The Role of sema2a in the Neural Compensatory
... between nerve 5, which carries auditory information, and AN-2, an auditory interneuron receiving this information, in a process known as deafferentation, does not result in the death of the AN-2 neuron (as might be expected) but rather in the growth of the AN-2 dendrites. Where the AN-2 dendrites on ...
... between nerve 5, which carries auditory information, and AN-2, an auditory interneuron receiving this information, in a process known as deafferentation, does not result in the death of the AN-2 neuron (as might be expected) but rather in the growth of the AN-2 dendrites. Where the AN-2 dendrites on ...
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter?
... • decreased glucocorticoid receptor density in HC and PFC ...
... • decreased glucocorticoid receptor density in HC and PFC ...
Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Placement and Functional
... neurons, but Martinotti cells are the ones with the highest spine density with about three to seven spines per 10 μm, approximately one fourth of the density on pyramidal cells (Gulyas et al. 1992; Kawaguchi et al. 2006). Martinotti cells also have longer spines than other spiny interneuron subtypes ...
... neurons, but Martinotti cells are the ones with the highest spine density with about three to seven spines per 10 μm, approximately one fourth of the density on pyramidal cells (Gulyas et al. 1992; Kawaguchi et al. 2006). Martinotti cells also have longer spines than other spiny interneuron subtypes ...
Biology 232 - Request a Spot account
... mechanoreceptors – dendrites or cells that detect mechanical distortions of cell membranes caused by touch or pressure, stretch or bend, vibrations photoreceptors – cells that detect electromagnetic stimuli (light) chemoreceptors – dendrites or cells that detect concentration of specific chemicals p ...
... mechanoreceptors – dendrites or cells that detect mechanical distortions of cell membranes caused by touch or pressure, stretch or bend, vibrations photoreceptors – cells that detect electromagnetic stimuli (light) chemoreceptors – dendrites or cells that detect concentration of specific chemicals p ...
Slide ()
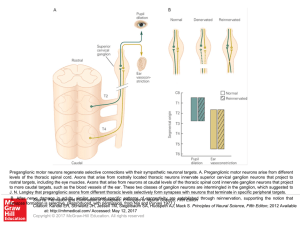
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
LO #1
... 3. Describe how neurotransmitter is released at chemical synapses, including the role of calcium. 4. Describe the mechanism by which neurotransmitter is cleared at chemical synapses. 5. Outline the key differences between chemical and electrical synapses. 6. Describe how temporal and spatial summati ...
... 3. Describe how neurotransmitter is released at chemical synapses, including the role of calcium. 4. Describe the mechanism by which neurotransmitter is cleared at chemical synapses. 5. Outline the key differences between chemical and electrical synapses. 6. Describe how temporal and spatial summati ...
Part IV- Single neuron computation
... Active= due to presence of voltage gated ion channels Supra linear summation Caused by signal amplification through local voltage gated ion channel (mostly Na, Ca ...
... Active= due to presence of voltage gated ion channels Supra linear summation Caused by signal amplification through local voltage gated ion channel (mostly Na, Ca ...
BGandcerebellum - UCSD Cognitive Science
... 1. Promoted by (+) from PFs, plateau potentials response. For the high spontaneous firing rates of PCs 2. Influx of Ca++ resulting from these currents is one of the factors that contributes to the motor learning mediated by the synaptic plasticity of PF PC synapses 3. Granular Layer a. Receives Mos ...
... 1. Promoted by (+) from PFs, plateau potentials response. For the high spontaneous firing rates of PCs 2. Influx of Ca++ resulting from these currents is one of the factors that contributes to the motor learning mediated by the synaptic plasticity of PF PC synapses 3. Granular Layer a. Receives Mos ...
Graded Potential - wquerryeducation
... What initiates signal entry of ions via channel above threshold graded potential ...
... What initiates signal entry of ions via channel above threshold graded potential ...
Segregated Cell Populations Enable Distinct Parallel Encoding
... populations. Following injections at respectively E14 and E17, they analyzed the transcriptional variability between the two portions. They confirmed previous immunochemistry studies that showed a difference in location of zinc-containing and calbindin-positive neurons along the radial axis of CA1 [ ...
