construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... in the future will require higher skills and an understanding of mathematics and science. As a result of the growing number of careers that require solid science and mathematics training, the methods of science education are undergoing major reform. To adequately equip students for technologically ...
... in the future will require higher skills and an understanding of mathematics and science. As a result of the growing number of careers that require solid science and mathematics training, the methods of science education are undergoing major reform. To adequately equip students for technologically ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... in the future will require higher skills and an understanding of mathematics and science. As a result of the growing number of careers that require solid science and mathematics training, the methods of science education are undergoing major reform. To adequately equip students for technologically ...
... in the future will require higher skills and an understanding of mathematics and science. As a result of the growing number of careers that require solid science and mathematics training, the methods of science education are undergoing major reform. To adequately equip students for technologically ...
UNRAVELING THE SENSE OF SMELL
... change in the structure of an odorant can change its perceived odor. For example, the close relative of a chemical that is perceived as pear can have the scent of an apple. In addition to odorants, the olfactory system detects pheromones, chemicals that are released from animals and act on members o ...
... change in the structure of an odorant can change its perceived odor. For example, the close relative of a chemical that is perceived as pear can have the scent of an apple. In addition to odorants, the olfactory system detects pheromones, chemicals that are released from animals and act on members o ...
Electrical membrane properties of rat subthalamic neurons in an in
... and the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus are exotatoryt~ _~u A review of the hterature reveals that there is only a cursory report on the electrophysiologlcal properties of STH neurons 15. Therefore, we have studied the electrophystologlcal characterisUcs of STH neurons in detail using an m vitro ...
... and the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus are exotatoryt~ _~u A review of the hterature reveals that there is only a cursory report on the electrophysiologlcal properties of STH neurons 15. Therefore, we have studied the electrophystologlcal characterisUcs of STH neurons in detail using an m vitro ...
Sound processing by local neural populations in the
... recordings, and large-scale activity monitored using electrophysiological or imaging techniques which sample and/or average the signal over hundreds of micrometers or more. Studies at both of these levels of resolution have revealed important findings about the AC. For example, single-cell studies h ...
... recordings, and large-scale activity monitored using electrophysiological or imaging techniques which sample and/or average the signal over hundreds of micrometers or more. Studies at both of these levels of resolution have revealed important findings about the AC. For example, single-cell studies h ...
Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Integration in Hypothalamic
... and whether the biosynthesis of these peptides by external and internal stimuli might represent a mechanism by which these neurons produce an integrated response. The purpose of this paper is to illustrate our research strategy by describing these two separate projects. These projects are focused on ...
... and whether the biosynthesis of these peptides by external and internal stimuli might represent a mechanism by which these neurons produce an integrated response. The purpose of this paper is to illustrate our research strategy by describing these two separate projects. These projects are focused on ...
The habenular nuclei - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... the midbrain/hindbrain. In this review, we will focus on the anatomy and connectivity of the habenulae and the interpeduncular nucleus (IPN). The latter is a major target of habenular efferent connectivity in all vertebrates and consequently plays a pivotal role in the modulation of nuclei downstrea ...
... the midbrain/hindbrain. In this review, we will focus on the anatomy and connectivity of the habenulae and the interpeduncular nucleus (IPN). The latter is a major target of habenular efferent connectivity in all vertebrates and consequently plays a pivotal role in the modulation of nuclei downstrea ...
[PDF]
... (fMRI), has enabled the characterization of large-scale neural systems involved in human cognitive processes. A set of regions that has been identified via functional MRI (fMRI) and includes hubs around the anterior and posterior medial cortex, bilateral temporal lobes, as well as superior frontal a ...
... (fMRI), has enabled the characterization of large-scale neural systems involved in human cognitive processes. A set of regions that has been identified via functional MRI (fMRI) and includes hubs around the anterior and posterior medial cortex, bilateral temporal lobes, as well as superior frontal a ...
Chapter 3
... participate in control of movement by providing input to lower motor neurons (Figure 16.7). – Local circuit neurons are located close to lower motor neuron cell bodies in the brain stem and spinal cord. – Local circuit neurons and lower motor neurons receive input from upper motor neurons. – Neurons ...
... participate in control of movement by providing input to lower motor neurons (Figure 16.7). – Local circuit neurons are located close to lower motor neuron cell bodies in the brain stem and spinal cord. – Local circuit neurons and lower motor neurons receive input from upper motor neurons. – Neurons ...
