Biology Name DNA Worksheet Period ______ Use your textbook to
... 12. Several scientists received the Nobel Prize for their contributions to the discovery of DNA structure. One who worked in this area did not receive the Nobel Prize. Who were they, and why weren’t they awarded the prize along with their colleagues? ...
... 12. Several scientists received the Nobel Prize for their contributions to the discovery of DNA structure. One who worked in this area did not receive the Nobel Prize. Who were they, and why weren’t they awarded the prize along with their colleagues? ...
1.3. Identity: Molecules and Cells Study Guide (Fisher)
... electrode. When the electricity is started, they move toward the positive electrode. Smaller bits are lighter and travel faster, so the bits get separated by size. This makes it possible to tell ...
... electrode. When the electricity is started, they move toward the positive electrode. Smaller bits are lighter and travel faster, so the bits get separated by size. This makes it possible to tell ...
1.3. Identity: Molecules and Cells Study Guide
... electrode. When the electricity is started, they move toward the positive electrode. Smaller bits are lighter and travel faster, so the bits get separated by size. This makes it possible to tell ...
... electrode. When the electricity is started, they move toward the positive electrode. Smaller bits are lighter and travel faster, so the bits get separated by size. This makes it possible to tell ...
DNA Technology Notes
... Medicine (insulin) Cures for disease Gene therapy Criminal cases agriculture ...
... Medicine (insulin) Cures for disease Gene therapy Criminal cases agriculture ...
MTHFr, Methylation and Metals
... Although inorganic arsenic is methylated enzymatically by arsenic methyltransferases, which have been found in many mammalian livers, the detection of such enzymes has not been successful in surgically removed human livers. Results of the present experiments demonstrated that methylvitamin B12 (meth ...
... Although inorganic arsenic is methylated enzymatically by arsenic methyltransferases, which have been found in many mammalian livers, the detection of such enzymes has not been successful in surgically removed human livers. Results of the present experiments demonstrated that methylvitamin B12 (meth ...
Increased BDNF Promoter Methylation in the
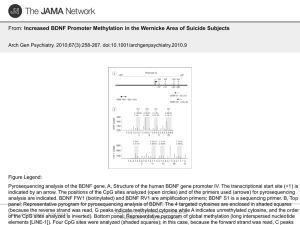
... Pyrosequencing analysis of the BDNF gene. A, Structure of the human BDNF gene promoter IV. The transcriptional start site (+1) is indicated by an arrow. The positions of the CpG sites analyzed (open circles) and of the primers used (arrows) for pyrosequencing analysis are indicated. BDNF FW1 (biotin ...
... Pyrosequencing analysis of the BDNF gene. A, Structure of the human BDNF gene promoter IV. The transcriptional start site (+1) is indicated by an arrow. The positions of the CpG sites analyzed (open circles) and of the primers used (arrows) for pyrosequencing analysis are indicated. BDNF FW1 (biotin ...
What Do Studies of Insect Polyphenisms Tell Us about
... the impact of diet on the epigenome. DNA methylation, the reversible addition of a methyl group to a cytosine residue in the DNA, is one way in which larvae respond to differences in their nutrition. Reducing the expression of the enzyme that establishes DNA methylation marks (Dnmt3) by RNA interfer ...
... the impact of diet on the epigenome. DNA methylation, the reversible addition of a methyl group to a cytosine residue in the DNA, is one way in which larvae respond to differences in their nutrition. Reducing the expression of the enzyme that establishes DNA methylation marks (Dnmt3) by RNA interfer ...
UV-Induced DNA Damage and Repair
... exposure decreases to background over 2 hours in E. coli. Many organisms exhibit photoreactivation. Photoreactivation is due the activity of a class of enzymes known as DNA photolyases. CPD Photolyases Single subunit protein. Bind to CPD lesions in dark. Catalyze reversal following exposure to 370 n ...
... exposure decreases to background over 2 hours in E. coli. Many organisms exhibit photoreactivation. Photoreactivation is due the activity of a class of enzymes known as DNA photolyases. CPD Photolyases Single subunit protein. Bind to CPD lesions in dark. Catalyze reversal following exposure to 370 n ...
