Lesser
... University of Wisconsin–Madison. These investigations used a technique called micromapping to record the electrical activity of small patches of neurons in the brains of rats as they were touched lightly on various parts of their bodies. ...
... University of Wisconsin–Madison. These investigations used a technique called micromapping to record the electrical activity of small patches of neurons in the brains of rats as they were touched lightly on various parts of their bodies. ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 8,9,11,12 The
... 62. This cerebral vein drains the internal structures of the hemisphere such as the choroid plexuses, basal ganglia, periventricular regions, diencephalons and will drain into the straight dural venous sinus. a. Deep cerebral veins b. Superficial cerebral veins c. Both of the above d. None of the ab ...
... 62. This cerebral vein drains the internal structures of the hemisphere such as the choroid plexuses, basal ganglia, periventricular regions, diencephalons and will drain into the straight dural venous sinus. a. Deep cerebral veins b. Superficial cerebral veins c. Both of the above d. None of the ab ...
Ch - Humble ISD
... Cerebral Palsy- permanent, nonprogressive damage to __________ control areas of the brain, occurs prior to or shortly after birth ...
... Cerebral Palsy- permanent, nonprogressive damage to __________ control areas of the brain, occurs prior to or shortly after birth ...
Machine learning and the brain - Intelligent Autonomous Systems
... Given the problematics mentioned in the previous section it is surprising how much is already known about the primate brain and its astonishing how little this is compared to what is still unknown. The mammalian brain is separated into various regions with respect to anatomy and functionality. In th ...
... Given the problematics mentioned in the previous section it is surprising how much is already known about the primate brain and its astonishing how little this is compared to what is still unknown. The mammalian brain is separated into various regions with respect to anatomy and functionality. In th ...
psychweek3 - Ms. Bishop`s Classroom
... 1. What would you have to measure in this experiment? (ie: overweight/normal, male/female, number of bites, number of items ordered, amount of food left, number of chews, amount of time spent eating) 2. How would you measure this? (count and record, tally, ...
... 1. What would you have to measure in this experiment? (ie: overweight/normal, male/female, number of bites, number of items ordered, amount of food left, number of chews, amount of time spent eating) 2. How would you measure this? (count and record, tally, ...
Chapter 19 study Questions key
... forced to experience the fear-inducing stimulus. This results in extinction of the fear response. 16. What is the evidence that NMDA receptors might be important in the elimination of fear when exposure therapy is used? D-cycloserine, an NMDA receptor agonist that acts on the glycine binding site, c ...
... forced to experience the fear-inducing stimulus. This results in extinction of the fear response. 16. What is the evidence that NMDA receptors might be important in the elimination of fear when exposure therapy is used? D-cycloserine, an NMDA receptor agonist that acts on the glycine binding site, c ...
primary cortex - u.arizona.edu
... • Projections to this area are from the posterior parietal cortex; this area in turn projects to parts of the secondary motor cortex, the primary cortex, and to the ...
... • Projections to this area are from the posterior parietal cortex; this area in turn projects to parts of the secondary motor cortex, the primary cortex, and to the ...
weiten6_PPT06
... basic premise of operant conditioning—that voluntary behavior is controlled by its consequences. These examples involve positive reinforcement (for a comparison of positive and negative reinforcement, see Figure 6.21). Table of Contents ...
... basic premise of operant conditioning—that voluntary behavior is controlled by its consequences. These examples involve positive reinforcement (for a comparison of positive and negative reinforcement, see Figure 6.21). Table of Contents ...
Quiz
... 13. In one cycle of neural communication, which is the correct order of events? a. Neurotransmitter release -‐> action potential -‐> threshold of excitation reached -‐> inhibitory or excitatory post-‐synaptic ...
... 13. In one cycle of neural communication, which is the correct order of events? a. Neurotransmitter release -‐> action potential -‐> threshold of excitation reached -‐> inhibitory or excitatory post-‐synaptic ...
…By the way, where is the fornix???
... • http://www9.biostr.washington.edu/da.html – Sylvius: • http://www.sylvius.com/ ...
... • http://www9.biostr.washington.edu/da.html – Sylvius: • http://www.sylvius.com/ ...
Neuroplasticity
... part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A’s efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased.’ ...
... part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A’s efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased.’ ...
File - Sneed - AP Psychology
... Spontaneous recovery- conditioned response observed after presenting the conditioned stimulus again after a lengthy period of time (after extinction) Contemporary Views of Classical Conditioning ...
... Spontaneous recovery- conditioned response observed after presenting the conditioned stimulus again after a lengthy period of time (after extinction) Contemporary Views of Classical Conditioning ...
middle ear
... intensity of the sound wave. Loudness refers to the perception of the sound wave. Amplitude is one factor. Frequency refers to the number of compressions per second and is measured in hertz. Related to the pitch (high to low) of a sound. ...
... intensity of the sound wave. Loudness refers to the perception of the sound wave. Amplitude is one factor. Frequency refers to the number of compressions per second and is measured in hertz. Related to the pitch (high to low) of a sound. ...
