Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... Neural comm. ii After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities ca ...
... Neural comm. ii After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities ca ...
Altman presentation - NeuronDevelopment.org
... autism, or degenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease? ...
... autism, or degenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease? ...
The Nervous System funtions and neuron
... Histology of the Neuron 3. Axons in CNS a. Myelin is produced by oligodendrocyte NOT schwann cells b. Myelinated nerve bundles are referred to as ...
... Histology of the Neuron 3. Axons in CNS a. Myelin is produced by oligodendrocyte NOT schwann cells b. Myelinated nerve bundles are referred to as ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... that travels down the axon. It is real electricity, capable of lighting up a light-bulb (if coupled with another handful of neurons). Refractory period = the “recharging phase” when a neuron after firing cannot immediately generate another action potential. Resting potential = state where neuron is ...
... that travels down the axon. It is real electricity, capable of lighting up a light-bulb (if coupled with another handful of neurons). Refractory period = the “recharging phase” when a neuron after firing cannot immediately generate another action potential. Resting potential = state where neuron is ...
Supporting Information S1.
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
Know Your Neurons: How to Classify Different Types of Neurons in
... catalogue neurons in their many forms—somewhat like the way scientists have classed living things into families and species and subspecies—you're going to need a lot more categories. Neurons differ from one another structurally, functionally and genetically, as well as in how they form connections w ...
... catalogue neurons in their many forms—somewhat like the way scientists have classed living things into families and species and subspecies—you're going to need a lot more categories. Neurons differ from one another structurally, functionally and genetically, as well as in how they form connections w ...
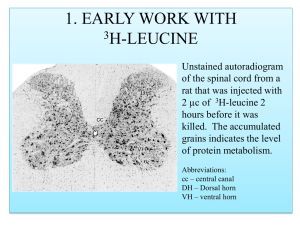
They Come From the Cortex - American Association of Sleep
... cell currents (produced by ionic channel activation) may contribute to the EEG but is still under investigation. Action potentials were once thought to contribute to the EEG but recently have been dismissed as their temporal limits are too short. Fig. 1 Pyramidal Cell ...
... cell currents (produced by ionic channel activation) may contribute to the EEG but is still under investigation. Action potentials were once thought to contribute to the EEG but recently have been dismissed as their temporal limits are too short. Fig. 1 Pyramidal Cell ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... between excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the rodent hippocampus. Our work describes a new form of short-term plasticity of inhibitory synapses that involves glutamate receptors, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. These receptors are located on the terminal axons of inhibitory n ...
... between excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the rodent hippocampus. Our work describes a new form of short-term plasticity of inhibitory synapses that involves glutamate receptors, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. These receptors are located on the terminal axons of inhibitory n ...
Neurons
... ALL-OR-NONE LAW The neural impulse is like a gun, either it fires or it doesn’t fire Action potentials are all the same size as well ...
... ALL-OR-NONE LAW The neural impulse is like a gun, either it fires or it doesn’t fire Action potentials are all the same size as well ...
KC Kajander GJ Giesler, Jr. KJ Gingrich JH Byrne YS Chan J
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
Cell-Type Specific Properties of Pyramidal
... these 2 genes is shown to identify L5 pyramidal neurons in the primary somatosensory (barrel) cortex (Fig. 1A,B), VC (Fig. 3), and other neocortical areas (data not shown). For each mouse line, an average density map was calculated showing the 2D soma distribution in 2 neighboring barrel columns (F ...
... these 2 genes is shown to identify L5 pyramidal neurons in the primary somatosensory (barrel) cortex (Fig. 1A,B), VC (Fig. 3), and other neocortical areas (data not shown). For each mouse line, an average density map was calculated showing the 2D soma distribution in 2 neighboring barrel columns (F ...
Neurons
... Classes of Neurons Afferent- do not have dendrites: transmit impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
... Classes of Neurons Afferent- do not have dendrites: transmit impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
Neuronal Organization of the Cerebellar Cortex
... • They are the most numerous neurons in the brain; about 3/4 of the brain's neurons are cerebellar granule cells. • A granule cell receives excitatory input from mossy fibers and inhibitory input from Golgi cells on its ‘Dendritic Claw’. • The axons of granule cells rise vertically to the molecular ...
... • They are the most numerous neurons in the brain; about 3/4 of the brain's neurons are cerebellar granule cells. • A granule cell receives excitatory input from mossy fibers and inhibitory input from Golgi cells on its ‘Dendritic Claw’. • The axons of granule cells rise vertically to the molecular ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... markers to characterize excitatory and inhibitory neuronal types in BNST. Specifically, I used the transgenic mice expressing fluorescent proteins in excitatory and inhibitory neurons to aid characterization of the BNST. I found that a great majority of BNST neurons are GABAergic inhibitory neurons ...
