Specificity in Inhibitory Systems Associated with Prefrontal Pathways to
... to inhibitory neurons labeled for calbindin (CB) or parvalbumin (PV), which differ in mode of inhibition. Projection neurons in area 10 originated mostly in layers 2--3 and were intermingled with CB inhibitory neurons. In contrast, projections from area 32 originated predominantly in layers 5--6 amo ...
... to inhibitory neurons labeled for calbindin (CB) or parvalbumin (PV), which differ in mode of inhibition. Projection neurons in area 10 originated mostly in layers 2--3 and were intermingled with CB inhibitory neurons. In contrast, projections from area 32 originated predominantly in layers 5--6 amo ...
Thalamic Circuit Diversity: Modulation of the Driver/Modulator
... a supralinear fashion. Such convergence therefore provides a mechanism for the synergistic amplification of signals within a narrow temporal window. In this case the convergence of two driver inputs may report the relative timing between sensory events and ongoing cortical activity. ...
... a supralinear fashion. Such convergence therefore provides a mechanism for the synergistic amplification of signals within a narrow temporal window. In this case the convergence of two driver inputs may report the relative timing between sensory events and ongoing cortical activity. ...
Distribution of GABA‐like immunoreactivity in the rat amygdaloid
... GABA-Li material. However, the pattern and location of The distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the the neurons varied, as did their shapes, the density of their amygdaloid complex has been studied by using specific distribution, and the intensity of the staining in the anti-GABA antibodies ...
... GABA-Li material. However, the pattern and location of The distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the the neurons varied, as did their shapes, the density of their amygdaloid complex has been studied by using specific distribution, and the intensity of the staining in the anti-GABA antibodies ...
Ventilatory disorders - Chirurgia toracica mini invasiva
... breathing patterns during sleep or wakefulness, or absence dyspnea during exercise may occur. Diagnosis is confirmed by demonstrating an abnormal ventilatory response to provoked hypercapnia, with normal or near normal response to hypoxia in the absence of infectious, cardiac, pulmonary, and neuromu ...
... breathing patterns during sleep or wakefulness, or absence dyspnea during exercise may occur. Diagnosis is confirmed by demonstrating an abnormal ventilatory response to provoked hypercapnia, with normal or near normal response to hypoxia in the absence of infectious, cardiac, pulmonary, and neuromu ...
Ulanovsky et al., 2003
... and how the brain processes them. For instance, neural responses in the visual (Ohzawa et al., 1982), auditory (Ulanovsky et al., 2003), somatosensory (Simons, 1978), and olfactory (Wilson, 1998) cortices rapidly diminish to repeated presentations of the same stimulus. Such sensory adaptation is con ...
... and how the brain processes them. For instance, neural responses in the visual (Ohzawa et al., 1982), auditory (Ulanovsky et al., 2003), somatosensory (Simons, 1978), and olfactory (Wilson, 1998) cortices rapidly diminish to repeated presentations of the same stimulus. Such sensory adaptation is con ...
Pansynaptic Enlargement at Adult Cortical
... measured PSF and found that the 2 values were in good agreement (AutoDeblur PSF, 0.17 μm). Therefore, we used the AutoDeblur PSF in the xy plane to monitor the effect of imaging putative synapses in tissue. We found that the AutoDeblur PSF enlarged to a maximum of 0.19 μm in the xy plane when imagin ...
... measured PSF and found that the 2 values were in good agreement (AutoDeblur PSF, 0.17 μm). Therefore, we used the AutoDeblur PSF in the xy plane to monitor the effect of imaging putative synapses in tissue. We found that the AutoDeblur PSF enlarged to a maximum of 0.19 μm in the xy plane when imagin ...
Fluorescent in situ hybridization technique for cell type identification
... Central nervous system consists of a myriad of cell types, including neurons, glias, endothelial cells, etc. On top of it, each cell type can be further subdivided into many different subtypes [4,27]. Considering that the neuronal circuit is an assembly of various neuronal types, the identification ...
... Central nervous system consists of a myriad of cell types, including neurons, glias, endothelial cells, etc. On top of it, each cell type can be further subdivided into many different subtypes [4,27]. Considering that the neuronal circuit is an assembly of various neuronal types, the identification ...
A Review of Cell Assemblies by Huyck and
... In a more complex form, two groups of cells can code for specific features, say lines of two given angles; activation of varying numbers or varying degrees of each set can represent an intermediate feature (Hubel and Wiesel, 1962). The degree of overlap is a topological issue (see Section 3.2) that ...
... In a more complex form, two groups of cells can code for specific features, say lines of two given angles; activation of varying numbers or varying degrees of each set can represent an intermediate feature (Hubel and Wiesel, 1962). The degree of overlap is a topological issue (see Section 3.2) that ...
