楈瑳汯杯捩污传杲湡穩瑡潩景琠敨䌠牥扥慲潃瑲硥
... cortex consisting of multimodal association areas (Fig. 9.18). The primary motor cortex and the premotor cortex form a functional system for the planning and control of movement. The prefrontal cortex is primarily concerned with cognitive tasks and the control of behavior. Premotor cortex. The premo ...
... cortex consisting of multimodal association areas (Fig. 9.18). The primary motor cortex and the premotor cortex form a functional system for the planning and control of movement. The prefrontal cortex is primarily concerned with cognitive tasks and the control of behavior. Premotor cortex. The premo ...
THALAMUS
... 1.Thalamocortical cells and thalamic reticular cells can generate action potentials either as rhythmic bursts or as tonic, single-spike acticvity, depending upon the membrane potential of the cell. Activation of muscarinic, alfa1-adrenergic, H1-histaminergic or metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGl ...
... 1.Thalamocortical cells and thalamic reticular cells can generate action potentials either as rhythmic bursts or as tonic, single-spike acticvity, depending upon the membrane potential of the cell. Activation of muscarinic, alfa1-adrenergic, H1-histaminergic or metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGl ...
What and Where Pathways
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
Document
... together in time) – Some argued that a critical factor behind classical conditioning is what is known – classical conditioning provides new knowledge of relationship between two stimuli – Research has shown a predictive relationship between CS & US more important than temporal contiguity or frequenc ...
... together in time) – Some argued that a critical factor behind classical conditioning is what is known – classical conditioning provides new knowledge of relationship between two stimuli – Research has shown a predictive relationship between CS & US more important than temporal contiguity or frequenc ...
Chapter 6
... continuously in brightness according to a sine-wave function, along a line perpendicular to their lengths A sine-wave grating is designated by its spatial frequency, or the relative width of the bands, measured in cycles per degree of visual angle The most important visual information is that contai ...
... continuously in brightness according to a sine-wave function, along a line perpendicular to their lengths A sine-wave grating is designated by its spatial frequency, or the relative width of the bands, measured in cycles per degree of visual angle The most important visual information is that contai ...
cerebellar projections to the superior colliculus in the cat1
... the positive cells appeared to be labeled strongly. The largest number of labeled cells was situated in the contralateral lateral nucleus, mostly ventrally, although we found some dorsally in the caudal part. Only in two animals was a neuron found in the anterior interpositus nucleus. Also, we found ...
... the positive cells appeared to be labeled strongly. The largest number of labeled cells was situated in the contralateral lateral nucleus, mostly ventrally, although we found some dorsally in the caudal part. Only in two animals was a neuron found in the anterior interpositus nucleus. Also, we found ...
Lecture 3 Slides
... • The supplementary motor area (SMA) constructs the motor plan at the most abstract level (sequencing of the critical components of an action) • Premotor area codes for details of each action • Primary motor areas code exactly how the muscles would be controlled to implement the required grasp on th ...
... • The supplementary motor area (SMA) constructs the motor plan at the most abstract level (sequencing of the critical components of an action) • Premotor area codes for details of each action • Primary motor areas code exactly how the muscles would be controlled to implement the required grasp on th ...
Biological Implementation of the Temporal Difference Algorithm for
... The actor– critic architecture (Barto et al., 1983) has the interesting property that the actor and critic units differ in only a relatively minor way that is nevertheless critical. Both units use the same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) an ...
... The actor– critic architecture (Barto et al., 1983) has the interesting property that the actor and critic units differ in only a relatively minor way that is nevertheless critical. Both units use the same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) an ...
Programmed Learning Review - Germantown School District
... Many times while we are attempting to solve a problem, the answer suddenly comes to us and the puzzle seems simple. This phenomena is called insight or the "aha phenomena.” Insight or the "aha phenomena" is the solving of a problem or puzzle by perceiving the complete ...
... Many times while we are attempting to solve a problem, the answer suddenly comes to us and the puzzle seems simple. This phenomena is called insight or the "aha phenomena.” Insight or the "aha phenomena" is the solving of a problem or puzzle by perceiving the complete ...
A Type of Basket Cell in Superficial Layers of the Cat Visual Cortex
... and 20). These synapses show a very thin postsynaptic density and are similar in m o r p h o l o g y to those formed by the axon o f other types of smooth stellate cells4,7,12,17,18,25,26. DISCUSSION This paper presents, for the first time, evidence for a type of interneuron whose axon terminals for ...
... and 20). These synapses show a very thin postsynaptic density and are similar in m o r p h o l o g y to those formed by the axon o f other types of smooth stellate cells4,7,12,17,18,25,26. DISCUSSION This paper presents, for the first time, evidence for a type of interneuron whose axon terminals for ...
Week7
... • Originating in the cell body, this spike travels down the axon and causes chemical neurotransmitters to be released at synaptic terminals. • This chemical diffuses across the synapse into dendrites of neighboring cells. ...
... • Originating in the cell body, this spike travels down the axon and causes chemical neurotransmitters to be released at synaptic terminals. • This chemical diffuses across the synapse into dendrites of neighboring cells. ...
Brainstem Nuclei and Tracts
... spinal cord and nuclei of the brain stem. The fibers destined for the spinal cord cross to the opposite side in the dorsal tegmental decussation and continue as tectospinal fibers. Efferent fibers for brain stem are called tectobulbar fibers directed bilaterally. They distribute fibers to the pretec ...