... markers to characterize excitatory and inhibitory neuronal types in BNST. Specifically, I used the transgenic mice expressing fluorescent proteins in excitatory and inhibitory neurons to aid characterization of the BNST. I found that a great majority of BNST neurons are GABAergic inhibitory neurons ...
Sense of Touch
... • Pain is detected by branching dendrites of sensory neurons that end freely throughout the skin, muscles, and most visceral organs • It is thought that these dendrites are sensitive to chemicals produced as cells are damaged; the greater the cellular damage, the greater the sensation of pain ...
... • Pain is detected by branching dendrites of sensory neurons that end freely throughout the skin, muscles, and most visceral organs • It is thought that these dendrites are sensitive to chemicals produced as cells are damaged; the greater the cellular damage, the greater the sensation of pain ...
Hourly2_2012 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... 2. Dr. Otis P. Kribblekoblitz discovers that a rare subterranean rodent, the shrew-faced schmoo, has a specialized sensory system for detecting microwave radiation. He identifies a thalamic nucleus that serves as the specific relay nucleus for the microwave sense, which he modestly names "the nucleu ...
... 2. Dr. Otis P. Kribblekoblitz discovers that a rare subterranean rodent, the shrew-faced schmoo, has a specialized sensory system for detecting microwave radiation. He identifies a thalamic nucleus that serves as the specific relay nucleus for the microwave sense, which he modestly names "the nucleu ...
Introduction to Neuroanatomy 1
... To understand hierarchical organization of a neural system To begin to become familiar with internal brain structure Organization of visual pathway Segue into… Functional organization of the thalamo-cortical systems Cortical circuitry Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system for touch Spinal and brain ...
... To understand hierarchical organization of a neural system To begin to become familiar with internal brain structure Organization of visual pathway Segue into… Functional organization of the thalamo-cortical systems Cortical circuitry Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system for touch Spinal and brain ...
- Experimental Neurobiology
... [16]. Considering that TCTP was remarkably localized in axon terminals of the mossy fibers (Fig. 3b), there is a possibility that TCTP might be involved in neurotransmitter release in mossy fibers. Given the role of microtubule stabilization and calciumbinding activities [17], we do not exclude the ...
... [16]. Considering that TCTP was remarkably localized in axon terminals of the mossy fibers (Fig. 3b), there is a possibility that TCTP might be involved in neurotransmitter release in mossy fibers. Given the role of microtubule stabilization and calciumbinding activities [17], we do not exclude the ...
CH 3 Practice Test
... Johnny was awakened by a loud, crashing sound in the middle of the night. He was frightened and he jumped out of bed to investigate. Johnny realized that the loud sound was just his cat playing around in the living room. Needless to say, Johnny was extremely relieved. Which subdivision of the nervou ...
... Johnny was awakened by a loud, crashing sound in the middle of the night. He was frightened and he jumped out of bed to investigate. Johnny realized that the loud sound was just his cat playing around in the living room. Needless to say, Johnny was extremely relieved. Which subdivision of the nervou ...
Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
... • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating ...
... • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating ...
neuroplasticity 2016
... • There must be multiple excitatory inputs into the hippocampal neuron that will exhibit LTP • The multiple inputs have an additive effect • The individual inputs do not have to be strong. Even weak inputs can show potentiation is they occur in association with strong inputs ...
... • There must be multiple excitatory inputs into the hippocampal neuron that will exhibit LTP • The multiple inputs have an additive effect • The individual inputs do not have to be strong. Even weak inputs can show potentiation is they occur in association with strong inputs ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... a. Sympathetic division b. Parasympathetic division Sensory (afferent) signals picked up by sensor receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus ...
... a. Sympathetic division b. Parasympathetic division Sensory (afferent) signals picked up by sensor receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus ...
Neuroscience 14b – Organisation of the Cerebral Cortex
... principal source of subcortical efferents i.e. it projects to the brainstem, spinal cord and corpus striatum. 6. Fusiform layer VI, which contains few large pyramidal neurons and many small spindle-like pyramidal and fusiform neurones; it sends efferent fibers to the thalamus, establishing a very pr ...
... principal source of subcortical efferents i.e. it projects to the brainstem, spinal cord and corpus striatum. 6. Fusiform layer VI, which contains few large pyramidal neurons and many small spindle-like pyramidal and fusiform neurones; it sends efferent fibers to the thalamus, establishing a very pr ...