MSdoc - Stevens County
... This plant was introduced from Europe and now grows widespread through the U.S. Grows along road sides and in fields as well as other disturbed sites ...
... This plant was introduced from Europe and now grows widespread through the U.S. Grows along road sides and in fields as well as other disturbed sites ...
Quiz 8.doc
... 1. Examples of non-vascular plants are a. ferns b. conifers c. flowering plants d. mosses and liverworts e. none of the above 2. Plant adaptations to life on land include all of these, except: a. chlorophyl b. cuticle , cork and bark c. stomata d. lignin e. xylem and phloem 3. The green, leaflike st ...
... 1. Examples of non-vascular plants are a. ferns b. conifers c. flowering plants d. mosses and liverworts e. none of the above 2. Plant adaptations to life on land include all of these, except: a. chlorophyl b. cuticle , cork and bark c. stomata d. lignin e. xylem and phloem 3. The green, leaflike st ...
The Plant Kingdom - Modesto Junior College
... • Cellulose synthesized by cells • Growth is unlimited ...
... • Cellulose synthesized by cells • Growth is unlimited ...
Chapter 5
... Plants of horticultural importance that are propagated almost totally by asexual means are termed clonal varieties. They are a type of cultivar. Runners are stems that grow along the ground and form new plants at one or more of their nodes. Stolons are aerial shoots that take root after coming into ...
... Plants of horticultural importance that are propagated almost totally by asexual means are termed clonal varieties. They are a type of cultivar. Runners are stems that grow along the ground and form new plants at one or more of their nodes. Stolons are aerial shoots that take root after coming into ...
Plants Study Guide
... 13. After fertilization, what happens to the ovary in the diagram? (pg. 278) It develops into a fruit. 14. Germination is when the plant is pushing out of the seed. This occurs when the seed absorbs water. 15. What is the difference between the stomata and the cuticle? stomata—small opening on the u ...
... 13. After fertilization, what happens to the ovary in the diagram? (pg. 278) It develops into a fruit. 14. Germination is when the plant is pushing out of the seed. This occurs when the seed absorbs water. 15. What is the difference between the stomata and the cuticle? stomata—small opening on the u ...
Scientific Identification of Plants
... The science and practice of growing, processing and marketing fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants Comes from the Latin word meaning “garden cultivation” ...
... The science and practice of growing, processing and marketing fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants Comes from the Latin word meaning “garden cultivation” ...
Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet
... Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet chlorophyll xylem embryo cellulose seed flowers ...
... Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet chlorophyll xylem embryo cellulose seed flowers ...
Plants junior
... Plants form the basis of the survival of all living things. In fact, they supply the majority of the oxygen that animals and men breathe and also the majority of the food that they consume. The plant kingdom includes about 350,000 very different species. In fact trees, shrubs, bushes, grasses, creep ...
... Plants form the basis of the survival of all living things. In fact, they supply the majority of the oxygen that animals and men breathe and also the majority of the food that they consume. The plant kingdom includes about 350,000 very different species. In fact trees, shrubs, bushes, grasses, creep ...
Plant/Flower Study Guide
... Here’s what you need to know….. Plants are “producers”. This means they have the ability to make their own food. The process is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Photosynthesis takes place in the plant’s leaves. The plant uses chlorophyll (found in chloroplast) along with water, carbon dioxide, and energy f ...
... Here’s what you need to know….. Plants are “producers”. This means they have the ability to make their own food. The process is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Photosynthesis takes place in the plant’s leaves. The plant uses chlorophyll (found in chloroplast) along with water, carbon dioxide, and energy f ...
Catchweed - Stevens County
... early in the season for new plants Biological – No known biological control Cultural – Planting a competitive crop or grass can help crowd out the weeds ...
... early in the season for new plants Biological – No known biological control Cultural – Planting a competitive crop or grass can help crowd out the weeds ...
3.2 Helping Plants Grow Well 9780435133290.indd
... word snake or flower shape by joining them together so that your friends have to find the ten words. For example: plants, grow, water, food … and so on. Draw them in a flower shape, if you can. ...
