Nervous System Function
... Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and ca ...
... Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and ca ...
Biology 4 Study Guide
... ______________ environment of the brain. They form a _____________ between the ________________ & the ___________. 2. _______________ are ____________-like __________________ that dispose of ______________. 3. __________________ cells line the _______________ of the brain & the spinal cord. They hel ...
... ______________ environment of the brain. They form a _____________ between the ________________ & the ___________. 2. _______________ are ____________-like __________________ that dispose of ______________. 3. __________________ cells line the _______________ of the brain & the spinal cord. They hel ...
Overview of the Nervous System (the most important system in the
... An action potential (AP) propagates over the surface of the axon membrane Na+ flows into the cell causing a dramatic depolarization In response to depolarization, adjacent voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels open, selfpropagating along the membrane K+ flows out of the cell causing a dramatic hyp ...
... An action potential (AP) propagates over the surface of the axon membrane Na+ flows into the cell causing a dramatic depolarization In response to depolarization, adjacent voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels open, selfpropagating along the membrane K+ flows out of the cell causing a dramatic hyp ...
How to get on the right track
... cycle, they must migrate to their appropriate location and send out processes to make functional connections with their target cells. A crucial step is determining which process will become the signal-conducting component, the axon, and which processes will become the input components, the dendrites ...
... cycle, they must migrate to their appropriate location and send out processes to make functional connections with their target cells. A crucial step is determining which process will become the signal-conducting component, the axon, and which processes will become the input components, the dendrites ...
ben_slides1
... Odor receptor changes shape and binds/activates an “olfactory-type” G protein G protein activates the lyase adenylate cyclase (LAC) LAC converts ATP into cAMP cAMP opens cyclic nucleotidegated ion channels Calcium and sodium ions to enter into the cell, depolarizing the ORN Calcium-dependent Chlorin ...
... Odor receptor changes shape and binds/activates an “olfactory-type” G protein G protein activates the lyase adenylate cyclase (LAC) LAC converts ATP into cAMP cAMP opens cyclic nucleotidegated ion channels Calcium and sodium ions to enter into the cell, depolarizing the ORN Calcium-dependent Chlorin ...
Neurons with Two Sites of Synaptic Integration Learn Invariant
... 1.2 The Computational Role of Invariances. As invariant response properties are such a ubiquitous property of sensory systems, what are their computational advantages? In many categorization tasks, the output should be unchanged—or invariant—when the input is subject to various transformations. An i ...
... 1.2 The Computational Role of Invariances. As invariant response properties are such a ubiquitous property of sensory systems, what are their computational advantages? In many categorization tasks, the output should be unchanged—or invariant—when the input is subject to various transformations. An i ...
02biologya
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
Nervous System - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... Short, tapering, and diffusely branched processes Extensions of neuronal cell body They are the receptive, or input, regions of the neuron Electrical signals are conveyed as graded potentials (not action potentials) (calcium spikes) Account for 90+% of surface area ...
... Short, tapering, and diffusely branched processes Extensions of neuronal cell body They are the receptive, or input, regions of the neuron Electrical signals are conveyed as graded potentials (not action potentials) (calcium spikes) Account for 90+% of surface area ...
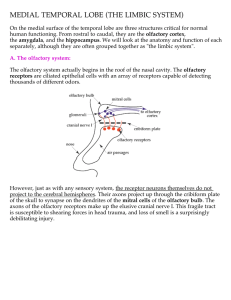
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... fornix (remember the fornix?), or it can pass along the information back to entorhinal cortex, which will relay it all back to sensory cortex. It is essentially one continuous pathway that begins in sensory cortex, traverses the hippocampus (loop-the-loop), and returns to sensory cortex. Somewhere i ...
... fornix (remember the fornix?), or it can pass along the information back to entorhinal cortex, which will relay it all back to sensory cortex. It is essentially one continuous pathway that begins in sensory cortex, traverses the hippocampus (loop-the-loop), and returns to sensory cortex. Somewhere i ...
Neuroplasticity
... • Habituation : reduction in response to a stimulus • Dishabituation: restoration/recovery of a response due to presentation of another strong stimulus • Sensitization: enhancement of response due to presentation of a strong stimulus ...
... • Habituation : reduction in response to a stimulus • Dishabituation: restoration/recovery of a response due to presentation of another strong stimulus • Sensitization: enhancement of response due to presentation of a strong stimulus ...
Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... extending from brain and spinal cord Peripheral nerves link all regions of the body to the CNS Ganglia are clusters of neuronal cell bodies ...
