
The Brain and the Neuron (1)
... • Communication goes directly from interneurons in spinal cord to motor neurons to move (reflexively) at the same time the info is going to the brain to be perceived ...
... • Communication goes directly from interneurons in spinal cord to motor neurons to move (reflexively) at the same time the info is going to the brain to be perceived ...
PIPE CLEANER NEURON LESSON PLAN Part A
... Students will form a circle and “send” the message around the room. Each student will be a different part of the neuron and do a different dance to represent the function of that part. 1s – cell body – thinking motion (thinking face—finger tapping lips?) 2s – dendrites – reach out hands, wiggle fing ...
... Students will form a circle and “send” the message around the room. Each student will be a different part of the neuron and do a different dance to represent the function of that part. 1s – cell body – thinking motion (thinking face—finger tapping lips?) 2s – dendrites – reach out hands, wiggle fing ...
Lugaro, Ernesto
... Mazzarello, 1999). Lugaro’s astute retort began by asserting that science needs both facts and hypotheses, and ended (in cauda venenum, the poison in the tail) by pointing out that Golgi himself had put forward some hypotheses, which, though subsequently refuted by new evidence, had nonetheless bee ...
... Mazzarello, 1999). Lugaro’s astute retort began by asserting that science needs both facts and hypotheses, and ended (in cauda venenum, the poison in the tail) by pointing out that Golgi himself had put forward some hypotheses, which, though subsequently refuted by new evidence, had nonetheless bee ...
Neurons - WordPress.com
... • found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. • Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. • Too little also leads to an increased appetite for carbohydrates (starchy foods) and trouble sleeping, which ...
... • found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. • Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. • Too little also leads to an increased appetite for carbohydrates (starchy foods) and trouble sleeping, which ...
Module 3:Neural conduction and transmission Lecture 13
... message into the neurons. Dendrites have small bumps known as dendritic spines which can receive signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at the end of the neurons. These terminal buttons contain neurotransmitters which plays important ...
... message into the neurons. Dendrites have small bumps known as dendritic spines which can receive signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at the end of the neurons. These terminal buttons contain neurotransmitters which plays important ...
05 - Nervous Tissue
... A single branch that arises from a conical projection of the cell body called the Axon Hillock. The axon is usually longer than the dendrites and is therefore called nerve fiber. They’re tubular with a fixed diameter. Their plasma membrane is called Axolemma. Their cytoplasm is called Axoplasm ...
... A single branch that arises from a conical projection of the cell body called the Axon Hillock. The axon is usually longer than the dendrites and is therefore called nerve fiber. They’re tubular with a fixed diameter. Their plasma membrane is called Axolemma. Their cytoplasm is called Axoplasm ...
Striate cortex April 2009
... neurons in an area of the visual cortex are 'responsible' for processing a stimulus of a given size, as a function of visual field location. In the center of the visual field, corresponding to the fovea of the retina, a very large number of neurons process information from a small region of the visu ...
... neurons in an area of the visual cortex are 'responsible' for processing a stimulus of a given size, as a function of visual field location. In the center of the visual field, corresponding to the fovea of the retina, a very large number of neurons process information from a small region of the visu ...
The Nervous System
... LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. LO 3.46 The student is able to describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information to produce a response. LO 3.47 The student is able to create a visual representation of complex nervous systems to describe/explai ...
... LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. LO 3.46 The student is able to describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information to produce a response. LO 3.47 The student is able to create a visual representation of complex nervous systems to describe/explai ...
nervous system development and histology
... tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
... tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
14-Taste & Smell
... From there , second-order neurns give rise to axons that cross the midline and join the Medial Lemniscus to end with fibers of touch , pain and temperature in the Ventrobasal Complex of the Thalamus . From the thalamus third-order neurons arise and ...
... From there , second-order neurns give rise to axons that cross the midline and join the Medial Lemniscus to end with fibers of touch , pain and temperature in the Ventrobasal Complex of the Thalamus . From the thalamus third-order neurons arise and ...
