Nervous System
... electrochemical nerve impulses to other neurons. • Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells. • Neuroglial cells provide support, insulation, and nutrients to neurons • Neurons consist of a cell body and extensions called dendrites and axons • Axons send information in the form of n ...
... electrochemical nerve impulses to other neurons. • Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells. • Neuroglial cells provide support, insulation, and nutrients to neurons • Neurons consist of a cell body and extensions called dendrites and axons • Axons send information in the form of n ...
nervous system ppt
... Our brain cells are constantly trying to bring some amount of serotonin back into the cells and out of the synapse using serotonin reuptake transporters. Ecstasy essentially takes these upkeep transporters and reverses their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into t ...
... Our brain cells are constantly trying to bring some amount of serotonin back into the cells and out of the synapse using serotonin reuptake transporters. Ecstasy essentially takes these upkeep transporters and reverses their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into t ...
Handout_Master_11
... height by age 2. If the continued to grow throughout their life as quickly as they do in the first two years, they would end up more than 12 feet tall. 3. True. The average infant has many more neurons and neural connections than we do, but about half of the neurons produced early in life die. The n ...
... height by age 2. If the continued to grow throughout their life as quickly as they do in the first two years, they would end up more than 12 feet tall. 3. True. The average infant has many more neurons and neural connections than we do, but about half of the neurons produced early in life die. The n ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
Text S1.
... axonal polarization along L1 at 3 DIV but, initially, any of the 4 growing neurites could have differentiated into an axon. The discrepancy between random choice at 1-2 DIV and axonal preference along L1 at 3 DIV corresponds to failures of polarization along curved lines. It is thus possible to calc ...
... axonal polarization along L1 at 3 DIV but, initially, any of the 4 growing neurites could have differentiated into an axon. The discrepancy between random choice at 1-2 DIV and axonal preference along L1 at 3 DIV corresponds to failures of polarization along curved lines. It is thus possible to calc ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... response also causes the neuron to expand its receptive connections, the dendrites, and it Dendrite creates more axon contacts for association. These are real physical changes and they can be demonstrated in experimental animals such as snails. While we are much more complex than a snail, these same ...
... response also causes the neuron to expand its receptive connections, the dendrites, and it Dendrite creates more axon contacts for association. These are real physical changes and they can be demonstrated in experimental animals such as snails. While we are much more complex than a snail, these same ...
neurocytol_lect
... sections of myelin made from a number of individual cells Remember, however, not all axons are myelinated. Small diameter axons generally have no myelin covering. ...
... sections of myelin made from a number of individual cells Remember, however, not all axons are myelinated. Small diameter axons generally have no myelin covering. ...
CH 8 Nervous part 1
... Our brain cells are constantly trying to bring some amount of serotonin back into the cells and out of the synapse using serotonin reuptake transporters. Ecstasy essentially takes these upkeep transporters and reverses their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into t ...
... Our brain cells are constantly trying to bring some amount of serotonin back into the cells and out of the synapse using serotonin reuptake transporters. Ecstasy essentially takes these upkeep transporters and reverses their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into t ...
What is the structure of the neuron? (continued)
... extending from the cell body—typically, one axon and many dendrites. The most common type of neuron in the CNS. ...
... extending from the cell body—typically, one axon and many dendrites. The most common type of neuron in the CNS. ...
kumc 05 nervous system review student
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
The Anterolateral System
... gray substance, and finally the intralaminar and posterior thalamus • The neospinothalamic tract distributes somatotopically in the ventral posterior thalamus: VPL - Leg, Trunk, Arms VPM - Face ...
... gray substance, and finally the intralaminar and posterior thalamus • The neospinothalamic tract distributes somatotopically in the ventral posterior thalamus: VPL - Leg, Trunk, Arms VPM - Face ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... carry impulses “in between” sensory neurons and motor neurons found in the spinal cord ...
... carry impulses “in between” sensory neurons and motor neurons found in the spinal cord ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell - what type of diffusion is this? ...
... 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell - what type of diffusion is this? ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
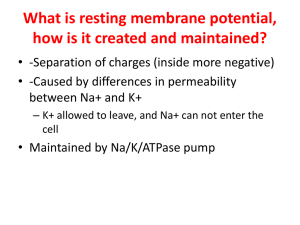
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... types of neurons? Describe the structure and functions of the three parts of a neuron • Sensory Neurons: take info from sensory receptors to the CNS • Interneurons: Receive input from all sensory and other interneurons and communicate with motor neurons • Motor: Takes info from CNS to rest of body • ...
... types of neurons? Describe the structure and functions of the three parts of a neuron • Sensory Neurons: take info from sensory receptors to the CNS • Interneurons: Receive input from all sensory and other interneurons and communicate with motor neurons • Motor: Takes info from CNS to rest of body • ...
October 25
... form patterns related to specific smells. Sensory map – activation of different areas of the glomeruli correspond to specific odors. The form of a map for each odor may be distinct. Temporal coding – the timing of action potentials along the axons may differentiate smells. ...
... form patterns related to specific smells. Sensory map – activation of different areas of the glomeruli correspond to specific odors. The form of a map for each odor may be distinct. Temporal coding – the timing of action potentials along the axons may differentiate smells. ...
Ch10 Reading Guide
... 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across ______________________________ and react with ____________________ that form structures called _______________ in or on the______________________ neuron membrane. 2. Some neurotransmitters cause ion channels to _________________________ , some cause ion c ...
... 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across ______________________________ and react with ____________________ that form structures called _______________ in or on the______________________ neuron membrane. 2. Some neurotransmitters cause ion channels to _________________________ , some cause ion c ...
Classifications of Neurons 1. Function 2. Structure 3. Shape
... Notes: "BRAINSTEM" is an imprecisely defined term which usually refers to the rhombencephalon and mesencephalon together. It may or may not include the cerebellum, and sometimes the diencephalon is included. "CEREBRUM" or "CEREBRAL HEMISHPHERES" refer to the ...
... Notes: "BRAINSTEM" is an imprecisely defined term which usually refers to the rhombencephalon and mesencephalon together. It may or may not include the cerebellum, and sometimes the diencephalon is included. "CEREBRUM" or "CEREBRAL HEMISHPHERES" refer to the ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
Document
... 2. Begins with initial segment 3. May be absent (amacrine cells) 4. Unique in most cells 5. May be myelinated or no 6. Never contains ribosomes 7. Smooth contours, cylindrical shape 8. The thinnest process at the origin 9. Ramifies by branching at obtuse angles 10. Gives rise to branches of same dia ...
... 2. Begins with initial segment 3. May be absent (amacrine cells) 4. Unique in most cells 5. May be myelinated or no 6. Never contains ribosomes 7. Smooth contours, cylindrical shape 8. The thinnest process at the origin 9. Ramifies by branching at obtuse angles 10. Gives rise to branches of same dia ...
sensory1
... of external stimuli. • Transduction: the conversion of a physical stimulus into a change in membrane potential (electrochemical signal) – Signals are transmitted in the form of graded potentials, action potentials, and synaptic interaction • Receptors: cells or regions of cells that respond to speci ...
... of external stimuli. • Transduction: the conversion of a physical stimulus into a change in membrane potential (electrochemical signal) – Signals are transmitted in the form of graded potentials, action potentials, and synaptic interaction • Receptors: cells or regions of cells that respond to speci ...