FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... FIGURE 24.8 Anatomy of ascending somatosensory paths. (A) Organization of the dorsal columnmedial lemniscal system from entry of large diameter afferents into the spinal cord to the termination of thalamocortical axons in the first somatosensory area of the cerebral cortex. An obligatory synapse occ ...
... FIGURE 24.8 Anatomy of ascending somatosensory paths. (A) Organization of the dorsal columnmedial lemniscal system from entry of large diameter afferents into the spinal cord to the termination of thalamocortical axons in the first somatosensory area of the cerebral cortex. An obligatory synapse occ ...
File - Perkins Science
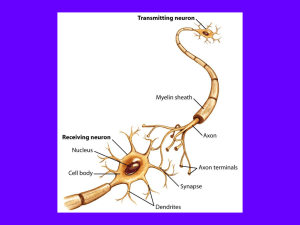
... 1)A cell body that contains the nucleus, Nissl bodies, and other organelles; cluster in groups called nuclei in the CNS and ganglia in the PNS 2)Dendrites: receive impulses and conducts a graded impulse toward the cell body 3)Axon: conducts action potentials away from the cell ...
... 1)A cell body that contains the nucleus, Nissl bodies, and other organelles; cluster in groups called nuclei in the CNS and ganglia in the PNS 2)Dendrites: receive impulses and conducts a graded impulse toward the cell body 3)Axon: conducts action potentials away from the cell ...
Axon - Perkins Science
... 1)A cell body that contains the nucleus, Nissl bodies, and other organelles; cluster in groups called nuclei in the CNS and ganglia in the PNS 2)Dendrites: receive impulses and conducts a graded impulse toward the cell body 3)Axon: conducts action potentials away from the cell ...
... 1)A cell body that contains the nucleus, Nissl bodies, and other organelles; cluster in groups called nuclei in the CNS and ganglia in the PNS 2)Dendrites: receive impulses and conducts a graded impulse toward the cell body 3)Axon: conducts action potentials away from the cell ...
Somatic Sensory System
... 2-point discrimination • Ability to discern 2 closely position points as 2 rather than 1. • Varies 20 fold throughout body • Fingertips have highest resolution – Due to high density of mechanoreceptors – Receptor subtypes with small receptive fields – More cortical neurons dedicated to decipherin ...
... 2-point discrimination • Ability to discern 2 closely position points as 2 rather than 1. • Varies 20 fold throughout body • Fingertips have highest resolution – Due to high density of mechanoreceptors – Receptor subtypes with small receptive fields – More cortical neurons dedicated to decipherin ...
Cellular Neuroanatomy II
... antennae of the neuron, thus are covered with thousands of synapses (stained red at right). Dendritic trees have a large variety of shapes and sizes to enhance this functionality. In addition, the dendritic membrane has many specialized protein molecules called receptors that detect the chemicals re ...
... antennae of the neuron, thus are covered with thousands of synapses (stained red at right). Dendritic trees have a large variety of shapes and sizes to enhance this functionality. In addition, the dendritic membrane has many specialized protein molecules called receptors that detect the chemicals re ...
Dopamine axons of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
Slide 1
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
6-8_TissueDamageRegen_SteinÁN
... damaged, the distal segment undergoes Wallerian degeneration, losing its myelin sheath. The proximal segment can either die by apoptosis or undergo the chromatolytic reaction, which is an attempt at repair. In PNS axonal sprouts form at the proximal stump and grow until they enter the distal stump. ...
... damaged, the distal segment undergoes Wallerian degeneration, losing its myelin sheath. The proximal segment can either die by apoptosis or undergo the chromatolytic reaction, which is an attempt at repair. In PNS axonal sprouts form at the proximal stump and grow until they enter the distal stump. ...
CHAPTER 10
... 14. All Or None Response: If the stimulus is strong enough to cause a response in the neuron, it responds _______________________. A greater intensity of stimulation produces more impulses per second; not a _______________________ impulse. For a very short time following passage of a nerve impulse, ...
