Lecture notes for Chapter 12
... Layer 1 consists mainly of apical dendrites from pyramidal cells from lower layers — plus axons synapsing on those dendrites. It contains almost no neuron cell bodies. Layer 2 contains many small densely-packed pyramidal neurons — giving it a granular appearance. Layer 3 contains medium-sized pyram ...
... Layer 1 consists mainly of apical dendrites from pyramidal cells from lower layers — plus axons synapsing on those dendrites. It contains almost no neuron cell bodies. Layer 2 contains many small densely-packed pyramidal neurons — giving it a granular appearance. Layer 3 contains medium-sized pyram ...
Declarative Memory
... quickly learns to do so. The rat is presumably using some combination of landmarks (the cue card) and path integration to solve this spatial problem. This is now the standard test for spatial learning in rodents. Lesioning the hippocampus prevents this spatial learning. A variety of interventions in ...
... quickly learns to do so. The rat is presumably using some combination of landmarks (the cue card) and path integration to solve this spatial problem. This is now the standard test for spatial learning in rodents. Lesioning the hippocampus prevents this spatial learning. A variety of interventions in ...
Multiple sites of spike initiation in a single dendritic
... Purkinje ceils of alligator cerebellumS, 9, pyramidal cells of cat hippocampus, crab eye stalk motor neuronslZ, 1~, and crayfish fast flexor m o t o r neurons15), the dendritic spikes contribute only subthreshold excitation to a main axonal spike initiating zone. Such dendritic spikes, which do not ...
... Purkinje ceils of alligator cerebellumS, 9, pyramidal cells of cat hippocampus, crab eye stalk motor neuronslZ, 1~, and crayfish fast flexor m o t o r neurons15), the dendritic spikes contribute only subthreshold excitation to a main axonal spike initiating zone. Such dendritic spikes, which do not ...
Actin , Synaptic plasticity in Parallel fibre-Purkinje Neuron
... enhanced the rate and depth of long term depression induced by conjuncive stimulation effected by depolarising Purkinje cells and stimulating Parallel fibres simultaneously. Jasplakinolide, an actin stabilizing agent blocked the induction of LTD by the same protocol. The possiblility that actin depo ...
... enhanced the rate and depth of long term depression induced by conjuncive stimulation effected by depolarising Purkinje cells and stimulating Parallel fibres simultaneously. Jasplakinolide, an actin stabilizing agent blocked the induction of LTD by the same protocol. The possiblility that actin depo ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
doc Chapter 13 Notes
... (a band inside the postsynaptic membrane that contains proteins, receptors and all that good stuff) It has also been suggested that LTP changes the synaptic structure and causes production of new synapses. - thin dendritic spines become fatter, mushroom shaped spines - also new dendrites can grow th ...
... (a band inside the postsynaptic membrane that contains proteins, receptors and all that good stuff) It has also been suggested that LTP changes the synaptic structure and causes production of new synapses. - thin dendritic spines become fatter, mushroom shaped spines - also new dendrites can grow th ...
The Nervous System
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
Brain development
... Knock-out mice Staggered Neurons in the cerebellum make contact, but receptor surface does not develop • Thus, a single gene deletion can interfere with the formation of synapses in the cerebellum ...
... Knock-out mice Staggered Neurons in the cerebellum make contact, but receptor surface does not develop • Thus, a single gene deletion can interfere with the formation of synapses in the cerebellum ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Diagram of the olfactory pathway. Information is transmitted from the olfactory bulb by axons of mitral and tufted relay neurons in the lateral olfactory tract. Mitral cells project to five regions of the olfactory cortex: anterior olfactory nucleus, olfactory tubercle, piriform cortex, and parts of ...
... Diagram of the olfactory pathway. Information is transmitted from the olfactory bulb by axons of mitral and tufted relay neurons in the lateral olfactory tract. Mitral cells project to five regions of the olfactory cortex: anterior olfactory nucleus, olfactory tubercle, piriform cortex, and parts of ...
P-retinal ganglion cells
... cells, large RFs, respond faster, and are not sensitive to color. Thus these layers encode gross features and movement. LGN RFs: Similar concentric RFs to those of ganglion cells, but with stronger (larger) surround. This translates to more sensitivity to contrast than ganglion cells. If you were to ...
... cells, large RFs, respond faster, and are not sensitive to color. Thus these layers encode gross features and movement. LGN RFs: Similar concentric RFs to those of ganglion cells, but with stronger (larger) surround. This translates to more sensitivity to contrast than ganglion cells. If you were to ...
Document
... cells, large RFs, respond faster, and are not sensitive to color. Thus these layers encode gross features and movement. LGN RFs: Similar concentric RFs to those of ganglion cells, but with stronger (larger) surround. This translates to more sensitivity to contrast than ganglion cells. If you were to ...
... cells, large RFs, respond faster, and are not sensitive to color. Thus these layers encode gross features and movement. LGN RFs: Similar concentric RFs to those of ganglion cells, but with stronger (larger) surround. This translates to more sensitivity to contrast than ganglion cells. If you were to ...
The Nervous System
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
Slide ()
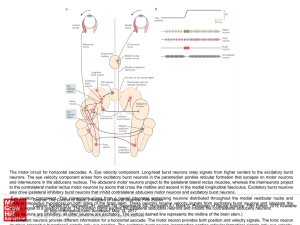
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
Neurons - Manatee School for the Arts
... • Neurons vary in size, shape & function • Mature neurons do NOT divide • All neurons have: • A cell body is the main component of a neuron. It contains cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus, & organelles. • The ER of a cell body is called the chromatophilic substance or nissl bodies (perform protei ...