Words in the brain`s language
... forming during language acquisition, in particular for those representing words. Cortical topographies of assemblies should be related to aspects of the meaning of the words they represent, and physiological signs of cell assembly ignition should be followed by possible indicators of reverberation. ...
... forming during language acquisition, in particular for those representing words. Cortical topographies of assemblies should be related to aspects of the meaning of the words they represent, and physiological signs of cell assembly ignition should be followed by possible indicators of reverberation. ...
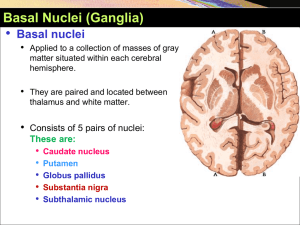
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... – (1) to determine how rapidly the movement is to be performed and – (2) to control how large the movement will be. • For instance, a person may write the letter "a" slowly or rapidly. Also, he or she may write a small "a" on a piece of paper or a large "a" on a chalkboard. Regardless of the choice, ...
... – (1) to determine how rapidly the movement is to be performed and – (2) to control how large the movement will be. • For instance, a person may write the letter "a" slowly or rapidly. Also, he or she may write a small "a" on a piece of paper or a large "a" on a chalkboard. Regardless of the choice, ...
Swim Initiation Neurons in Tritonia diomedea1
... FIG. 4. DRI does not appear to function as a CPG element. DRI, C2 and 2 DSIs were impaled with intracellular electrodes. The two DSIs were stimulated to fire at 20 Hz for 20 sec (hatched bar) while DRI was hyperpolarized to prevent its spiking. This procedure failed to prevent the swim motor program ...
... FIG. 4. DRI does not appear to function as a CPG element. DRI, C2 and 2 DSIs were impaled with intracellular electrodes. The two DSIs were stimulated to fire at 20 Hz for 20 sec (hatched bar) while DRI was hyperpolarized to prevent its spiking. This procedure failed to prevent the swim motor program ...
Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus activation contributes to
... dysfunction is characterized by low cardiac output and neurohumoral excitation (NHE). In the meantime, the sympathoexcitation is considered as an important characteristic of heart failure [1]. A growing number of experimental studies suggest that interventions at the central nervous system (CNS) lev ...
... dysfunction is characterized by low cardiac output and neurohumoral excitation (NHE). In the meantime, the sympathoexcitation is considered as an important characteristic of heart failure [1]. A growing number of experimental studies suggest that interventions at the central nervous system (CNS) lev ...
Intrinsic and synaptic plasticity in the vestibular system
... in Purkinje cells has little effect on baseline oculomotor behavior, but impairs short-term learning in the VOR that is induced by visual–vestibular mismatch training [9]. Interestingly, long-term learning in the VOR does not appear to rely on cerebellar LTD; both increases and decreases in VOR gain ...
... in Purkinje cells has little effect on baseline oculomotor behavior, but impairs short-term learning in the VOR that is induced by visual–vestibular mismatch training [9]. Interestingly, long-term learning in the VOR does not appear to rely on cerebellar LTD; both increases and decreases in VOR gain ...
mechanisms and biological role of thalamocortical oscillations
... TC neurons posses a large set of intrinsic currents that enable them to contribute to the various oscillatory activities and/or mediated some of them. The electrophysiological identification of a TC neuron is shown in Fig. 2. Usually, a small depolarization of TC neurons with intracellular DC curren ...
... TC neurons posses a large set of intrinsic currents that enable them to contribute to the various oscillatory activities and/or mediated some of them. The electrophysiological identification of a TC neuron is shown in Fig. 2. Usually, a small depolarization of TC neurons with intracellular DC curren ...
(2003). Prefrontal and medial temporal lobe interactions in
... effects of hippocampal or fornix lesions on recognition15,22,23 whereas other researchers have reported deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses ...
... effects of hippocampal or fornix lesions on recognition15,22,23 whereas other researchers have reported deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses ...
The basal ganglia and cortex implement optimal decision making
... Wang, 2002) assume that there exist connections from neurons representing stimuli, to the appropriate cortical neurons representing actions (these connections may develop during the months of training the animals undergo before these experiments). These cortical connections are assumed to encode the ...
... Wang, 2002) assume that there exist connections from neurons representing stimuli, to the appropriate cortical neurons representing actions (these connections may develop during the months of training the animals undergo before these experiments). These cortical connections are assumed to encode the ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system regulates body activities that are under conscious control, such as the movement of skeletal muscles. Most of the time you have control over skeletal muscle movement, but when your body is in danger the central nervous system may take over. ...
... Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system regulates body activities that are under conscious control, such as the movement of skeletal muscles. Most of the time you have control over skeletal muscle movement, but when your body is in danger the central nervous system may take over. ...
PREFRONTAL AND MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE INTERACTIONS IN
... effects of hippocampal or fornix lesions on recognition15,22,23 whereas other researchers have reported deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses ...
... effects of hippocampal or fornix lesions on recognition15,22,23 whereas other researchers have reported deficits13,24. The importance of the perirhinal cortex for familiarity-based memory is less controversial. Electrophysiological studies have found perirhinal neurons that show diminished responses ...
The Effect of Slow Electrical Stimuli to Achieve Learning in Cultured
... activity in a large number of neurons. To facilitate access to such a large number of neurons, several groups now use preparations of cultured neurons grown over a multi electrode array (MEA, see Figure 1). This enables simultaneous measurement from multiple electrodes, as well as network manipulati ...
... activity in a large number of neurons. To facilitate access to such a large number of neurons, several groups now use preparations of cultured neurons grown over a multi electrode array (MEA, see Figure 1). This enables simultaneous measurement from multiple electrodes, as well as network manipulati ...
Full Text - Anesth Pain Med
... with focal transient neurological deficit such as: visual, speech and/or language, sensory, motor, brainstem or retinal deficit (1). The widely accepted theory suggests that cortical spreading depression (CSD), a wave of neuronal hyperactivity followed by an area of cortical depression, accounts for ...
... with focal transient neurological deficit such as: visual, speech and/or language, sensory, motor, brainstem or retinal deficit (1). The widely accepted theory suggests that cortical spreading depression (CSD), a wave of neuronal hyperactivity followed by an area of cortical depression, accounts for ...
Supplementary Motor Area and Presupplementary Motor Area
... Supplementary Motor Area and Presupplementary Motor Area: Targets of Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Output Dalila Akkal,2 Richard P. Dum,2 and Peter L. Strick1,2,3 1Pittsburgh Veterans Affairs Medical Center, 2Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition and Department of Neurobiology, and 3Department of ...
... Supplementary Motor Area and Presupplementary Motor Area: Targets of Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Output Dalila Akkal,2 Richard P. Dum,2 and Peter L. Strick1,2,3 1Pittsburgh Veterans Affairs Medical Center, 2Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition and Department of Neurobiology, and 3Department of ...
Neurotransmitter Profile of Saccadic Omnipause Neurons in
... 1989; Langer and Kaneko, 1990), the exact sources of inputs and synaptic mechanisms producing the characteristic firing pattern of OPNs are still not clear. Pharmacological experiments in cats suggest that the tonic activity of OPNs is controlled by inhibitory serotoninergic inputs. while the genera ...
... 1989; Langer and Kaneko, 1990), the exact sources of inputs and synaptic mechanisms producing the characteristic firing pattern of OPNs are still not clear. Pharmacological experiments in cats suggest that the tonic activity of OPNs is controlled by inhibitory serotoninergic inputs. while the genera ...
This article was originally published in the
... sensory cues, rewards, and motor responses were systematically altered. Monkeys were presented with one of two cues that instructed one of two motor responses (either saccade or maintain fixation), and each motor response either was or was not associated with a reward. All combinations of parameters ...
... sensory cues, rewards, and motor responses were systematically altered. Monkeys were presented with one of two cues that instructed one of two motor responses (either saccade or maintain fixation), and each motor response either was or was not associated with a reward. All combinations of parameters ...
Spike-Timing Theory of Working Memory
... In the model presented here, PNGs get spontaneously reactivated due to stochastic synaptic noise. Short-term strengthening of the synapses of selected PNGs can bias these reactivations, i.e., increase the reactivation rate of the selected PNGs, which results in activity patterns similar to those obs ...
... In the model presented here, PNGs get spontaneously reactivated due to stochastic synaptic noise. Short-term strengthening of the synapses of selected PNGs can bias these reactivations, i.e., increase the reactivation rate of the selected PNGs, which results in activity patterns similar to those obs ...
Mirror neurons in humans: Consisting or confounding
... for action observation. Therefore, a close inspection of the results presented in this study does not seem to support ‘mirror’ properties within the human brain. Grezes, Armony, Rowe, and Passingham (2003) conducted an fMRI study specifically designed to test ‘mirror’ activity within the human brain. ...
... for action observation. Therefore, a close inspection of the results presented in this study does not seem to support ‘mirror’ properties within the human brain. Grezes, Armony, Rowe, and Passingham (2003) conducted an fMRI study specifically designed to test ‘mirror’ activity within the human brain. ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.