The Major Transitions in Evolution
... absent in drm2 mutants and ago4 mutants, it is possible that DNA methylation (blue circles) also stimulates siRNA generation and reinforces silencing. ...
... absent in drm2 mutants and ago4 mutants, it is possible that DNA methylation (blue circles) also stimulates siRNA generation and reinforces silencing. ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... absent in drm2 mutants and ago4 mutants, it is possible that DNA methylation (blue circles) also stimulates siRNA generation and reinforces silencing. ...
... absent in drm2 mutants and ago4 mutants, it is possible that DNA methylation (blue circles) also stimulates siRNA generation and reinforces silencing. ...
to get the file - Chair of Computational Biology
... The genomes of several plants have been sequenced, and those of many others are under way. But genetic information alone cannot fully address the fundamental question of how genes are differentially expressed during cell differentiation and plant development, as the DNA sequences in all cells in a p ...
... The genomes of several plants have been sequenced, and those of many others are under way. But genetic information alone cannot fully address the fundamental question of how genes are differentially expressed during cell differentiation and plant development, as the DNA sequences in all cells in a p ...
Methylation of an upstream Alu sequence on the Imprinted H19
... Genomic imprinting involves “marking” parental alleles as either maternal or paternal. Such imprints are established during gamete production and involve differential DNA methylation. Unfortunately, however, the exact imprinting mechanism is unknown. DNA methylation is aided by the enzyme DNA methyl ...
... Genomic imprinting involves “marking” parental alleles as either maternal or paternal. Such imprints are established during gamete production and involve differential DNA methylation. Unfortunately, however, the exact imprinting mechanism is unknown. DNA methylation is aided by the enzyme DNA methyl ...
Epigenetics seminar 9-7-2014
... were once thought of as ‘junk’, but it is now found to have important roles in regulating how, where, & when genes are expressed. •An NIH study found large number of disease-associated GWAS variants located in regulatory DNA regions that are active during foetal development suggesting that environme ...
... were once thought of as ‘junk’, but it is now found to have important roles in regulating how, where, & when genes are expressed. •An NIH study found large number of disease-associated GWAS variants located in regulatory DNA regions that are active during foetal development suggesting that environme ...
DNA
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
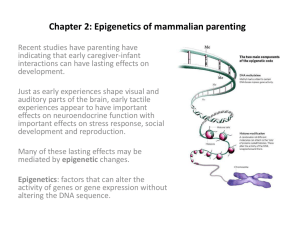
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... • Decrease hippocampal plasticity – reduced learning and memory capacity • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
... • Decrease hippocampal plasticity – reduced learning and memory capacity • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
Test Study Guide
... 15. What is the center of the chromosome called? 16. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 17. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replication? 18. What enzyme attempts to “fix” this problem? How? ...
... 15. What is the center of the chromosome called? 16. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 17. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replication? 18. What enzyme attempts to “fix” this problem? How? ...
name period ______ date
... 10. There is a diagram of DNA Replication on the back of this paper. Color each part one specific color. Identify those colors on the key at the bottom of the diagram. Explain what you think is going on during replication. ...
... 10. There is a diagram of DNA Replication on the back of this paper. Color each part one specific color. Identify those colors on the key at the bottom of the diagram. Explain what you think is going on during replication. ...
Researchers ACT on DNA Storage
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
Epigenetics Glossary FINAL
... CpG island shores: Regions of DNA that lie at the outskirts of CpG islands rather than in the islands itself. They have variable methylation and have been proposed to be enriched in methylation differences between tissue types or between normal and cancer samples. CpG island: Regions of DNA enriched ...
... CpG island shores: Regions of DNA that lie at the outskirts of CpG islands rather than in the islands itself. They have variable methylation and have been proposed to be enriched in methylation differences between tissue types or between normal and cancer samples. CpG island: Regions of DNA enriched ...
Lecture 7 - Brandeis Life Sciences
... male parent, it is expressed in the heart and no other tissue. If it is inherited from the female parent, it is not expressed at all. This pattern of expression correlates precisely with a parentally imprinted methylation state evident in all tissues. Methylation of the transgene is acquired by its ...
... male parent, it is expressed in the heart and no other tissue. If it is inherited from the female parent, it is not expressed at all. This pattern of expression correlates precisely with a parentally imprinted methylation state evident in all tissues. Methylation of the transgene is acquired by its ...
Two Epigenetic Mechanisms
... Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cells giving rise to gametes ...
... Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cells giving rise to gametes ...
Gender and epigenetics - Association for Contextual Behavioral
... and voluntary exercise, enhances long-term potentiation (LTP) not only in these enriched mice but also in their future offspring through early adolescence, even if the offspring never experience EE. In both generations, LTP induction is augmented by a newly appearing cAMP/p38 MAP kinase-dependent si ...
... and voluntary exercise, enhances long-term potentiation (LTP) not only in these enriched mice but also in their future offspring through early adolescence, even if the offspring never experience EE. In both generations, LTP induction is augmented by a newly appearing cAMP/p38 MAP kinase-dependent si ...
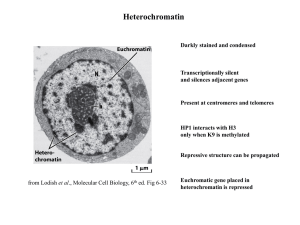
Heterochromatin-2015
... Epigenetically imposed restrictions to plasticity are erased in the germ line ...