... spinal cord and nuclei of the brain stem. The fibers destined for the spinal cord cross to the opposite side in the dorsal tegmental decussation and continue as tectospinal fibers. Efferent fibers for brain stem are called tectobulbar fibers directed bilaterally. They distribute fibers to the pretec ...
Kenji Doya 2001
... from the basal ganglia and the theory of reinforceFigure 5. A schematic diagram of the circuit of the basal ganglia and their loop ment learning, the role of the basal ganglia has beconnection with the cerebral cortex. The labels in italics show the hypothetical come much clearer in the last several ...
... from the basal ganglia and the theory of reinforceFigure 5. A schematic diagram of the circuit of the basal ganglia and their loop ment learning, the role of the basal ganglia has beconnection with the cerebral cortex. The labels in italics show the hypothetical come much clearer in the last several ...
Cortical and Brainstem Control of Motor Function
... Decrebrate rgidity- removal of the cortical control over the medullary reticulospinal keeps pontine reticulospinal unchecked leads to hyperactivity of anti-gravity muscles. University of Jordan ...
... Decrebrate rgidity- removal of the cortical control over the medullary reticulospinal keeps pontine reticulospinal unchecked leads to hyperactivity of anti-gravity muscles. University of Jordan ...
Motor Systems - University of Sunderland
... • A muscle is made up of multiple muscle fibers—multinucleate cells in mammals that contain myosin and actin (elastic). These are excitable cells like neurons. • In higher vertebrates, each fiber is innervated by a single motoneuron, but a single motoneuron can innervate many fibers of a single type ...
... • A muscle is made up of multiple muscle fibers—multinucleate cells in mammals that contain myosin and actin (elastic). These are excitable cells like neurons. • In higher vertebrates, each fiber is innervated by a single motoneuron, but a single motoneuron can innervate many fibers of a single type ...
Operant Conditioning
... • Conditioning – learning that involves association between environmental stimuli and the organism’s response • Pavlov – Russian physiologist - salivation in dogs Why salivate to other things? How did they know? ...
... • Conditioning – learning that involves association between environmental stimuli and the organism’s response • Pavlov – Russian physiologist - salivation in dogs Why salivate to other things? How did they know? ...
Operant Conditioning
... • Conditioning – learning that involves association between environmental stimuli and the organism’s response • Pavlov – Russian physiologist - salivation in dogs Why salivate to other things? How did they know? ...
... • Conditioning – learning that involves association between environmental stimuli and the organism’s response • Pavlov – Russian physiologist - salivation in dogs Why salivate to other things? How did they know? ...
Okami Study Guide
... though they learn a great many things for which they were not biologically prepared. 3. Habituation and sensitization are the simplest forms of learning. Habituation occurs when a stimulus at first causes a strong response, but due to repeated exposure over time response is lessened. Sensitization o ...
... though they learn a great many things for which they were not biologically prepared. 3. Habituation and sensitization are the simplest forms of learning. Habituation occurs when a stimulus at first causes a strong response, but due to repeated exposure over time response is lessened. Sensitization o ...
Classical Conditioning
... and the arms were raised in a characteristic manner. On the second stimulation the same thing occurred, and in addition the lips began to pucker and tremble. On the third stimulation the child broke into a sudden crying fit. This is the first time an emotional situation in the laboratory has produce ...
... and the arms were raised in a characteristic manner. On the second stimulation the same thing occurred, and in addition the lips began to pucker and tremble. On the third stimulation the child broke into a sudden crying fit. This is the first time an emotional situation in the laboratory has produce ...
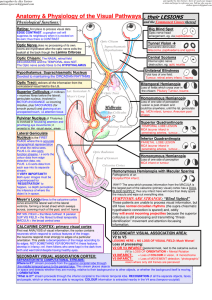
Literature What is Learning
... !Taste -> Nausea works better than Light -> Nausea! !Solution: Make learning rate ! dependent on CS-US combinations! ...
... !Taste -> Nausea works better than Light -> Nausea! !Solution: Make learning rate ! dependent on CS-US combinations! ...
Somatic senses
... and has connection with it Integrates sensory information like temperature and pressure coming from the primary somatosensory cortex. Forms understanding of the stimulus like size, texture, and relationship of parts Ex.: putting the hand in the pocket and feeling something. The center integrat ...
... and has connection with it Integrates sensory information like temperature and pressure coming from the primary somatosensory cortex. Forms understanding of the stimulus like size, texture, and relationship of parts Ex.: putting the hand in the pocket and feeling something. The center integrat ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... principal nucleus of trigeminal tract (receives somatosensory input from face) Sensory nucleus extends throughout entire brain stem and high cervical spinal cord. nucleus of the trigeminal tract (receives somatosensory input from face via the descending trigeminal tract.) Motor nuclei caudal to rost ...
... principal nucleus of trigeminal tract (receives somatosensory input from face) Sensory nucleus extends throughout entire brain stem and high cervical spinal cord. nucleus of the trigeminal tract (receives somatosensory input from face via the descending trigeminal tract.) Motor nuclei caudal to rost ...
Chapter 8 - The Adaptive Mind: Learning MULTIPLE CHOICE 1
... c. Learning associated with latent inhibition is slow; resulting in relatively poor learning. d. Learning associated with latent inhibition is slow: resulting in very effective learning. 42. At dinner Candace eats several familiar food (pasta, salad, bread) and an unfamiliar food (mussels). Later th ...
... c. Learning associated with latent inhibition is slow; resulting in relatively poor learning. d. Learning associated with latent inhibition is slow: resulting in very effective learning. 42. At dinner Candace eats several familiar food (pasta, salad, bread) and an unfamiliar food (mussels). Later th ...