Plant Categories and Types
... group of shrubs and trees that do not lose their leaves and do not have needle or scalelike foliage. ...
... group of shrubs and trees that do not lose their leaves and do not have needle or scalelike foliage. ...
MSdoc - Stevens County
... Giant hogweed is native to the Caucasus mountain region of Eurasia & southwestern Asia; it has been introduced to many areas as a garden ornamental Giant hogweed may colonize a wide variety of habitats but is most common along rights-of-way, vacant lots, streams, and rivers It has been put on ...
... Giant hogweed is native to the Caucasus mountain region of Eurasia & southwestern Asia; it has been introduced to many areas as a garden ornamental Giant hogweed may colonize a wide variety of habitats but is most common along rights-of-way, vacant lots, streams, and rivers It has been put on ...
Dioscorea deltoidea Wall. ex Griseb. Photo Courtesy: A.B.D. Selvam
... long, solitary, rarely in pairs, slender; flowers small, in clusters; perianth segments broadly oblong; stamens 6. Female spikes 8-16 cm long, solitary, broader than leaf; flowers few. Capsules 1.5-2.5 × 2.5-5 cm, orbicular, deltoid or obtusely quadrate. Seeds winged. Medicinal properties and other ...
... long, solitary, rarely in pairs, slender; flowers small, in clusters; perianth segments broadly oblong; stamens 6. Female spikes 8-16 cm long, solitary, broader than leaf; flowers few. Capsules 1.5-2.5 × 2.5-5 cm, orbicular, deltoid or obtusely quadrate. Seeds winged. Medicinal properties and other ...
Veronicastrum virginicum – Culver`s Root
... since the seeds are difficult to germinate. Divide mature plants making sure the each section has a bud and root. SITE REQUIREMENTS: Wet to dry, open woods, wet-mesic prairie, shaded rocky slopes. Growth is best in rich loamy soil. NATURAL RANGE: Throughout Wisconsin, except the far north. New Engla ...
... since the seeds are difficult to germinate. Divide mature plants making sure the each section has a bud and root. SITE REQUIREMENTS: Wet to dry, open woods, wet-mesic prairie, shaded rocky slopes. Growth is best in rich loamy soil. NATURAL RANGE: Throughout Wisconsin, except the far north. New Engla ...
Handout
... Basic taxonomic criteria for groupings were based on morphology of reproductive parts, parts least apt to be influenced by environment. However, his system was artificial and is not longer being used; depended on no. of stamens and carpels as a method of grouping plants. Credited with establishment ...
... Basic taxonomic criteria for groupings were based on morphology of reproductive parts, parts least apt to be influenced by environment. However, his system was artificial and is not longer being used; depended on no. of stamens and carpels as a method of grouping plants. Credited with establishment ...
Plants As Resources
... Plants Give Us Food We eat different types of foods that come from a plant. We eat the stems, roots, leaves, flowers, and seeds of a food. ...
... Plants Give Us Food We eat different types of foods that come from a plant. We eat the stems, roots, leaves, flowers, and seeds of a food. ...
Plants Study Guide 1. The green pigment found in specialized plant
... 38. A grapevine coiling around a fence post is an example of _____________________________________________. 39. What tropism do roots display when they respond to the environment by growing downward? ______________ 40. What determines the time of flowering in many plants? ___________________________ ...
... 38. A grapevine coiling around a fence post is an example of _____________________________________________. 39. What tropism do roots display when they respond to the environment by growing downward? ______________ 40. What determines the time of flowering in many plants? ___________________________ ...
Seed
... nutrients upwards and food away from leaves; support/structure Roots: Absorbs water and nutrients from soil; anchors plant to the ground ...
... nutrients upwards and food away from leaves; support/structure Roots: Absorbs water and nutrients from soil; anchors plant to the ground ...
Dichotomous Key for MN Leaves
... Dichotomous Key for MN Leaves Directions: 1. )Uses pressed plants, at least six.. ...
... Dichotomous Key for MN Leaves Directions: 1. )Uses pressed plants, at least six.. ...
Plant Morphology
... Plant Morphology • Meristem Tissue- embryonic tissue located at the tips of roots and stem apices (herbaceous & woody plants) and cambium layers (woody plants). • Parenchyma - unspecialized cells occurring throughout the plant. ...
... Plant Morphology • Meristem Tissue- embryonic tissue located at the tips of roots and stem apices (herbaceous & woody plants) and cambium layers (woody plants). • Parenchyma - unspecialized cells occurring throughout the plant. ...
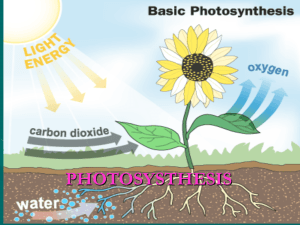
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... • Photosynthesis is how plants use light and water to make sugar. Sugar is created in the green parts of a plant and every animal on earth depends on it. • Without plants we would have no food to eat or oxygen to breath. Here is a picture to show how it happens. ...