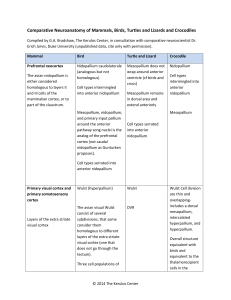
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
... birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
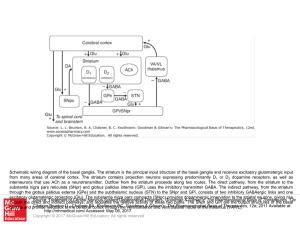
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Development of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses
... L1 immunoglobulin family, along the PC soma-AIS axis, and such gradient requires ankyrinG, a membrane adaptor protein that recruits neurofascin (Ango et al. 2004). Interestingly, another member of the same family of adhesion molecules, CHL1, is localized along Bergmann glia fibers and stellate cells ...
... L1 immunoglobulin family, along the PC soma-AIS axis, and such gradient requires ankyrinG, a membrane adaptor protein that recruits neurofascin (Ango et al. 2004). Interestingly, another member of the same family of adhesion molecules, CHL1, is localized along Bergmann glia fibers and stellate cells ...
neurons and the nervous system
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
Look at brain imaging article.
... research to determine the full extent of cell-type diversity in this small part of the nervous system, because the range of cell types continues to grow as the analysis becomes more refined. Moreover, neuronal cellular architecture is so variable from one region to the next that no single area of th ...
... research to determine the full extent of cell-type diversity in this small part of the nervous system, because the range of cell types continues to grow as the analysis becomes more refined. Moreover, neuronal cellular architecture is so variable from one region to the next that no single area of th ...
The Nervous System
... LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. LO 3.46 The student is able to describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information to produce a response. LO 3.47 The student is able to create a visual representation of complex nervous systems to describe/explai ...
... LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. LO 3.46 The student is able to describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information to produce a response. LO 3.47 The student is able to create a visual representation of complex nervous systems to describe/explai ...
Exercise 5: Synaptic Integration - הפקולטה למדעי הבריאות
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
Long-term depression
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
Nerve
... a) dorsal horn (more pointy) -dorsal horn neurons are responsible for somatosensation, temperature sensation and pain sensation (innervate the skin) b) ventral horn (more rounded) -ventral horn neurons are responsible for movement (innervate skeletal muscle) C. The Brain 1. Cerebral Cortex (slide #1 ...
... a) dorsal horn (more pointy) -dorsal horn neurons are responsible for somatosensation, temperature sensation and pain sensation (innervate the skin) b) ventral horn (more rounded) -ventral horn neurons are responsible for movement (innervate skeletal muscle) C. The Brain 1. Cerebral Cortex (slide #1 ...
15-1 Section Summary
... called neurons, or nerve cells. The message that a neuron carries is called a nerve impulse. A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. The cell body has threadlike extensions. One kind of extension, a dendrite, carries impulses toward the cell body of the neuron. An axon carries impu ...
... called neurons, or nerve cells. The message that a neuron carries is called a nerve impulse. A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. The cell body has threadlike extensions. One kind of extension, a dendrite, carries impulses toward the cell body of the neuron. An axon carries impu ...
Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]
... conduct the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body or soma • Soma – the cell body, contains the nucleus • Axon – long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the soma • Myelin Sheath – electrically insulating layer around the ...
... conduct the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body or soma • Soma – the cell body, contains the nucleus • Axon – long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the soma • Myelin Sheath – electrically insulating layer around the ...
How the Nervous System Works
... environment and converts each stimulus into a nerve impulse. An interneuron is a neuron that carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another. A motor neuron sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, and the muscle or gland then reacts in response. Nerve impulses begin in a dendrite, move toward the c ...
... environment and converts each stimulus into a nerve impulse. An interneuron is a neuron that carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another. A motor neuron sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, and the muscle or gland then reacts in response. Nerve impulses begin in a dendrite, move toward the c ...
biopsychology-2-synaptic-transmission
... AQA A Specification:The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. The process of synaptic transmission, including reference to neurotransmitters, excitation and inhibition. ...
... AQA A Specification:The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. The process of synaptic transmission, including reference to neurotransmitters, excitation and inhibition. ...
The Nervous System
... - is the metabolic center of the neuron (where energy is made). - contains the nucleus (center) of the cell - most proteins needed for functioning are made here - incoming signals from dendrites meet here. ...
... - is the metabolic center of the neuron (where energy is made). - contains the nucleus (center) of the cell - most proteins needed for functioning are made here - incoming signals from dendrites meet here. ...
Development
... Axons (with growth cones on end) form a synapse with other neurons or tissue (e.g. muscle) ...
... Axons (with growth cones on end) form a synapse with other neurons or tissue (e.g. muscle) ...

















![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)



