L7-Brainstem Student..
... • Trochlear nerve (CN IV) nucleus which also controls movements of some eye muscles . • Red Nucleus: gives out Sends Rubrospinal tract which is inhibitory to spinal Gamma Efferents neurons ( & stretch reflex /muscle tone ) • Substantia Nigra: Collection of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbr ...
... • Trochlear nerve (CN IV) nucleus which also controls movements of some eye muscles . • Red Nucleus: gives out Sends Rubrospinal tract which is inhibitory to spinal Gamma Efferents neurons ( & stretch reflex /muscle tone ) • Substantia Nigra: Collection of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbr ...
Slide ()
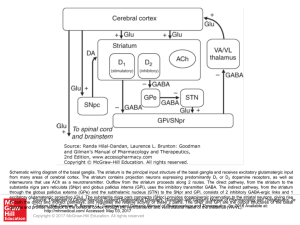
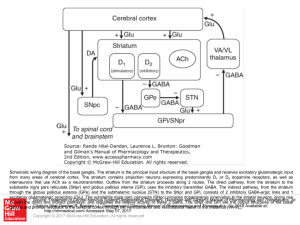
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... GENERAL OBJECTIVE The general objective of this subject is for students to acquire a basic knowledge of the structural, molecular and functional aspects of the mechanisms that control the working of the nervous system, the skin and the senses. This basic knowledge will allow students at a later stag ...
... GENERAL OBJECTIVE The general objective of this subject is for students to acquire a basic knowledge of the structural, molecular and functional aspects of the mechanisms that control the working of the nervous system, the skin and the senses. This basic knowledge will allow students at a later stag ...
17-1 Chapter 17 ACTIVITIES INVOLVING THE CEREBRAL
... limbic system. Knowledge of the limbic system is quite old; it was named by the surgeon, Broca, in the last century. Actually, little research was done to link the limbic system with emotion until about 1937 when the neuroanatomist, Papez, published a proposed mechanism of emotion involving the limb ...
... limbic system. Knowledge of the limbic system is quite old; it was named by the surgeon, Broca, in the last century. Actually, little research was done to link the limbic system with emotion until about 1937 when the neuroanatomist, Papez, published a proposed mechanism of emotion involving the limb ...
Heart-brain communication Veen, Frederik Martin van der
... pressure decrease are found (Neafsey, 1990; Cechetto & Saper, 1990; Powell et al., 1990). The most interesting evidence for a role of the ACC in cardiovascular control comes from a series of studies with rabbits. In these studies it is found that the ACC plays an important role in mediating cardiova ...
... pressure decrease are found (Neafsey, 1990; Cechetto & Saper, 1990; Powell et al., 1990). The most interesting evidence for a role of the ACC in cardiovascular control comes from a series of studies with rabbits. In these studies it is found that the ACC plays an important role in mediating cardiova ...
Mitochondrial diseases affecting nervous system and muscle
... Final goal: production of ATP Respiratory chain proteins are synthesized from two different genomes: mtDNA and nDNA •mtDNA encodes 13 respiratory chain polypeptides, 2 rRNAs and 22 tRNAs •nDNA encodes the majority of respiratory chain polipeptides Transport of cytosolic proteins and their assembly w ...
... Final goal: production of ATP Respiratory chain proteins are synthesized from two different genomes: mtDNA and nDNA •mtDNA encodes 13 respiratory chain polypeptides, 2 rRNAs and 22 tRNAs •nDNA encodes the majority of respiratory chain polipeptides Transport of cytosolic proteins and their assembly w ...
Notes - Cort W. Rudolph, Ph.D.
... § “Unconditioned” = things that are reflexive/occur without any learning. • Conditioned stimulus (CS) refers to an environmental event whose significance is learned. • Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) has innate, built-in meaning to the organism. • Conditioned responses (CRs) are learned reactions • Unc ...
... § “Unconditioned” = things that are reflexive/occur without any learning. • Conditioned stimulus (CS) refers to an environmental event whose significance is learned. • Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) has innate, built-in meaning to the organism. • Conditioned responses (CRs) are learned reactions • Unc ...