... • Photosynthesis is how plants use light and water to make sugar. Sugar is created in the green parts of a plant and every animal on earth depends on it. • Without plants we would have no food to eat or oxygen to breath. Here is a picture to show how it happens. ...
File - Mrs. Rothenberg`s Science
... Anything from the readings can be on the test. In addition, anything from our discussion in class can also be on the test. You should use your class notes, textbook, review homework that we corrected in class and this review sheet to help you prepare. When studying please pay close attention the fol ...
... Anything from the readings can be on the test. In addition, anything from our discussion in class can also be on the test. You should use your class notes, textbook, review homework that we corrected in class and this review sheet to help you prepare. When studying please pay close attention the fol ...
Common name - Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants
... 2. Programs to educate homeowners about the problems associated with this plant and proper identification 3. Maintain good ground cover and mixture of plant species to reduce establishment ...
... 2. Programs to educate homeowners about the problems associated with this plant and proper identification 3. Maintain good ground cover and mixture of plant species to reduce establishment ...
Science Study Guide: Chapter 2 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants
... Science Study Guide: Chapter 2 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to live. 3. Know where the chloroplast is located in a plant cell. 4. A pine needle and a tulip leaf are both kinds of leaves. 5. Stems carry materials and support the plant. 6. Daisy’s ha ...
... Science Study Guide: Chapter 2 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to live. 3. Know where the chloroplast is located in a plant cell. 4. A pine needle and a tulip leaf are both kinds of leaves. 5. Stems carry materials and support the plant. 6. Daisy’s ha ...
Organisms can be classified into two major groups
... How are plants classified? • Plants have many parts and make their own food. • Some produce flowers while others do not. • Flowering plants are plants that make seeds within flowers (ex: grass, roses, fruit trees) • Some flowers become fruit. • Non-flowering plants are plants that make seeds wit ...
... How are plants classified? • Plants have many parts and make their own food. • Some produce flowers while others do not. • Flowering plants are plants that make seeds within flowers (ex: grass, roses, fruit trees) • Some flowers become fruit. • Non-flowering plants are plants that make seeds wit ...
6-2.4 notes Plants - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... Absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Store extra food for the plants. The more root space that is available, the more water and nutrients it can absorb. There are two types of root systems: fibrous roots and taproots. 1. Fibrous roots consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass ...
... Absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Store extra food for the plants. The more root space that is available, the more water and nutrients it can absorb. There are two types of root systems: fibrous roots and taproots. 1. Fibrous roots consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass ...
Document
... c. gravitropism- the growth of a plant in response to gravity. Ex. The roots grow down toward soil and the stem grows up toward the sun ...
... c. gravitropism- the growth of a plant in response to gravity. Ex. The roots grow down toward soil and the stem grows up toward the sun ...
6-2.6 Differentiate between the processes of sexual and asexual
... 6-2.6 Differentiate between the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction of flowering plants. Sexual reproduction •A process of reproduction that requires a sperm cell (in pollen) and an egg cell (in the ovule) to combine to produce a new organism. •All flowering plants undergo sexual reproducti ...
... 6-2.6 Differentiate between the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction of flowering plants. Sexual reproduction •A process of reproduction that requires a sperm cell (in pollen) and an egg cell (in the ovule) to combine to produce a new organism. •All flowering plants undergo sexual reproducti ...
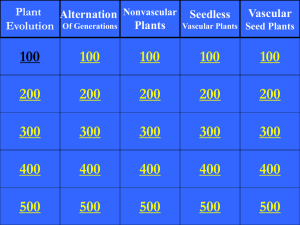
BIO101 Unit 4
... the haploid generation of alternation of generations life cycle of plants; produces the gametes that unite to form a diploid zygote which develops into the sporophyte generation. gymnosperms a type of woody seed plant where the seeds are produced “naked” in cones. herbaceous A plant with soft, green ...
... the haploid generation of alternation of generations life cycle of plants; produces the gametes that unite to form a diploid zygote which develops into the sporophyte generation. gymnosperms a type of woody seed plant where the seeds are produced “naked” in cones. herbaceous A plant with soft, green ...
Seed dispersal
... Seed Bank in the UK. The UK has about 1400 different types of flowering plants, which we want to collect from all the different areas in which they grow. It is quite windy and wet here, but perhaps this is why the plants are growing well as all plants like to have water! I have been looking out for ...
... Seed Bank in the UK. The UK has about 1400 different types of flowering plants, which we want to collect from all the different areas in which they grow. It is quite windy and wet here, but perhaps this is why the plants are growing well as all plants like to have water! I have been looking out for ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.