Slide 1
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
research_paper_.edt_
... extinct. To evoke this previously learned salivation response, one can ring a bell paired with food. After extinction, relearning can be accomplished at a more rapid rate compared to what was required initially. However, re-extinction occurs if the response is not strengthened again. Stimulus genera ...
... extinct. To evoke this previously learned salivation response, one can ring a bell paired with food. After extinction, relearning can be accomplished at a more rapid rate compared to what was required initially. However, re-extinction occurs if the response is not strengthened again. Stimulus genera ...
Student Cortical Organization
... Thes current flows between soma & dendrites , when summated from many cells , contribute to production of EEG waves Saturday, April 2010 ,10 ...
... Thes current flows between soma & dendrites , when summated from many cells , contribute to production of EEG waves Saturday, April 2010 ,10 ...
Document
... distinction between the vocational-oriented media and engineering courses and the academically-oriented law and science courses. Teachers on the vocational courses seemed to work as a team. Therefore the students expected joined-up input from the different but related units of work. The use of three ...
... distinction between the vocational-oriented media and engineering courses and the academically-oriented law and science courses. Teachers on the vocational courses seemed to work as a team. Therefore the students expected joined-up input from the different but related units of work. The use of three ...
LeDoux outlines his theory of emotions and memory
... activates the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate and blood pressure, and the sensory motor system, which controls muscle movement. LeDoux and his colleagues sought to find out where the brain stores the emotional memory, which pairs the tone and shock. They began by making small les ...
... activates the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate and blood pressure, and the sensory motor system, which controls muscle movement. LeDoux and his colleagues sought to find out where the brain stores the emotional memory, which pairs the tone and shock. They began by making small les ...
PowerPoint Slides Chapter 6
... (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and parietal lobes – parietal cortex ---dorsal stream of visual information – inferotemporal (lower part of temporal lobe) ---the ventral stream of visual information ...
... (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and parietal lobes – parietal cortex ---dorsal stream of visual information – inferotemporal (lower part of temporal lobe) ---the ventral stream of visual information ...
Document
... Assessment criterions for the synaptic hypothesis: (From Martin and Morris 2002) 1. DETECTABILITY: If an animal displays memory of some previous experience (or has learnt a new task), a change in synaptic efficacy should be detectable somewhere in its nervous system. 2. MIMICRY: If it were possible ...
... Assessment criterions for the synaptic hypothesis: (From Martin and Morris 2002) 1. DETECTABILITY: If an animal displays memory of some previous experience (or has learnt a new task), a change in synaptic efficacy should be detectable somewhere in its nervous system. 2. MIMICRY: If it were possible ...
A103 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
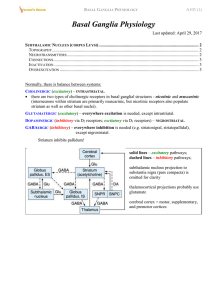
... Normally, there is balance between systems: CHOLINERGIC (excitatory) – INTRASTRIATAL. there are two types of cholinergic receptors in basal ganglial structures - nicotinic and muscarinic (interneurons within striatum are primarily muscarinic, but nicotinic receptors also populate striatum as well ...
... Normally, there is balance between systems: CHOLINERGIC (excitatory) – INTRASTRIATAL. there are two types of cholinergic receptors in basal ganglial structures - nicotinic and muscarinic (interneurons within striatum are primarily muscarinic, but nicotinic receptors also populate striatum as well ...
Reflex, Taxis, and Instinct
... – CS, US both Contingent and Contiguous • Delay, Trace Conditioning – CS, US Contingent but Not Contiguous • Simultaneous Conditioning – CS, US Contiguous but not Contingent • Backwards Conditioning, Extinction (Below Zero) – CS Predicts Absence of US ...
... – CS, US both Contingent and Contiguous • Delay, Trace Conditioning – CS, US Contingent but Not Contiguous • Simultaneous Conditioning – CS, US Contiguous but not Contingent • Backwards Conditioning, Extinction (Below Zero) – CS Predicts Absence of US ...
Symposium: Classical and instrumental conditioning. presented at
... symposium on human conditioning, as part of the scientific program of the 34th Meeting of Experimental Psychologists (Tagung experimentell arbeitender Psychologen, TeaP). This year's conference was organized by the Department of Psychology at the University of Osnabrueck, F.R.G. (13-16 April, 1992). ...
... symposium on human conditioning, as part of the scientific program of the 34th Meeting of Experimental Psychologists (Tagung experimentell arbeitender Psychologen, TeaP). This year's conference was organized by the Department of Psychology at the University of Osnabrueck, F.R.G. (13-16 April, 1992). ...
Visualizing the Brain
... dendrites as well as glial cells) and underling white matter (formed of bundles or tracts of mylinated nerve fibers (Axons), its white appearance is due to lipid composition of the myelin. The cerebral cortex is characterized by numerous folds and grooves called convolutions. The elevated folds are ...
... dendrites as well as glial cells) and underling white matter (formed of bundles or tracts of mylinated nerve fibers (Axons), its white appearance is due to lipid composition of the myelin. The cerebral cortex is characterized by numerous folds and grooves called convolutions. The elevated folds are ...