4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
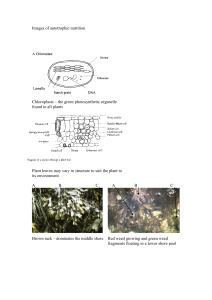
... (Growing) Textbook Reading 371 - 374 HW: Reading & Notetaking p.179 182 ...
... (Growing) Textbook Reading 371 - 374 HW: Reading & Notetaking p.179 182 ...
Alocasia cucullata
... location for a few days. I would use a minimum of a 5”-6” (diameter) pot; a one gallon would be even better. The thing your plant really wants is a LOT OF WATER to help it get over the transplanting and long, dry trip. I would plant in a rich, water-retaining potting mix and set the whole pot in a p ...
... location for a few days. I would use a minimum of a 5”-6” (diameter) pot; a one gallon would be even better. The thing your plant really wants is a LOT OF WATER to help it get over the transplanting and long, dry trip. I would plant in a rich, water-retaining potting mix and set the whole pot in a p ...
Article
... seeds stick to clothing, hair and feathers. Blueweed is occasionally found in nurseries as a gardening plant since it attracts butterflies and not deer or rabbits. Deer, as well as most grazing animals on pastures and rangelands, will avoid blueweed since it is unpalatable; therefore, a small infest ...
... seeds stick to clothing, hair and feathers. Blueweed is occasionally found in nurseries as a gardening plant since it attracts butterflies and not deer or rabbits. Deer, as well as most grazing animals on pastures and rangelands, will avoid blueweed since it is unpalatable; therefore, a small infest ...
Seasonal Changes in Plants Quiz Answers
... 9. More flowers bloom during the spring and summer than other months. This means that a) there are more long-day plants than short–day plants. b) there are more short-day plants than long-day plants. c) plants like the warm temperatures. d) both (a) and (c) are correct. ...
... 9. More flowers bloom during the spring and summer than other months. This means that a) there are more long-day plants than short–day plants. b) there are more short-day plants than long-day plants. c) plants like the warm temperatures. d) both (a) and (c) are correct. ...
PARTRIDGEBERRY
... PARTRIDGEBERRY Mitchella repens This is a low-growing, evergreen plant with creeping stems. The stems root as they grow along the ground so a single plant will grow over a large area. The dark green leaves may have a white pattern of veins. The small flowers are white and produced in pairs. The two ...
... PARTRIDGEBERRY Mitchella repens This is a low-growing, evergreen plant with creeping stems. The stems root as they grow along the ground so a single plant will grow over a large area. The dark green leaves may have a white pattern of veins. The small flowers are white and produced in pairs. The two ...
Science Study Guide (Unit A ~ Plants #1)
... fruit – the part of a flowering plant that surrounds and protects the seed ...
... fruit – the part of a flowering plant that surrounds and protects the seed ...
pattys calathea care
... Patty’s Plants Calathea Calatheas are from eastern Brazil. They are a great colorful foliage plant for the home or office. Grow Calatheas in meduim to bright curtain filtered light. They can tolerate a little lower light too. An east or west window is perfect. To much light will burn their leaves. L ...
... Patty’s Plants Calathea Calatheas are from eastern Brazil. They are a great colorful foliage plant for the home or office. Grow Calatheas in meduim to bright curtain filtered light. They can tolerate a little lower light too. An east or west window is perfect. To much light will burn their leaves. L ...
Plants and Animals
... B. Cuticles hold in moisture, while stomata can open or close to retain or release moisture. ...
... B. Cuticles hold in moisture, while stomata can open or close to retain or release moisture. ...
Chapter 2 - Vocabulary List
... transpiration – The movement of water vapor out of a plant and into the air. vascular system – Long, tube-like tissues in plants through which water and nutrients move from one part of the plant to another. (xylem up; phloem down) ...
... transpiration – The movement of water vapor out of a plant and into the air. vascular system – Long, tube-like tissues in plants through which water and nutrients move from one part of the plant to another. (xylem up; phloem down) ...
Botany 6/16/2014 Kingdom Plantae
... oxygen and carbon dioxide cannot diffuse either ii. Stomata are small pores on the underside of leaves, which open and close to control movements of water, carbon ...
... oxygen and carbon dioxide cannot diffuse either ii. Stomata are small pores on the underside of leaves, which open and close to control movements of water, carbon ...
Chapter 20 Plant Diversity
... roots Gametophyte is the dominant generation Require water for reproduction ...
... roots Gametophyte is the dominant generation Require water for reproduction ...
What is a Plant?
... Plants do photosynthesis, a complicated process, and without plants, we'd all be dead.” ...
... Plants do photosynthesis, a complicated process, and without plants, we'd all be dead.” ...
8/25/2009 Ponytail Plant - ARID DOME The ponytail plant grows in
... but it is more closely related to agave or yucca than palm trees. These related plants are native to Mexico. They used to be in the same botanical family, but recent reclassification has separated them into different families. The scientific name is Beaucarnea recurvata. The common name ponytail pla ...
... but it is more closely related to agave or yucca than palm trees. These related plants are native to Mexico. They used to be in the same botanical family, but recent reclassification has separated them into different families. The scientific name is Beaucarnea recurvata. The common name ponytail pla ...
Plant Nomenclature
... binomial names. • This means they have 2 Latin Names • 1st is the Genus • 2nd is the Epithet ...
... binomial names. • This means they have 2 Latin Names • 1st is the Genus • 2nd is the Epithet ...
Plant Kingdom - najicschoolbus
... Live in aquatic areas (majority of them live in freshwater, but some do live in ocean) Differences between species are microscopic Ex. Spirogyra, Oedogonium, and Ulothrix ...
... Live in aquatic areas (majority of them live in freshwater, but some do live in ocean) Differences between species are microscopic Ex. Spirogyra, Oedogonium, and Ulothrix ...
Name - Fairfield Public Schools
... What are the differences between monocots and dicots in terms of venation, cotyledons, petal number, and leaf vein pattern. Be able to give examples of each. Ch. 29 Plant Structures: ...
... What are the differences between monocots and dicots in terms of venation, cotyledons, petal number, and leaf vein pattern. Be able to give examples of each. Ch. 29 Plant Structures: ...
Plants YEAR 2 End of unit Assessment
... 3) Use the words in the box to label the parts of the plant below. One has been done for you ...
... 3) Use the words in the box to label the parts of the plant below. One has been done for you ...
PLANT REPRODUCTION AND BREEDING
... - people adapt plants to meet their needs. - selective breeding is choosing specific for their special characteristics. ...
... - people adapt plants to meet their needs. - selective breeding is choosing specific for their special characteristics. ...
• Ferns: Any of numerous seedless vascular plants belonging to the
... Herbs: are, technically, plants with aerial parts used for seasoning foods, and a spice (also called seasoning) is any substance used for seasoning foods; many herbs are used as spices Ferns: Any of numerous seedless vascular plants belonging to the phylum Pterophyta that ...
... Herbs: are, technically, plants with aerial parts used for seasoning foods, and a spice (also called seasoning) is any substance used for seasoning foods; many herbs are used as spices Ferns: Any of numerous seedless vascular plants belonging to the phylum Pterophyta that ...
Plant adaptations - Parkland School District
... leaves that only grow after it rains. Plant adaptations.com ...
... leaves that only grow after it rains. Plant adaptations.com ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.