Pain in Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) and Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
... •Neuropathic hyperalgesia can be both primary and secondary •Primary hyperalgesia occurs directly at the site of injury •Secondary hyperalgesia involves undamaged nociceptive fibers near the injury site and is thought to involve central nervous system sensitization •Secondary hyperalgesia responds o ...
... •Neuropathic hyperalgesia can be both primary and secondary •Primary hyperalgesia occurs directly at the site of injury •Secondary hyperalgesia involves undamaged nociceptive fibers near the injury site and is thought to involve central nervous system sensitization •Secondary hyperalgesia responds o ...
Chapter 3
... participate in control of movement by providing input to lower motor neurons (Figure 16.7). – Local circuit neurons are located close to lower motor neuron cell bodies in the brain stem and spinal cord. – Local circuit neurons and lower motor neurons receive input from upper motor neurons. – Neurons ...
... participate in control of movement by providing input to lower motor neurons (Figure 16.7). – Local circuit neurons are located close to lower motor neuron cell bodies in the brain stem and spinal cord. – Local circuit neurons and lower motor neurons receive input from upper motor neurons. – Neurons ...
Cuneiform Neurons Activated during
... Control animals. In previous work (Morales et al., 1999), we compared data from AS-carbachol cats with those from animals in quiet wakef ulness. In the present report, we examined, as before, two control cats in which the same procedures were followed, except that 0.1 l of saline was injected inste ...
... Control animals. In previous work (Morales et al., 1999), we compared data from AS-carbachol cats with those from animals in quiet wakef ulness. In the present report, we examined, as before, two control cats in which the same procedures were followed, except that 0.1 l of saline was injected inste ...
INFUSION OF NERVE GROWTH FACTOR (NGF) INTO KITTEN
... performed over primary visual cortex. Animals were then paralyzed by intravenous delivery of gallamine triethiodide (10 mg/ kg/h) dissolved in 5% Ringer's solution with dextrose and were switched to arti¢cial respiration. Following an initial bolus of 15 mg/kg, the dura was retracted, and gallamine ...
... performed over primary visual cortex. Animals were then paralyzed by intravenous delivery of gallamine triethiodide (10 mg/ kg/h) dissolved in 5% Ringer's solution with dextrose and were switched to arti¢cial respiration. Following an initial bolus of 15 mg/kg, the dura was retracted, and gallamine ...
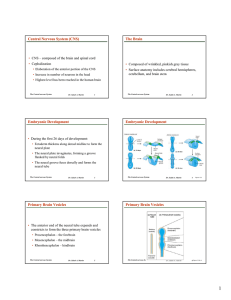
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... the midbrain. In rodents, these axons are found in three distinct groups. In other species there are 1-3 groups. The AOT axons carry information about movement throughout large receptive fields, as occurs during head movements. See “Cortical Neuromodulation during sleep.”In the midbrain reticular fo ...
... the midbrain. In rodents, these axons are found in three distinct groups. In other species there are 1-3 groups. The AOT axons carry information about movement throughout large receptive fields, as occurs during head movements. See “Cortical Neuromodulation during sleep.”In the midbrain reticular fo ...
Neuronal Interaction Dynamics in Cat Primary Visual Cortex
... During the recent years neurons of the visual cortex have been extensively investigated according to a diversity of feature attributes. In search of optimal stimulus conditions, they were classified with respect to differing receptive field (RF) properties. However, RFs can exhibit complex, nonpredi ...
... During the recent years neurons of the visual cortex have been extensively investigated according to a diversity of feature attributes. In search of optimal stimulus conditions, they were classified with respect to differing receptive field (RF) properties. However, RFs can exhibit complex, nonpredi ...
The Control of Voluntary Eye Movements: New Perspectives
... The Control of Voluntary Eye Movements: New Perspectives RICHARD J. KRAUZLIS Systems Neurobiology Laboratory Salk Institute for Biological Studies ...
... The Control of Voluntary Eye Movements: New Perspectives RICHARD J. KRAUZLIS Systems Neurobiology Laboratory Salk Institute for Biological Studies ...
Fig. 2 - eNeuro
... M), which specifically binds with nicotinic receptors at the tadpole neuromuscular junctions (Li et al., 2004b; Li et al., 2014). After immobilization with ␣-bungarotoxin, the tadpole was re-pinned in the dissection bath and further cuts were made to remove ependymal cells from the inside of the hi ...
... M), which specifically binds with nicotinic receptors at the tadpole neuromuscular junctions (Li et al., 2004b; Li et al., 2014). After immobilization with ␣-bungarotoxin, the tadpole was re-pinned in the dissection bath and further cuts were made to remove ependymal cells from the inside of the hi ...
