Fun Facts About Plants
... water and nutrients. -Vascular plants grow taller and wider. -Non-vascular plants don’t have tubes. -Since non-vascular plants don’t have tubes’ the water and nutrients are transported from cell to cell. ...
... water and nutrients. -Vascular plants grow taller and wider. -Non-vascular plants don’t have tubes. -Since non-vascular plants don’t have tubes’ the water and nutrients are transported from cell to cell. ...
MSdoc - Stevens County
... 700-17,000 hard-coated seeds per plant remain viable when buried for more than 50 years Native to Asia where fiber is used to make rope, bags, nets and paper-introduced in North America in 1700’s as a potential fiber crop Serious row crop (corn/soybeans) weed in the mid-West Found infrequent ...
... 700-17,000 hard-coated seeds per plant remain viable when buried for more than 50 years Native to Asia where fiber is used to make rope, bags, nets and paper-introduced in North America in 1700’s as a potential fiber crop Serious row crop (corn/soybeans) weed in the mid-West Found infrequent ...
Name Date Period ______ Vocabulary | Plant Diversity, Growth
... _______________ are multicellular eukaryotes. Most live on land and use ______________________ to make their own source of food, or energy. One species of _____ _____ is the _____________ of all plants. It belongs to the class _______________. Tiny holes in the cuticle of plant leaves, called ______ ...
... _______________ are multicellular eukaryotes. Most live on land and use ______________________ to make their own source of food, or energy. One species of _____ _____ is the _____________ of all plants. It belongs to the class _______________. Tiny holes in the cuticle of plant leaves, called ______ ...
Unit B: Topic 3 PLANT REPRODUCTION AND BREEDING Asexual
... ● selective __________ is choosing specific plants for their special ______________ ● the plants are ____________and their offspring inherit the ____________ of both parents. ● ____________can change plants by going inside the plant ________and changing some of ...
... ● selective __________ is choosing specific plants for their special ______________ ● the plants are ____________and their offspring inherit the ____________ of both parents. ● ____________can change plants by going inside the plant ________and changing some of ...
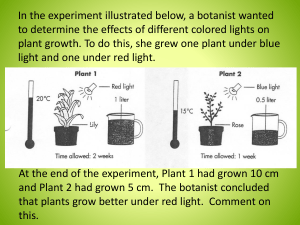
WHICH PLANT GROWS WHERE?
... Sheltered from wind and grazing animals small tender plants can grow underneath the woody hedge. Spring blossoming plants flower under the hedgerow before the sun is blocked by leaves on the hedge. Moorland Windy and cold in winter. Plants have to endure harsh conditions on moorland. Low growing pla ...
... Sheltered from wind and grazing animals small tender plants can grow underneath the woody hedge. Spring blossoming plants flower under the hedgerow before the sun is blocked by leaves on the hedge. Moorland Windy and cold in winter. Plants have to endure harsh conditions on moorland. Low growing pla ...
Vocabulary for Plants
... 1. Plants – are multicellular eukaryotes, most of which make their own food through photosynthesis and have adapted to live on land. 2. cuticle – is a waxy, waterproof layer that helps hold in moisture in plants. 3. stomata – tiny holes in the cuticle. Special cells allow stomata to close to prevent ...
... 1. Plants – are multicellular eukaryotes, most of which make their own food through photosynthesis and have adapted to live on land. 2. cuticle – is a waxy, waterproof layer that helps hold in moisture in plants. 3. stomata – tiny holes in the cuticle. Special cells allow stomata to close to prevent ...
Plant growth - WordPress.com
... Plant hormones auxins cause rapid growth in shady parts of the plant causing the plant to aim towards the sun ...
... Plant hormones auxins cause rapid growth in shady parts of the plant causing the plant to aim towards the sun ...
Plant Life
... outgrowth from the plant stem; its primary functions are to perform photosynthesis and transpiration nectar – the sweet liquid made by plants that attracts insects and other animals oxygen – a gas that plants release; animals need this in order to live petal – the colorful leaf that surrounds the re ...
... outgrowth from the plant stem; its primary functions are to perform photosynthesis and transpiration nectar – the sweet liquid made by plants that attracts insects and other animals oxygen – a gas that plants release; animals need this in order to live petal – the colorful leaf that surrounds the re ...
Plants Diversity Unit - Everglades High School
... Know characteristics (adaptations) as well as factors that affect survival of plants on land. ...
... Know characteristics (adaptations) as well as factors that affect survival of plants on land. ...
Learn About Plants
... •Its small yellow flowers develop into ripe tomatoes •It needs at least six hours of warm sunlight each day Let's see other plants ...
... •Its small yellow flowers develop into ripe tomatoes •It needs at least six hours of warm sunlight each day Let's see other plants ...
Plant Kingdom PPT
... Adaptations for living on land • Plants get water and nutrients from the soil • Plants lose water through transpiration • Plants have a cuticle to keep them from drying out. • Some plants use a system of tubelike structures called Vascular Tissue to move materials. • Vascular tissue also supports s ...
... Adaptations for living on land • Plants get water and nutrients from the soil • Plants lose water through transpiration • Plants have a cuticle to keep them from drying out. • Some plants use a system of tubelike structures called Vascular Tissue to move materials. • Vascular tissue also supports s ...
Control Systems In Plants
... The study of plants began when early humans began to distinguish edible plants from poisonous ones. Then began to make things from wood and other plant products. ...
... The study of plants began when early humans began to distinguish edible plants from poisonous ones. Then began to make things from wood and other plant products. ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... Topic: Review First Term Objective: To recall information of Unit 1, 2 and 3 ...
... Topic: Review First Term Objective: To recall information of Unit 1, 2 and 3 ...
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
... • Symptoms are caused by the insertion of a small segment of transfer DNA from a plasmid into the plant cell, which is implanted in a random location in the genome. ...
... • Symptoms are caused by the insertion of a small segment of transfer DNA from a plasmid into the plant cell, which is implanted in a random location in the genome. ...
Plants-General information
... *Plants probably evolved from algae. *There is an alternation of generations-meaning 2 phases in life cycle. *1st land plants had to be able to survive harsh conditions-thus they developed a ____________________ -waxy,waterproof layer that coats the parts of plant exposed to air--helps keep it from ...
... *Plants probably evolved from algae. *There is an alternation of generations-meaning 2 phases in life cycle. *1st land plants had to be able to survive harsh conditions-thus they developed a ____________________ -waxy,waterproof layer that coats the parts of plant exposed to air--helps keep it from ...
Plant Kingdom: Study Guide Questions BIOLOGY 1. What do all
... 11. Why is it beneficial for plants to have methods for seeds to be spread far away from the parent plants and what adaptations are found? (p. 337) 12. What role do hormones have in the life cycle of a plant ? (p.324-5) a. Describe three ways that plant hormones control the growth response to extern ...
... 11. Why is it beneficial for plants to have methods for seeds to be spread far away from the parent plants and what adaptations are found? (p. 337) 12. What role do hormones have in the life cycle of a plant ? (p.324-5) a. Describe three ways that plant hormones control the growth response to extern ...
Plant Defenses
... organisms. Include: alkaloids - caffeine, nicotine, cocaine tannins oils - peppermint, sage ...
... organisms. Include: alkaloids - caffeine, nicotine, cocaine tannins oils - peppermint, sage ...
ss 1 biology - Danbo International Schools
... Classification of plants simply means the grouping of plants into their kinds. STEP II ...
... Classification of plants simply means the grouping of plants into their kinds. STEP II ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.