Emotion Explained
... 4.5.4 Effects of damage to the orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.5 Neurophysiology and functional neuroimaging ofthe orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.6 The human orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.7 A neurophysiological and computational basis for stimulus-reinforcer association learning and reversal in the orbitofrontal cort ...
... 4.5.4 Effects of damage to the orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.5 Neurophysiology and functional neuroimaging ofthe orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.6 The human orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.7 A neurophysiological and computational basis for stimulus-reinforcer association learning and reversal in the orbitofrontal cort ...
Motor Cortex
... because the selection of a particular movement is impaired. Supplementary motor area (medial area 6): Patient cannot tie shoe laces (impaired selection of a particular movement sequence). Parietal association: Patient has no sock on one foot because of sensory neglect. Patient has ataxia (inaccurate ...
... because the selection of a particular movement is impaired. Supplementary motor area (medial area 6): Patient cannot tie shoe laces (impaired selection of a particular movement sequence). Parietal association: Patient has no sock on one foot because of sensory neglect. Patient has ataxia (inaccurate ...
Learning Strengthens the Response of Primary Visual Cortex to
... may have shifted toward the trained stimulus. The observed changes in V1 could be produced locally or could result from feedback from higher cortical areas. Studies of V1 with single-unit recording report different neural effects of learning than those observed here [14–16]. None of the studies repo ...
... may have shifted toward the trained stimulus. The observed changes in V1 could be produced locally or could result from feedback from higher cortical areas. Studies of V1 with single-unit recording report different neural effects of learning than those observed here [14–16]. None of the studies repo ...
adrenal glands
... Ganglion cells are also present in the medulla. Their axons extend peripherally to the parenchyma of the adrenal cortex to modulate its secretory activity and innervate blood vessels. Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla have a secretory function, the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
... Ganglion cells are also present in the medulla. Their axons extend peripherally to the parenchyma of the adrenal cortex to modulate its secretory activity and innervate blood vessels. Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla have a secretory function, the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
CHAPTER 15 THE CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS
... can be explained solely on the basis of retinal processing, but others cannot. To fully explain how we perceive our visual world, we need to consider the whole system, including the many levels of processing that occur in the brain. 15.1.1. Parallel and hierarchical processing. In all sensory system ...
... can be explained solely on the basis of retinal processing, but others cannot. To fully explain how we perceive our visual world, we need to consider the whole system, including the many levels of processing that occur in the brain. 15.1.1. Parallel and hierarchical processing. In all sensory system ...
pdf - Llano Lab
... 1974; Ottersen and Ben-Ari, 1979; Clugnet et al., 1990)). The degree to which this heterogeneity may be reflected in different distributions of calcium-binding proteins has not yet been addressed. In the current study, we take advantage of the tripartite organization of the auditory thalamus, which c ...
... 1974; Ottersen and Ben-Ari, 1979; Clugnet et al., 1990)). The degree to which this heterogeneity may be reflected in different distributions of calcium-binding proteins has not yet been addressed. In the current study, we take advantage of the tripartite organization of the auditory thalamus, which c ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Mr. Padron`s Psychology
... – Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): any stimulus that will always and naturally ELICIT a response – Unconditioned Response (UCR): any response that always and naturally occurs at the presentation of the UCS – Neutral Stimulus (NS): any stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response associated with t ...
... – Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): any stimulus that will always and naturally ELICIT a response – Unconditioned Response (UCR): any response that always and naturally occurs at the presentation of the UCS – Neutral Stimulus (NS): any stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response associated with t ...
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter?
... Not all depressed people have a history of ELS Not all people with history of ELS are depressed However, HPA dysregulation is clearly linked to ELS and ELS clearly linked to depression ...
... Not all depressed people have a history of ELS Not all people with history of ELS are depressed However, HPA dysregulation is clearly linked to ELS and ELS clearly linked to depression ...
Classical Conditioning
... Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchantchief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talen ...
... Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchantchief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talen ...
Vestibular senses
... rays to AC circuits; its wavelength is measured in nanometers. - What are the 3 perceived characteristics of light? 1. Hue, corresponding to the spectrum (wavelength) of light. 2. Brightness, corresponding to intensity of wavelength. 3. Saturation, corresponding to the purity of wavelength. - What a ...
... rays to AC circuits; its wavelength is measured in nanometers. - What are the 3 perceived characteristics of light? 1. Hue, corresponding to the spectrum (wavelength) of light. 2. Brightness, corresponding to intensity of wavelength. 3. Saturation, corresponding to the purity of wavelength. - What a ...
LECTURE15.VoluntaryMovement
... Cerebellum critical for integrating desired task and sensory inputs into motor planning and execution Cerebellum is a major site for learning within motor circuits Basal ganglia control muscle tone (readiness) and execution of rapid motor tasks ...
... Cerebellum critical for integrating desired task and sensory inputs into motor planning and execution Cerebellum is a major site for learning within motor circuits Basal ganglia control muscle tone (readiness) and execution of rapid motor tasks ...
Social Learning - Ms. Zolpis` Classes
... cupboard. • You have never eaten any of them. You reach in, take one out, cook it, and eat it. You do the same thing with the other two later on. • The one you like best you will probably reach for and cook again. • In this case, you have been operantly conditioned by your actions (operations) and t ...
... cupboard. • You have never eaten any of them. You reach in, take one out, cook it, and eat it. You do the same thing with the other two later on. • The one you like best you will probably reach for and cook again. • In this case, you have been operantly conditioned by your actions (operations) and t ...
神经系统传导通路
... The auditory pathway organ of Corti →bipolar cell (exchange neuron) →cochlear nerve →ventral cochlear nucleusdorsal and cochlear nucleus (exchange neuron) →trapezoid body of pons overlaps to the opposite side →lateral lemniscus →the dorsi-lateral part of tegmentum of midbrain →inferior colliculus ( ...
... The auditory pathway organ of Corti →bipolar cell (exchange neuron) →cochlear nerve →ventral cochlear nucleusdorsal and cochlear nucleus (exchange neuron) →trapezoid body of pons overlaps to the opposite side →lateral lemniscus →the dorsi-lateral part of tegmentum of midbrain →inferior colliculus ( ...
Compared to other cortical areas, muscle contraction is most easily
... long-term effects are less pronounced than often assumed. Careful testing is required to discern long-term motor deficits and, although much emphasis has been placed on species differences, comparable deficits follow pyramidal-tract transections in macaque monkeys, marsupial phalangers, rats, and ha ...
... long-term effects are less pronounced than often assumed. Careful testing is required to discern long-term motor deficits and, although much emphasis has been placed on species differences, comparable deficits follow pyramidal-tract transections in macaque monkeys, marsupial phalangers, rats, and ha ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA
... Accordingly, the loss of striatopallidal GABAergic neurons leads to increased activity of inhibitcry pallidosubthalamic neurons. The reduced activity of the subtalamo-nigral projection then leads to reduced inhibition of the nigro-thalamic neurons which finally results in increased thalamocortical a ...
... Accordingly, the loss of striatopallidal GABAergic neurons leads to increased activity of inhibitcry pallidosubthalamic neurons. The reduced activity of the subtalamo-nigral projection then leads to reduced inhibition of the nigro-thalamic neurons which finally results in increased thalamocortical a ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA
... Accordingly, the loss of striatopallidal GABAergic neurons leads to increased activity of inhibitcry pallidosubthalamic neurons. The reduced activity of the subtalamo-nigral projection then leads to reduced inhibition of the nigro-thalamic neurons which finally results in increased thalamocortical a ...
... Accordingly, the loss of striatopallidal GABAergic neurons leads to increased activity of inhibitcry pallidosubthalamic neurons. The reduced activity of the subtalamo-nigral projection then leads to reduced inhibition of the nigro-thalamic neurons which finally results in increased thalamocortical a ...