... 14. All Or None Response: If the stimulus is strong enough to cause a response in the neuron, it responds _______________________. A greater intensity of stimulation produces more impulses per second; not a _______________________ impulse. For a very short time following passage of a nerve impulse, ...
nervous07
... •Soma producing: Free ribosomes, protein, RNA and other molecules. •The axon and myelin sheath distal to the lesion degenerates as far as the axon collateral •sprouting of the axon into endoneurium •guiding by proliferating Schwann cells toward the target •regeneration in the presence of macrophages ...
... •Soma producing: Free ribosomes, protein, RNA and other molecules. •The axon and myelin sheath distal to the lesion degenerates as far as the axon collateral •sprouting of the axon into endoneurium •guiding by proliferating Schwann cells toward the target •regeneration in the presence of macrophages ...
awl review q answers
... integrates these sources of information to determine appropriate behavioural strategies. When there is a deviation from homeostatic norms of, for example, body fluid-level, behaviour is biased in favour of seeking and ingesting water. This is the negative feedback mode of control, where, with the he ...
... integrates these sources of information to determine appropriate behavioural strategies. When there is a deviation from homeostatic norms of, for example, body fluid-level, behaviour is biased in favour of seeking and ingesting water. This is the negative feedback mode of control, where, with the he ...
Power Point
... Fig. 3. SAPNS allows axons to regenerate through the lesion site in brain. The dark-field composite photos are parasagittal sections from animals 30 days after lesion and treatment. (a) Section from brain of 30-day-old hamster with 10 µl of saline injected in the lesion at P2. The cavity shows the ...
... Fig. 3. SAPNS allows axons to regenerate through the lesion site in brain. The dark-field composite photos are parasagittal sections from animals 30 days after lesion and treatment. (a) Section from brain of 30-day-old hamster with 10 µl of saline injected in the lesion at P2. The cavity shows the ...
Exam
... c. demyelination in the right side of the basilar pons (pontine protuberance) d. axonal degeneration in the pyramids of the medulla on the left side e. axonal degeneration in spinal nerves on the left side ...
... c. demyelination in the right side of the basilar pons (pontine protuberance) d. axonal degeneration in the pyramids of the medulla on the left side e. axonal degeneration in spinal nerves on the left side ...
Axon Guidance
... • Growth cones express surface receptors for guidance cues, and the receptors trigger regulation of growth cone motility to produce turns and navigation. • Local guidance cues change as an axon moves along its path. • Adhesive cues mark pathways for axon elongation. • Locally produced guidance m ...
... • Growth cones express surface receptors for guidance cues, and the receptors trigger regulation of growth cone motility to produce turns and navigation. • Local guidance cues change as an axon moves along its path. • Adhesive cues mark pathways for axon elongation. • Locally produced guidance m ...
Specificity of Synaptic Connections II (i.e. Target Selection by Axons)
... Eph/ephrin signaling establishes topography of the nasal-temporal axis of the retinotectal projection: - Knockout of the genes for the ephrins or Eph resulted in loss of normal topography in the retinal projection. - Misexpression of ephrin-A2 in high concentration across the entire tectum prevent ...
... Eph/ephrin signaling establishes topography of the nasal-temporal axis of the retinotectal projection: - Knockout of the genes for the ephrins or Eph resulted in loss of normal topography in the retinal projection. - Misexpression of ephrin-A2 in high concentration across the entire tectum prevent ...
Cellular and Molecul..
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
Nervous System
... Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
... Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
NeuroReview3
... • First axons to reach their target have pioneer growth cones, and use guidance molecules to guide them • Later axons use trail blazed by pioneer growth cones • Fasciculation: tendency for developing axons to stick together and grow along established pathways • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs): on sur ...
... • First axons to reach their target have pioneer growth cones, and use guidance molecules to guide them • Later axons use trail blazed by pioneer growth cones • Fasciculation: tendency for developing axons to stick together and grow along established pathways • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs): on sur ...