Inglés - SciELO España
... behaviors of the disease. Epigenetics is a term used to describe the mechanisms than may modify at various levels the expression of specific genes without altering the corresponding DNA sequence, including DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, and other processes mediated by non-coding RNA molecule ...
... behaviors of the disease. Epigenetics is a term used to describe the mechanisms than may modify at various levels the expression of specific genes without altering the corresponding DNA sequence, including DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, and other processes mediated by non-coding RNA molecule ...
Chapter 12 Review PPT
... _________________ are weak bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together, but also allow the DNA to separate and replicate. Hydrogen bonds ...
... _________________ are weak bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together, but also allow the DNA to separate and replicate. Hydrogen bonds ...
point of view that is personal rather than scientific
... _________________ are weak bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together, but also allow the DNA to separate and replicate. Hydrogen bonds ...
... _________________ are weak bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together, but also allow the DNA to separate and replicate. Hydrogen bonds ...
The Seductive Allure of Behavioral Epigenetics. Science.
... of Alabama, Birmingham. Sweatt’s lab and others have since found evidence that epigenetic mechanisms play important roles in learning and memory in adult rodents. One recent study even suggests that these mechanisms may help explain why memory declines with age. Sweatt’s team recently discovered tha ...
... of Alabama, Birmingham. Sweatt’s lab and others have since found evidence that epigenetic mechanisms play important roles in learning and memory in adult rodents. One recent study even suggests that these mechanisms may help explain why memory declines with age. Sweatt’s team recently discovered tha ...
R 9.1
... biotechnology. Some examples include sequencing genes, copying (or cloning) genes, chemically mutating genes, analyzing and organizing genetic information with computer databases, and transferring genes between organisms. In many of these research areas, DNA must first be cut so that it can be studi ...
... biotechnology. Some examples include sequencing genes, copying (or cloning) genes, chemically mutating genes, analyzing and organizing genetic information with computer databases, and transferring genes between organisms. In many of these research areas, DNA must first be cut so that it can be studi ...
The Importance of Epigenetic Phenomena in Regulating Activity of
... DNA methylation may lead to harmful consequences, such as cancer, autoimmune disease, and a range of birth defects. A second epigenetic mechanism is histone modification. Histones are chromosomal proteins that are important for DNA packaging into the chromosome structure. Strings of DNA wrap around ...
... DNA methylation may lead to harmful consequences, such as cancer, autoimmune disease, and a range of birth defects. A second epigenetic mechanism is histone modification. Histones are chromosomal proteins that are important for DNA packaging into the chromosome structure. Strings of DNA wrap around ...
Procaryotic chromosome
... 30nm fiber is interrupted by the binding of a sequence-specific regulatory protein - Longer regions of DNase I hypersensitivity where transcription is taking place ...
... 30nm fiber is interrupted by the binding of a sequence-specific regulatory protein - Longer regions of DNase I hypersensitivity where transcription is taking place ...
regulatory transcription factors
... chromosomes during interphase – During gene activation, tightly packed chromatin must be converted to an open conformation in order for transcription to occur ...
... chromosomes during interphase – During gene activation, tightly packed chromatin must be converted to an open conformation in order for transcription to occur ...
Thesis
... positioning and compaction, thus play pivotal roles in chromatin remodelling and in gene regulation. Histone modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitinylation, etc., among which histone lysine methylation plays essential roles in the epigenetic processes. Histone l ...
... positioning and compaction, thus play pivotal roles in chromatin remodelling and in gene regulation. Histone modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitinylation, etc., among which histone lysine methylation plays essential roles in the epigenetic processes. Histone l ...
Part I, for Exam 1: 1. Based on Chargaff`s rules, which of the
... act at the membrane to restrict the passage of certain molecules into the cell. are highly specialized ribonucleases that degrade mRNA soon after its synthesis. are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases. are very specific proteases that cleave peptides at only certain sequences. catalyze the addition ...