... • Neurons vary in size, shape & function • Mature neurons do NOT divide • All neurons have: • A cell body is the main component of a neuron. It contains cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus, & organelles. • The ER of a cell body is called the chromatophilic substance or nissl bodies (perform protei ...
Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons
... receptor antagonist, blocked the IPSP. (C) Action potentials of seven excitatory (E) and seven inhibitory (I) presynaptic neurons superimposed to show the differences in spike duration. (Figure modified from Ref. 12.) dendrites of various configurations, inhibitory (GABA-mediated) synaptic function, ...
... receptor antagonist, blocked the IPSP. (C) Action potentials of seven excitatory (E) and seven inhibitory (I) presynaptic neurons superimposed to show the differences in spike duration. (Figure modified from Ref. 12.) dendrites of various configurations, inhibitory (GABA-mediated) synaptic function, ...
Dendritic Signal Integration
... Each granule cell receives on average only four excitatory inputs, each made onto a very short dendrite. Because the dendrites are so short, their influence on synaptic integration is minimal. This also offers technical advantages for studying synaptic physiology with patch-clamp recordings from the ...
... Each granule cell receives on average only four excitatory inputs, each made onto a very short dendrite. Because the dendrites are so short, their influence on synaptic integration is minimal. This also offers technical advantages for studying synaptic physiology with patch-clamp recordings from the ...
document
... synapses. Each of the 1012 neurons (1,000 billion, i.e. 1 trillion) has on average 7,000 synaptic connections to other neurons. It hast been estimated that the brain of a three-year-old child has about 1016 synapses (10,000 trillion). This number declines with age, stabilizing by adulthood. Estimate ...
... synapses. Each of the 1012 neurons (1,000 billion, i.e. 1 trillion) has on average 7,000 synaptic connections to other neurons. It hast been estimated that the brain of a three-year-old child has about 1016 synapses (10,000 trillion). This number declines with age, stabilizing by adulthood. Estimate ...
Learning Objectives
... Conveys afferents signals to Soma Usually multiple and small in length Thickness decreases near terminals Arborized terminals ...
... Conveys afferents signals to Soma Usually multiple and small in length Thickness decreases near terminals Arborized terminals ...
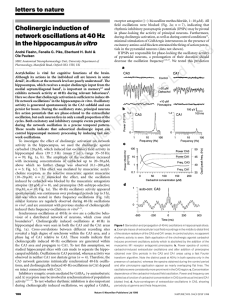
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... to reduce the extracellular oscillation (Fig. 2c). However, in contrast to 40-Hz oscillations induced by metabotropic glutamate receptors in the CA1 area7, cholinergically induced oscillations require ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors. In both CA3 and CA1 the oscillatory activity was completel ...
... to reduce the extracellular oscillation (Fig. 2c). However, in contrast to 40-Hz oscillations induced by metabotropic glutamate receptors in the CA1 area7, cholinergically induced oscillations require ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors. In both CA3 and CA1 the oscillatory activity was completel ...
ImageSurfer: Visualization of Dendritic Spines
... long arm-like structure called an axon. At the end of the axon the impulse sets off a chemical transfer. The chemicals diffuse across a gap to dendrites, on neighboring receiver neurons. These neurons then fire their own electrical impulses thus propagating the signal. Dendritic spines are tiny stru ...
... long arm-like structure called an axon. At the end of the axon the impulse sets off a chemical transfer. The chemicals diffuse across a gap to dendrites, on neighboring receiver neurons. These neurons then fire their own electrical impulses thus propagating the signal. Dendritic spines are tiny stru ...
The Nervous System
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
L11Nervous tissue strusture 11
... cell. The end of the axon is called the terminal bouton . Axon terminal)Each signal travels along the neuron's axon to the terminal bouton, where it is then transmitted to the next neuron. The axon is covered in myelin, a thick phospholipid substance that insulates the nerve to help transmit the ele ...
... cell. The end of the axon is called the terminal bouton . Axon terminal)Each signal travels along the neuron's axon to the terminal bouton, where it is then transmitted to the next neuron. The axon is covered in myelin, a thick phospholipid substance that insulates the nerve to help transmit the ele ...
Ren - University of Illinois Archives
... R.-S. Chen, S. Hong, and Y. Li. Neuroscience Program, Beckman Institute, Dept. of Molecular & Integrative Physiology, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801. Studies using cortical and hippocampal brain slices suggest that many young central synapses initially contain only NMDA rece ...
... R.-S. Chen, S. Hong, and Y. Li. Neuroscience Program, Beckman Institute, Dept. of Molecular & Integrative Physiology, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801. Studies using cortical and hippocampal brain slices suggest that many young central synapses initially contain only NMDA rece ...
Doktryna neuronu
... potential can be determined by measuring the reversal potential of the end-plate current. The voltage of the muscle membrane is clamped at different potentials, and the synaptic current is measured when the nerve is stimulated. A. If Na+ flux alone were responsible for the endplate current, the reve ...
... potential can be determined by measuring the reversal potential of the end-plate current. The voltage of the muscle membrane is clamped at different potentials, and the synaptic current is measured when the nerve is stimulated. A. If Na+ flux alone were responsible for the endplate current, the reve ...