... Epigenetically imposed restrictions to plasticity are erased in the germ line ...
centromere
... lipoprotein receptor gene (LDLR) are a common genetic cause of heart disease due to hypercholesterolemia. • The LDLR gene is 45kb long with Alu (highlyrepetitive class) repeats in its introns. Recombination between 2 of these leads to a truncated gene and defective protein. ...
... lipoprotein receptor gene (LDLR) are a common genetic cause of heart disease due to hypercholesterolemia. • The LDLR gene is 45kb long with Alu (highlyrepetitive class) repeats in its introns. Recombination between 2 of these leads to a truncated gene and defective protein. ...
DNA extraction activity
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
Invertebrate epigenomics: the brave new world of
... to have suffered from an evolutionary loss of DNA methylation. One such organism is the nematode C. elegans which, due to its precise developmental lineage map, relatively small genome and amenability to genetic manipulation, has become one of the all-time favorite epigenetic models. The review by G ...
... to have suffered from an evolutionary loss of DNA methylation. One such organism is the nematode C. elegans which, due to its precise developmental lineage map, relatively small genome and amenability to genetic manipulation, has become one of the all-time favorite epigenetic models. The review by G ...
THE STUDY OF HERITABLE CHANGES IN GENE FUNCTION THAT
... Higher than normal obesity rates as adults; higher rates of diabetes, heart disease and schizophrenia. ...
... Higher than normal obesity rates as adults; higher rates of diabetes, heart disease and schizophrenia. ...
Teacher PowerPoint - UNC Institute for the Environment
... Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cells giving rise to gametes ...
... Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cells giving rise to gametes ...
Companion PowerPoint slide
... Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cells giving rise to gametes ...
... Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cells giving rise to gametes ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... d. degradation of the transposon while it is moving 7. Oxidative stress can damage DNA by a. causing single-strand breaks b, causing double-strand breaks c. oxidation of guanine to 8-oxo-guanine d. b and c e. all of the above 8. Which of the following is not true regarding DNA photolyases a. repair ...
... d. degradation of the transposon while it is moving 7. Oxidative stress can damage DNA by a. causing single-strand breaks b, causing double-strand breaks c. oxidation of guanine to 8-oxo-guanine d. b and c e. all of the above 8. Which of the following is not true regarding DNA photolyases a. repair ...
press alert - the Gregor Mendel Institute
... Transposons are parasitic mobile DNA elements, contained in large quantities in plant and animal DNA, which normally move from place to place within the genome, unless inactivated by defense mechanisms such as DNA methylation. But besides acting as harmful mutators, transposons contribute to importa ...
... Transposons are parasitic mobile DNA elements, contained in large quantities in plant and animal DNA, which normally move from place to place within the genome, unless inactivated by defense mechanisms such as DNA methylation. But besides acting as harmful mutators, transposons contribute to importa ...
Nature Rev.Genet. 8
... by progressive restriction of cellular plasticity accompanied by acquisition of epigenetic modifications ...
... by progressive restriction of cellular plasticity accompanied by acquisition of epigenetic modifications ...
Obesity caused BBC tumors to form at a faster rate compared to lean
... extracting DNA or RNA and hybridizing different pieces representing different genes to a transcript • It allows us to measure how many copies of each gene is expressed • This can tell us whether there is no, some or a lot of RNA transcript present ...
... extracting DNA or RNA and hybridizing different pieces representing different genes to a transcript • It allows us to measure how many copies of each gene is expressed • This can tell us whether there is no, some or a lot of RNA transcript present ...
DNA methylation

DNA methylation is a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA. Methylation modifies the function of the DNA, typically acting to suppress gene transcription. DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, suppression of repetitive elements, and carcinogenesis.Two of DNA's four nucleotides, cytosine and adenine, can be methylated. Adenine methylation is restricted to prokaryotes.The rate of cytosine DNA methylation differs strongly between species: 14% of cytosines are methylated in Arabidopsis thaliana, 4% in Mus musculus, 2.3% in Escherichia coli, 0.03% in Drosophila, and virtually none (< 0.0002%) in yeast species.DNA methylation can stably alter the expression of genes in cells as cells divide and differentiate from embryonic stem cells into specific tissues. The resulting change is normally permanent and unidirectional, preventing a cell from reverting to a stem cell or converting into a different cell type. However, DNA methylation can be removed either passively, by dilution as cells divide, or by a faster, active, process. The latter process occurs via hydroxylation of the methyl groups that are to be removed, rather than by complete removal of methyl groups. DNA methylation is typically removed during zygote formation and re-established through successive cell divisions during development. Methylation modifications that regulate gene expression are usually heritable through mitotic cell division; some methylation is also heritable through the specialized meiotic cell division that creates egg and sperm cells, resulting in genomic imprinting. DNA methylation suppresses the expression of endogenous retroviral genes and other harmful stretches of DNA that have been incorporated into the host genome over time. DNA methylation also forms the basis of chromatin structure, which enables a single cell to grow into multiple organs or perform multiple functions. DNA methylation also plays a crucial role in the development of nearly all types of cancer.DNA methylation at the 5 position of cytosine has the specific effect of reducing gene expression and has been found in every vertebrate examined. In adult somatic cells (cells in the body, not used for reproduction), DNA methylation typically occurs in a CpG dinucleotide context; non-CpG methylation is prevalent in embryonic stem cells, and has also been indicated in neural development.