... act at the membrane to restrict the passage of certain molecules into the cell. are highly specialized ribonucleases that degrade mRNA soon after its synthesis. are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases. are very specific proteases that cleave peptides at only certain sequences. catalyze the addition ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... that bind to unmethylated CpGs and initiate gene transcription. In contrast, methylated CpGs are generally associated with silent DNA, can block methylation-sensitive proteins and can be easily mutated. The loss of normal DNA methylation patterns is the best understood epigenetic cause of disease. I ...
... that bind to unmethylated CpGs and initiate gene transcription. In contrast, methylated CpGs are generally associated with silent DNA, can block methylation-sensitive proteins and can be easily mutated. The loss of normal DNA methylation patterns is the best understood epigenetic cause of disease. I ...
Epigenetics and Culture
... • DNA contains nucleotides which code for amino acids which eventually make a protein • Together, all of the nucleotides needed to make that protein together are a gene • Genes can be turned on or off depending on what type of cell it is and what the needs of that cell are ...
... • DNA contains nucleotides which code for amino acids which eventually make a protein • Together, all of the nucleotides needed to make that protein together are a gene • Genes can be turned on or off depending on what type of cell it is and what the needs of that cell are ...
Methylation
... allowed to bind protein. Bound and unbound populations are separated, and strands are cleaved at the modified bases. Bases critical for protein binding will not appear as bands in the bound population. Methylation and uracil interference techniques differ in the base(s) targeted, and in the method u ...
... allowed to bind protein. Bound and unbound populations are separated, and strands are cleaved at the modified bases. Bases critical for protein binding will not appear as bands in the bound population. Methylation and uracil interference techniques differ in the base(s) targeted, and in the method u ...
Dr Anthony Isles
... – histone modifications • Modifications of residues in the histone ‘tails’ • >40 possible modifications • Modification alter 3-D structure and make DNA more, or less, accessible • Acetylation found in regions of increased gene expression DNA-methylation and chromatin interact – differential recruitm ...
... – histone modifications • Modifications of residues in the histone ‘tails’ • >40 possible modifications • Modification alter 3-D structure and make DNA more, or less, accessible • Acetylation found in regions of increased gene expression DNA-methylation and chromatin interact – differential recruitm ...
DNA REPLICATION HANDOUT
... 1) Template strands: Original DNA strands that were ripped apart. 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running ...
... 1) Template strands: Original DNA strands that were ripped apart. 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running ...
DNA methylation

DNA methylation is a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA. Methylation modifies the function of the DNA, typically acting to suppress gene transcription. DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, suppression of repetitive elements, and carcinogenesis.Two of DNA's four nucleotides, cytosine and adenine, can be methylated. Adenine methylation is restricted to prokaryotes.The rate of cytosine DNA methylation differs strongly between species: 14% of cytosines are methylated in Arabidopsis thaliana, 4% in Mus musculus, 2.3% in Escherichia coli, 0.03% in Drosophila, and virtually none (< 0.0002%) in yeast species.DNA methylation can stably alter the expression of genes in cells as cells divide and differentiate from embryonic stem cells into specific tissues. The resulting change is normally permanent and unidirectional, preventing a cell from reverting to a stem cell or converting into a different cell type. However, DNA methylation can be removed either passively, by dilution as cells divide, or by a faster, active, process. The latter process occurs via hydroxylation of the methyl groups that are to be removed, rather than by complete removal of methyl groups. DNA methylation is typically removed during zygote formation and re-established through successive cell divisions during development. Methylation modifications that regulate gene expression are usually heritable through mitotic cell division; some methylation is also heritable through the specialized meiotic cell division that creates egg and sperm cells, resulting in genomic imprinting. DNA methylation suppresses the expression of endogenous retroviral genes and other harmful stretches of DNA that have been incorporated into the host genome over time. DNA methylation also forms the basis of chromatin structure, which enables a single cell to grow into multiple organs or perform multiple functions. DNA methylation also plays a crucial role in the development of nearly all types of cancer.DNA methylation at the 5 position of cytosine has the specific effect of reducing gene expression and has been found in every vertebrate examined. In adult somatic cells (cells in the body, not used for reproduction), DNA methylation typically occurs in a CpG dinucleotide context; non-CpG methylation is prevalent in embryonic stem cells, and has also been indicated in neural development.