... extending from brain and spinal cord Peripheral nerves link all regions of the body to the CNS Ganglia are clusters of neuronal cell bodies ...
NervousSystem2
... etc., take place within the CNS itself. They are mechanisms of interneurons, a part of, and have their effect on, interneuronal circuitry within the CNS. By having excitatory and inhibitory neurons, the interneuronal circuitry modulates the wave of afferent excitation and brings about the variable c ...
... etc., take place within the CNS itself. They are mechanisms of interneurons, a part of, and have their effect on, interneuronal circuitry within the CNS. By having excitatory and inhibitory neurons, the interneuronal circuitry modulates the wave of afferent excitation and brings about the variable c ...
Why light
... The rightmost extreme is called distributed coding. It assumes that each different stimulus activates all brain neurons, with a different pattern of activity for each stimlus. So all neurons are active at all times. They just sing different songs to different objects. It is very likely that neither ...
... The rightmost extreme is called distributed coding. It assumes that each different stimulus activates all brain neurons, with a different pattern of activity for each stimlus. So all neurons are active at all times. They just sing different songs to different objects. It is very likely that neither ...
Untitled 2
... - In the brain finer dendrites are highly specialised for collecting information, bristling with dendrites spines which represent points of close contact - synapses - with other neurons ...
... - In the brain finer dendrites are highly specialised for collecting information, bristling with dendrites spines which represent points of close contact - synapses - with other neurons ...
The Two Messenger Services of the Brain
... In fact you can expect feeling to return at a rate of about 1 millimeter a day!!!) ...
... In fact you can expect feeling to return at a rate of about 1 millimeter a day!!!) ...
The Cells of the Nervous System Lab
... dragging the mouse to rotate. The purkinje cell axons, not shown here, are inhibitory, and provide the entire output of the cerebellar cortex. Excitatory neurons Neurons in the same brain region may also have very different morphologies reflecting their unique function in the brain. In the cerebral ...
... dragging the mouse to rotate. The purkinje cell axons, not shown here, are inhibitory, and provide the entire output of the cerebellar cortex. Excitatory neurons Neurons in the same brain region may also have very different morphologies reflecting their unique function in the brain. In the cerebral ...
Synapses - JNCASR Desktop
... Impulses arriving simultaneously are added together and, if sufficiently strong, lead to the generation of an electrical discharge, known as an action potential (a 'nerve impulse'). The action potential then forms the input to the next neuron in the network. What is brain made up of? The bulk of the ...
... Impulses arriving simultaneously are added together and, if sufficiently strong, lead to the generation of an electrical discharge, known as an action potential (a 'nerve impulse'). The action potential then forms the input to the next neuron in the network. What is brain made up of? The bulk of the ...
Drug Addiction - Perelman School of Medicine at the
... body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. ...
... body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
Histology of Nervous Tissue
... • Amount of voltage change (graded) dependent on # of gates open at one time and how long – Change is localized (not conducted) – Change may be depolarization or hyperpolarization • Usually limited to dendrites and cell body of neurons, and many sensory cells • Synapse - postsynaptic potential, Sens ...
... • Amount of voltage change (graded) dependent on # of gates open at one time and how long – Change is localized (not conducted) – Change may be depolarization or hyperpolarization • Usually limited to dendrites and cell body of neurons, and many sensory cells • Synapse - postsynaptic potential, Sens ...
Slide 1
... Brainstem mechanisms of controlling postural muscle tone and locomotion in cats. (A) Signals from the MLR activate muscle-tone excitatory and rhythmgenerating systems. The rhythm-generating system is from the excitatory reticulospinal tract arising from the ventromedial MRF (v-MRF) and CPG in the sp ...
... Brainstem mechanisms of controlling postural muscle tone and locomotion in cats. (A) Signals from the MLR activate muscle-tone excitatory and rhythmgenerating systems. The rhythm-generating system is from the excitatory reticulospinal tract arising from the ventromedial MRF (v-MRF) and CPG in the sp ...
mspn12a
... layer, through the layer consisting of amacrine, bipolar, and horizontal cells, before finally reaching the photorecptor layer. The retina is oriented in this fashion because of the need for the photoreceptor cells to be adjacent to the pigment epithelium and adjacent choroid. This epithelium contai ...
... layer, through the layer consisting of amacrine, bipolar, and horizontal cells, before finally reaching the photorecptor layer. The retina is oriented in this fashion because of the need for the photoreceptor cells to be adjacent to the pigment epithelium and adjacent choroid. This epithelium contai ...