... word snake or flower shape by joining them together so that your friends have to find the ten words. For example: plants, grow, water, food … and so on. Draw them in a flower shape, if you can. ...
Plants Can be Dangerous
... Most plants make their food during photosynthesis and normally get necessary water and nutrients from the soil. However, some plants have evolved other methods of surviving. These plants are called parasitic, epiphytic, or carnivorous plants. Parasitic Plants: attach themselves onto other plants cal ...
... Most plants make their food during photosynthesis and normally get necessary water and nutrients from the soil. However, some plants have evolved other methods of surviving. These plants are called parasitic, epiphytic, or carnivorous plants. Parasitic Plants: attach themselves onto other plants cal ...
Begonia dregei - American Begonia Society
... B. dregei is an easy plant to grow, but does need careful watching. Mealy bugs will appear on this plant in abundance before they even show up on nearby plants. It is also very prone to powdery mildew. It does not need a lot of water, nor does it require a large pot as the caudex stores moisture. B. ...
... B. dregei is an easy plant to grow, but does need careful watching. Mealy bugs will appear on this plant in abundance before they even show up on nearby plants. It is also very prone to powdery mildew. It does not need a lot of water, nor does it require a large pot as the caudex stores moisture. B. ...
10 Easy Steps to Prevent Common Garden Diseases
... the previous season’s crops may harbor diseases and insects 2. Purchase high quality plants and seeds. Select plants with healthy-looking leaves and strong stems. Avoid collecting seeds from your own plants - fungal diseases are often transmitted on or in seed. 3. Rotate Crops. Grow your crops in di ...
... the previous season’s crops may harbor diseases and insects 2. Purchase high quality plants and seeds. Select plants with healthy-looking leaves and strong stems. Avoid collecting seeds from your own plants - fungal diseases are often transmitted on or in seed. 3. Rotate Crops. Grow your crops in di ...
Study Guide for Plant Kingdom
... 3. __________________Tough outer part of plant cells that provides protection and support. 4. __________________ Process that occurs in the mitochondria that uses oxygen to break down glucose in order to release cellular energy (ATP). 5. __________________ Pigment found in the chloroplast that is re ...
... 3. __________________Tough outer part of plant cells that provides protection and support. 4. __________________ Process that occurs in the mitochondria that uses oxygen to break down glucose in order to release cellular energy (ATP). 5. __________________ Pigment found in the chloroplast that is re ...
Botany Review Questions
... 2. ________________ is the unique ability of plant cells to retain all of the genetic information (encoded in DNA) necessary to develop into a complete plant. That characteristic is the main reason vegetative (or asexual) reproduction works. 3. ________________ tissues are the site of rapid and cont ...
... 2. ________________ is the unique ability of plant cells to retain all of the genetic information (encoded in DNA) necessary to develop into a complete plant. That characteristic is the main reason vegetative (or asexual) reproduction works. 3. ________________ tissues are the site of rapid and cont ...
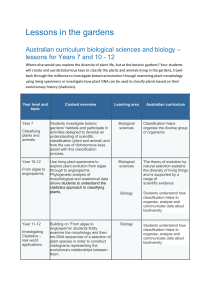
Curriculum information for Biological sciences and Biology
... back through the millennia to investigate botanical evolution through examining plant morphology using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
... back through the millennia to investigate botanical evolution through examining plant morphology using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
Introduction - Plants in Action
... Many other higher plants are periodically waterlogged through flooding of the land. Roots are often primarily affected but leaves and stems might also be inundated, leading after several days to tissue damage, slower growth and some-times plant death. Tolerance to these conditions varies greatly, wi ...
... Many other higher plants are periodically waterlogged through flooding of the land. Roots are often primarily affected but leaves and stems might also be inundated, leading after several days to tissue damage, slower growth and some-times plant death. Tolerance to these conditions varies greatly, wi ...
Plant Classification.pub
... The conservatory’s permanent collection has a large number of the plants from the Arecaceae (palm), Bromeliaceae (bromeliad), and Orchidaceae (orchid) families. ...
... The conservatory’s permanent collection has a large number of the plants from the Arecaceae (palm), Bromeliaceae (bromeliad), and Orchidaceae (orchid) families. ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.