we present is learned. That means there is no involvement of phenotypes in our be ...
... Behaviorism and the learning perspective are composed of many fields, but Pavlov´s discovery led to a branch of behaviorism in psychology. These psychologists believe that every single reaction, action, and emotion we present is learned. That means there is no involvement of phenotypes in our be ...
Basic Structure and Function of Neurons
... Some human behavior is innate and follows a stereotypic pattern, basically in all individuals. Examples of such behavior pattern are swallowing when taken by surprise. Centrals programs in the nervous system can coordinate the motoneurons do not require additional incoming sensory feedback for the c ...
... Some human behavior is innate and follows a stereotypic pattern, basically in all individuals. Examples of such behavior pattern are swallowing when taken by surprise. Centrals programs in the nervous system can coordinate the motoneurons do not require additional incoming sensory feedback for the c ...
Classical v Operant Conditioning Handout
... Even if you are not a psychology student, you have probably at least heard about Pavlov's dogs. In his famous experiment, Ivan Pavlov noticed dogs began to salivate in response to a tone after the sound had been repeatedly paired with presenting food. Pavlov quickly realized that this was a learned ...
... Even if you are not a psychology student, you have probably at least heard about Pavlov's dogs. In his famous experiment, Ivan Pavlov noticed dogs began to salivate in response to a tone after the sound had been repeatedly paired with presenting food. Pavlov quickly realized that this was a learned ...
PROJECTIONS OF THE AMYGDALOID BODY TO THE INSULAR
... of the thalamus) which terminates in the insular cortex. It reaches, according to our results, both the agranular insular cortex and the anterior part of the granular insular cortex. According to Krettek and Price (5), this projection terminates in the posterior part of the granular insular cortex ...
... of the thalamus) which terminates in the insular cortex. It reaches, according to our results, both the agranular insular cortex and the anterior part of the granular insular cortex. According to Krettek and Price (5), this projection terminates in the posterior part of the granular insular cortex ...
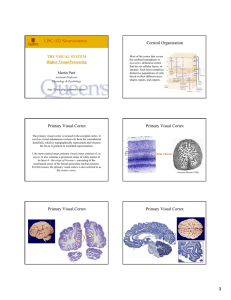
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... Neurons in the dorsal stream exhibit properties that are related to the spatial relationships of objects. At the highest levels in this pathway, visual neurons in the monkey posterior parietal cortex respond preferentially to optic flow. ...
... Neurons in the dorsal stream exhibit properties that are related to the spatial relationships of objects. At the highest levels in this pathway, visual neurons in the monkey posterior parietal cortex respond preferentially to optic flow. ...
3 - smw15.org
... Methods of Studying Classical Conditioning Eyeblink Conditioning Skin Conductance Response Conditioned Taste Aversion Evaluative Conditioning ...
... Methods of Studying Classical Conditioning Eyeblink Conditioning Skin Conductance Response Conditioned Taste Aversion Evaluative Conditioning ...
Strength in more than numbers
... properties improve the capacity of a read-out neuron (the model analog of a Purkinje cell) to discriminate among mossy fiber input patterns. It remains to be seen whether granule cell spike latency differences help to discriminate naturally occurring input patterns and, if so, how these differences ...
... properties improve the capacity of a read-out neuron (the model analog of a Purkinje cell) to discriminate among mossy fiber input patterns. It remains to be seen whether granule cell spike latency differences help to discriminate naturally occurring input patterns and, if so, how these differences ...
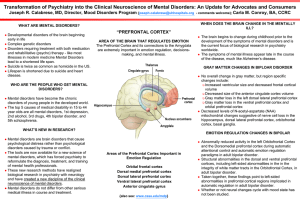
Transformation of Psychiatry into the Clinical Neuroscience of
... Mental disorders are brain disorders that cause psychological distress rather than psychological disorders caused by trauma or conflict. The tools are now available for a new science of mental disorders, which has forced psychiatry to reformulate the diagnosis, treatment, and training of mental he ...
... Mental disorders are brain disorders that cause psychological distress rather than psychological disorders caused by trauma or conflict. The tools are now available for a new science of mental disorders, which has forced psychiatry to reformulate the diagnosis, treatment, and training of mental he ...