Neural correlates of a decision in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of
... regardless of whether the evidence was strong or weak, and whether it was interpreted correctly or incorrectly. These properties are evident in the PFC response. Motion strength affected the response of many PFC neurons (Fig. 5a and b). For this analysis, we selected neurons that predicted the monke ...
... regardless of whether the evidence was strong or weak, and whether it was interpreted correctly or incorrectly. These properties are evident in the PFC response. Motion strength affected the response of many PFC neurons (Fig. 5a and b). For this analysis, we selected neurons that predicted the monke ...
Mirror Neurons Responding to Observation of Actions Made with
... food with the stick to the whole holding phase. In contrast, when the experimenter grasped food with the hand (B), during the approaching and grasping phase, there was a complete inhibition of the neuron response. However, the holding phase, similarly to condition A, was excitatory. Thus, the discri ...
... food with the stick to the whole holding phase. In contrast, when the experimenter grasped food with the hand (B), during the approaching and grasping phase, there was a complete inhibition of the neuron response. However, the holding phase, similarly to condition A, was excitatory. Thus, the discri ...
Down - 서울대 : Biointelligence lab
... all presynaptic spike trains) in simulation of an IF-neuron with 1000 input channels. The spike trains that lead to the results shown by stars were generated with each weight value fixed to value 0.015. The cross-correlations are consistent with zero when considered within the variance indicated by ...
... all presynaptic spike trains) in simulation of an IF-neuron with 1000 input channels. The spike trains that lead to the results shown by stars were generated with each weight value fixed to value 0.015. The cross-correlations are consistent with zero when considered within the variance indicated by ...
studying the isolated central nervous system
... their pupils. One became interested in the subject, read around it, and in the end knew much more than would be required by the yearly examination. Subjects, people and places, all came to life and were as real to me as the everyday events. In the sixth form my main teacher, "Jasper" Machin did not ...
... their pupils. One became interested in the subject, read around it, and in the end knew much more than would be required by the yearly examination. Subjects, people and places, all came to life and were as real to me as the everyday events. In the sixth form my main teacher, "Jasper" Machin did not ...
Critical role of extracellularly secreted neuronal pentraxin 1 in
... Background: Developing brain is highly susceptible to hypoxic-ischemic injury leading to severe neurological disabilities in surviving infants and children. Previously we reported induction of neuronal pentraxin 1 (NP1) in hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal brain and NP1 co-localization with the ex ...
... Background: Developing brain is highly susceptible to hypoxic-ischemic injury leading to severe neurological disabilities in surviving infants and children. Previously we reported induction of neuronal pentraxin 1 (NP1) in hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal brain and NP1 co-localization with the ex ...
Central Nervous System (CNS) The Brain Embryonic Development
... • Ascending sensory tract nuclei, including nucleus cuneatus and nucleus gracilis • Cardiovascular control center – adjusts force and rate of heart contraction • Respiratory centers – control rate and depth of ...
... • Ascending sensory tract nuclei, including nucleus cuneatus and nucleus gracilis • Cardiovascular control center – adjusts force and rate of heart contraction • Respiratory centers – control rate and depth of ...
A Model of Prefrontal Cortical Mechanisms for Goal-directed Behavior Michael E. Hasselmo Abstract
... spreads over connections Wg from the goR population in the ‘‘Reward’’ minicolumn to the input population gi in the ‘‘East’’ state minicolumn. These connections were strengthened during previous exploration of the environment (as described in the Methods section below), allowing units in go to activa ...
... spreads over connections Wg from the goR population in the ‘‘Reward’’ minicolumn to the input population gi in the ‘‘East’’ state minicolumn. These connections were strengthened during previous exploration of the environment (as described in the Methods section below), allowing units in go to activa ...
The Cerebellum - krigolson teaching
... the cerebellum arise from the deep nuclei and project through the superior cerebellar peduncle. The main exception is a group of Purkinje cells in the flocculonodular lobe that projects to vestibular nuclei in the brain stem. The surface of the cerebellum is highly convoluted, with many parallel fol ...
... the cerebellum arise from the deep nuclei and project through the superior cerebellar peduncle. The main exception is a group of Purkinje cells in the flocculonodular lobe that projects to vestibular nuclei in the brain stem. The surface of the cerebellum is highly convoluted, with many parallel fol ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.





![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/018857880_1-2902819511122c26b8adde597bea8c3a-300x300.png)