... populations. Following injections at respectively E14 and E17, they analyzed the transcriptional variability between the two portions. They confirmed previous immunochemistry studies that showed a difference in location of zinc-containing and calbindin-positive neurons along the radial axis of CA1 [ ...
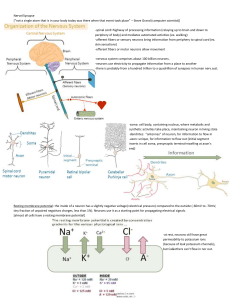
Nervous System
... cells where myelin is not complete. Saltatory conduction= jump from node to node. ...
... cells where myelin is not complete. Saltatory conduction= jump from node to node. ...
Nervous tissue Nervous system
... reach their effector targets, skeletal muscle. In contrast, interneurons of the CNS (Golgi type II neurons) have very short axons. Although an axon may give rise to a recurrent branch near the cell body (i.e., one that turns back toward the cell body) and to other collateral branches, the branching ...
... reach their effector targets, skeletal muscle. In contrast, interneurons of the CNS (Golgi type II neurons) have very short axons. Although an axon may give rise to a recurrent branch near the cell body (i.e., one that turns back toward the cell body) and to other collateral branches, the branching ...
nervous system
... The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues— yet it's the most complex of all known living structures. Up to one trillion nerve cells work together and coordinate the physical actions and mental processes that set humans apart from other species. ...
... The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues— yet it's the most complex of all known living structures. Up to one trillion nerve cells work together and coordinate the physical actions and mental processes that set humans apart from other species. ...
Physiology 1B
... The point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another are known as Synapse ...
... The point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another are known as Synapse ...
Ling 8700: Lecture Notes 1 A Model of Neural Activation
... (this is a linear function on the sum of pos/neg ions in the neuron); 4. if potential changes enough, voltage-gated channels come open; 5. voltage-gated channels let in many Na+ /Ca++ ions; neuron depolarizes (this is a non-linear threshold function on the sum of positive/negative ions in the neuron ...
... (this is a linear function on the sum of pos/neg ions in the neuron); 4. if potential changes enough, voltage-gated channels come open; 5. voltage-gated channels let in many Na+ /Ca++ ions; neuron depolarizes (this is a non-linear threshold function on the sum of positive/negative ions in the neuron ...
lec4 vision 01142010
... cylinders, extending from layer II through layer VI make up an elementary unit of organization, for they are activated by stimulation of the same single class of peripheral receptors, from almost identical peripheral receptive fields, at latencies which are not significantly different for the cells ...
... cylinders, extending from layer II through layer VI make up an elementary unit of organization, for they are activated by stimulation of the same single class of peripheral receptors, from almost identical peripheral receptive fields, at latencies which are not significantly different for the cells ...
Hearing the Call of Neurons PowerPoint
... cerebellum, illustrating its treelike structure in great detail ...
... cerebellum, illustrating its treelike structure in great detail ...
PNS Teacher
... • Sensory- carry messages from receptors in sense organs, or in the skin, TO CNS • Motor- carry messages FROM CNS to muscles and glands • Interneuron- located in CNS, links between sensory and motor neurons. ...
... • Sensory- carry messages from receptors in sense organs, or in the skin, TO CNS • Motor- carry messages FROM CNS to muscles and glands • Interneuron- located in CNS, links between sensory and motor neurons. ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -excitatory synapses are only found on spines, inhibitory synapses are found on dendrites shafts or soma ...
... -excitatory synapses are only found on spines, inhibitory synapses are found on dendrites shafts or soma ...
Ch. 2 the LGN and Striate Cortex
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission
... • Generally involved in regulatory motor activity • In the basal ganglia, involved in mood, sensory perception, and attention ...
... • Generally involved in regulatory motor activity • In the basal ganglia, involved in mood, sensory perception, and attention ...
Neurons_and_Neurotranmission
... • Generally involved in regulatory motor activity • In the basal ganglia, involved in mood, sensory perception, and attention ...
... • Generally involved in regulatory motor activity • In the basal ganglia, involved in mood, sensory perception, and attention ...